Long-Term Chlorinated Solvent Treatment using a Controlled-Release Microemulsion
PROJECT SUMMARY
- Dry cleaning operations resulted in a chlorinated solvent plume with concentrations as high as 700 micrograms per liter (μg/L) in chlorinated solvents
- Typical Midwestern geology: Silty clay with intermittent sand stringers underlain by a clay till confining layer
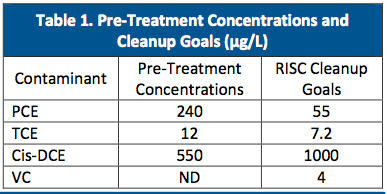
- Contaminants of concern within the silty clay aquifer included tetrachloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethene (TCE) (see Table 1)
- High sulfate environment (~100 mg/L) – potential inhibitor for successful remediation
- Cleanup goals were based on the Industrial Risk Integrated System of Closure (RISC) levels
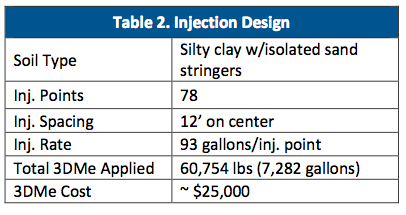
- Enhanced anaerobic bioremediation of chlorinated solvents in groundwater using 3-D Microemulsion (3DMe)®
- $195,000 (Costs include 3DMe® material, injection, field oversight, 2 yrs post injection monitoring, project management and report writing)
RESULTS
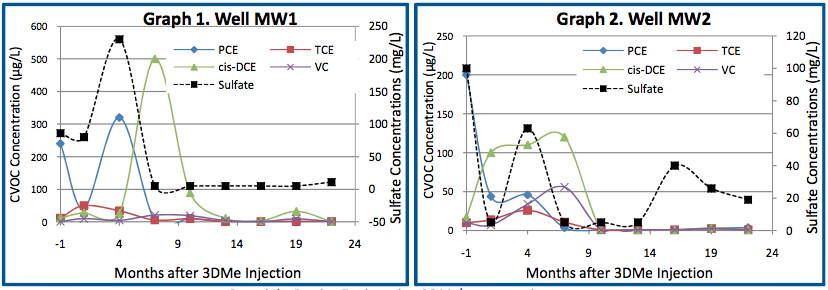
- The 3DMe application overcame high sulfate levels and resulted in a reducing environment lasting almost 2 years
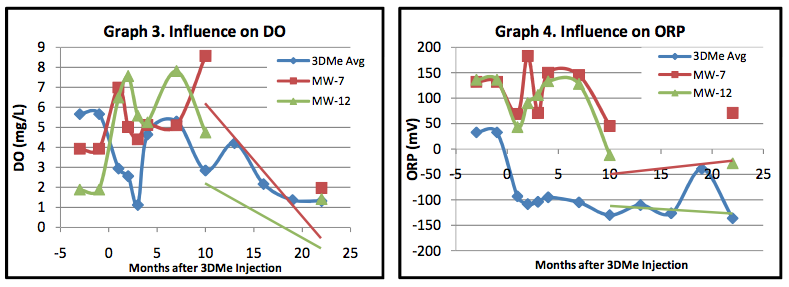
- Sampling at 22 months post-3DMe indicated sustained low levels of ORP (-136mV) and DO (1.3mg/L)
- Reduction of chlorinated solvents by 83% to 98% in all impacted wells
- Site is pending closure from regulatory agency
ELECTRON DONOR INFLUENCE
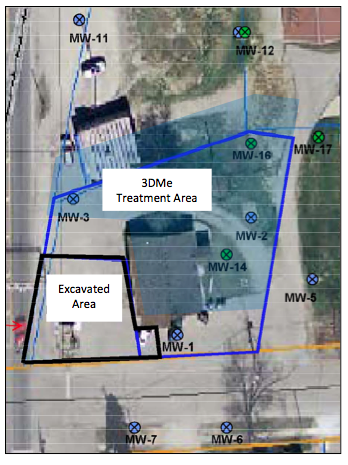
Analytical parameters including oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), dissolved oxygen (DO) and total organic acids (TOAs) were monitored to verify the influence of the electron donor post-injection. The monitoring wells likely influenced by 3DMe (MW1-3, MW5, MW14-17) were analyzed on average and compared to background wells MW7 and MW12.
Within the 3DMe influence area:
- On average, ORP reduced to -100mV and DO levels declined to ~2mg/L (Graphs 3 and 4)
- Concentrations of TOAs were detected at >1,000 mg/L during the first 10 months of
monitoring


 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español


