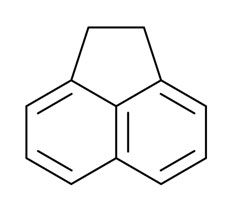
 What is Acenaphthene?
What is Acenaphthene?
Acenaphthene appears as white needles. Melting point 93.6°C. Soluble in hot alcohol. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. May irritate skin and mucous membranes. Emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes when heated to decomposition. Derived from coal tar
Uses
Acenaphthene is used to make dyes, pharmaceuticals, insecticides, fungicides, and plastics.
Sources & Potential Exposure
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a group of over 100 differentchemicals that are formed during the incomplete burning of coal, oil and gas, garbage, or other organic substances like tobacco or charbroiled meat. PAHs are usually found as a mixture containing two or more of these compounds, such as soot. Some PAHs are manufactured. These pure PAHs usually exist as colorless, white, or pale yellow-green solids. PAHs are found in coal tar, crude oil, creosote, and roofing tar, but a few are used in medicines or to make dyes, plastics, and pesticides.
Federal Regulations
EPA: Confirmed human carcinogen.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español



