Sequential Anaerobic and Aerobic Treatment of Chlorinated Solvents Achieves MCLs
Project Highlights
- All target compounds reduced to below Maximum Contaminant Level (MCLs) in onsite wells
- Anaerobic biodegradation using Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC®) treats tetrachloroethylene (PCE) and 1,1 dichloroethene (DCE) to below federal MCLs
- Aerobic biodegradation using ORC Advanced® treats vinyl chloride (VC) and 1,1-DCE to below MCLs
- ORC Advanced provided oxygen for a period of 15 months in the target treatment zone

Project Summary
The site is located in the Coastal Plain of South Carolina and is a former light industrial facility. Baseline concentrations of total chlorinated VOCs – which included PCE, dechlorination daughter products, and 1,1- DCE – were as high as 2,000 μg/L in the near-source groundwater.
Initial groundwater treatment injected 2,400 pounds of HRC at the site using direct push technology. VOC concentrations in the target monitoring wells decreased to below federal MCLs for all contaminants except for VC and 1,1-DCE, which appeared to have stabilized between 10-15 μg/L and 7-30 μg/L, respectively.
In an attempt to meet the MCLs for all contaminants and attain regulatory closure, the treatment approach was shifted to aerobic bioremediation to accelerate degradation of residual VC and 1,1-DCE. This approach was based on evidence that aerobic biodegradation of daughter products such as VC can be much faster than anaerobic processes. The aerobic treatment involved injection of 1,360 pounds of ORC Advanced via direct push technology into 22 temporary points.
Technology Description
ORC Advanced is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen to enhance aerobic biodegradation.
HRC is a controlled release, electron donor material that, when hydrated, is specifically designed to produce a controlled release of soluble lactate. The newly available lactic acid is highly efficient for the production of dissolved hydrogen to fuel anaerobic biodegradation processes in soil and groundwater.
Results
After initial groundwater treatment of HRC and following application of ORC Advanced, groundwater monitoring showed reductions in VC to below MCL except for periodic detections between 2-3 μg/L and reductions in 1,1-DCE to below the MCL of 7 μg/L onsite. The VOC concentrations and the dissolved oxygen levels demonstrated that ORC Advanced released oxygen for 15 months in the target treatment zone.
Bedrock Treatment Remediates NJ Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- 3-D Microemulsion injections created 30-foot ROI in fractured bedrock
- TCE concentrations reduced through reductive dechlorination and daughter products reduced to ethene within 12-month study
- Pilot study results allowed for: full-scale design, maximized product ROI, minimized bedrock injection well drilling, and resulted in reduced overall project costs
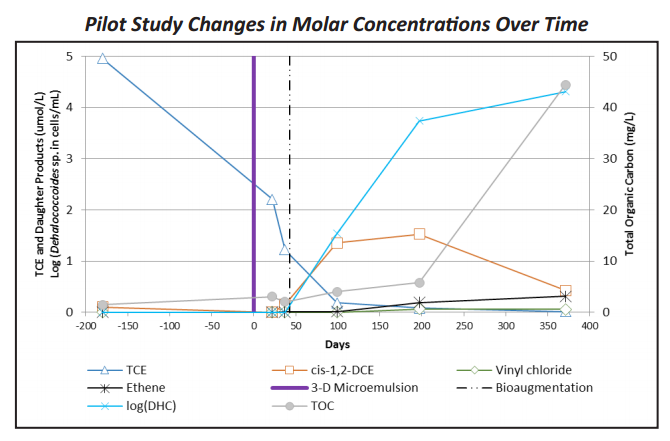
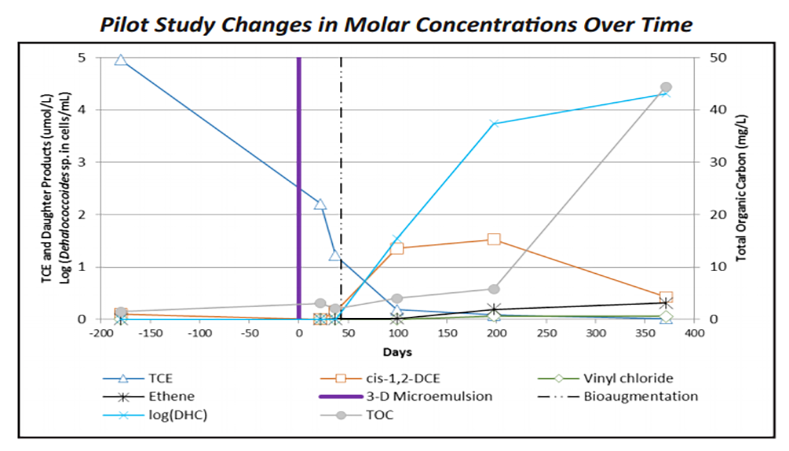
Project Summary
Previous manufacturing activities impacted a fractured bedrock aquifer with TCE. The plume migrated approximately 600 feet downgradient along fractures at 70-80 feet (shallow) and 105-115 feet (intermediate) below ground surface. Remediation at the site was planned as a phased approach including a source area pilot evaluation of enhanced reductive dechlorination, bioaugmentation, and radius of influence (ROI). A larger source area treatment and property boundary barrier was to be determined based upon the pilot study results.
The pilot study found that injection of 3-D Microemulsion was capable of initially influencing a 30-40 feet ROI based on visual (turbidity) and geochemical data. Over a 12-month period, TOC levels remained elevated at concentrations above 10 mg/L at a shallow well 20-feet away. At the two intermediate wells 40-feet away, TOC concentrations increased to >40 mg/L during this period. During this same pilot study period, TCE concentrations decreased, cis-1,2-DCE concentrations increased then attenuated, and VC and ethane concentrations increased. Bioaugmentation, occurring 6 weeks after the 3-D Microemulsion injection resulted in Dehalococcoides sp. populations that increased and sustained at elevated concentrations (104 cells/mL).
Remediation Approach
Injections of 3-D Microemulsion were introduced by packer into 2 injection wells across four 10-foot fracture intervals (60-115 feet bgs). Monitoring was conducted in two shallow bedrock wells at 70-80 feet bgs and two intermediate bedrock wells at 105-115 feet bgs. ROI monitoring was conducted at these four monitoring wells that were located 20 feet, 40 feet, and 55 feet away from the injection wells. Bioaugmentation was performed 6 weeks after 3-D Microemulsion injections. Full-scale treatment is planned, which will include a larger treatment in the source area and a downgradient barrier at the property boundary.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor technology that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile pHneutral chemistry, and unique subsurface distribution properties.
Roadside Fuel Transport Spill Treated with Combined Remediation Approach
Project Highlights
- Combined remediation approach treats contaminants that remained following emergency excavation
- RegenOx® and ORC Advanced® selected to eliminate need for dedicated groundwater treatment infrastructure
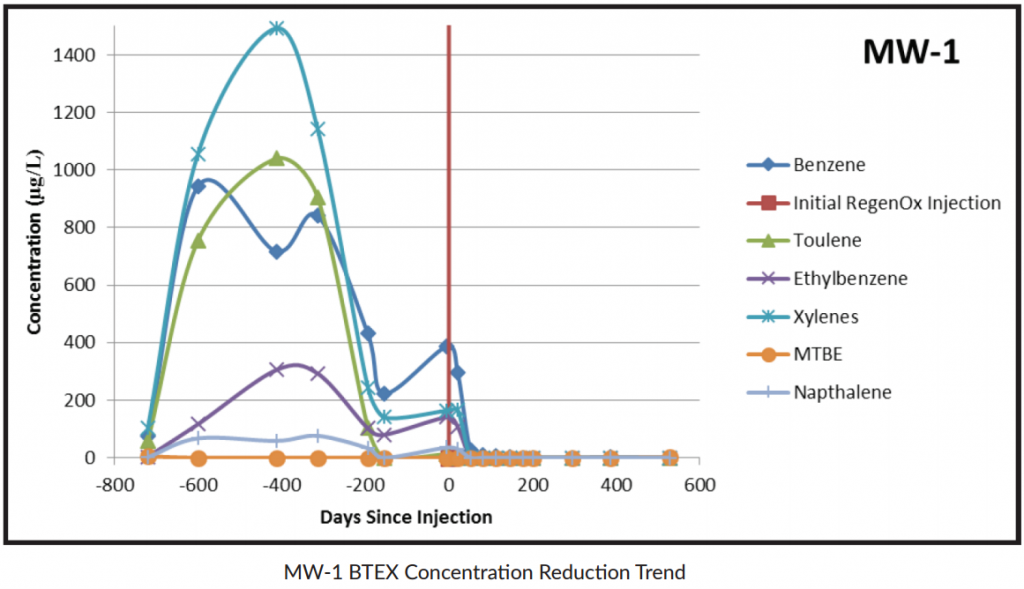
- BTEX levels reduced by 97% to below non-detect levels in the two highest concentration wells
Project Summary
A rural site located in south-central North Carolina required remediation to treat petroleum contamination from an overturned tanker truck. Excavation activities during an emergency response removed much of the contaminant mass, however additional contamination in soil and groundwater remained after the excavation was completed.
In the two highest-concentration wells, total BTEX averaged more than 1,300 μg/L in the four quarterly groundwater monitoring events prior to treatment.
A combined chemical oxidation and aerobic bioremediation treatment was employed to eliminate the need for dedicated groundwater treatment infrastructure at this roadside location to advance the site to regulatory closure.
The products selected were RegenOx, an in situ chemical oxidant, and ORC Advanced, an enhanced aerobic bioremediation product. The treatment covered a 3,900-square-foot area through 30 direct-push injection points in the former spill area.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
ORC Advanced is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
Results
Within 18 months of treatment, the site was under natural attenuation monitoring prior to regulatory closure with five of the six wells already below stringent regulatory requirements.
Excavation Treatment Reduces Contamination Below Clean-Up Target Levels
Project Highlights
- Remediation activities included excavating a 1,600-square-foot area contaminated with BTEX and TPH.
- ORC Advanced Pellets applied on-site to stimulate aerobic biodegradation during backfill activities.
- Two monitoring wells reduced to below groundwater contaminant targets.
Project Summary
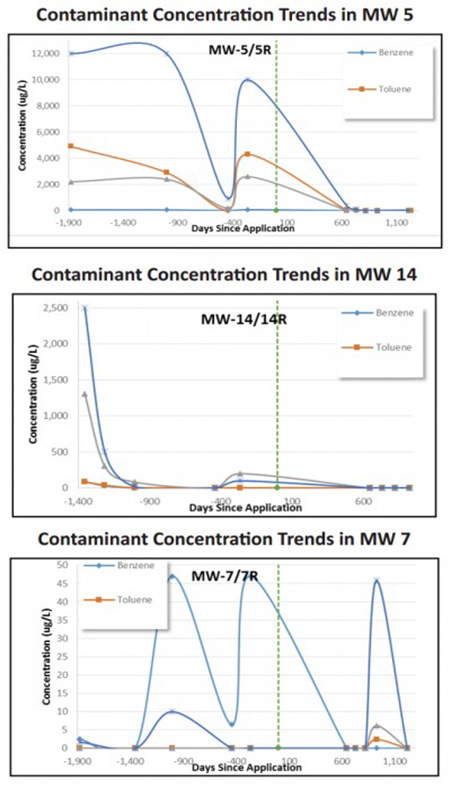
The Bryant Grocery and Saw Co. site in the Florida Panhandle was the subject of excavation activities to remediate significant BTEX and TPH contamination as a result of historical releases from gasoline underground storage tanks (USTs). Excavation activities were planned for an area of approximately 1,600-square-feet to a depth of 14 feet below ground surface.
Remediation Approach
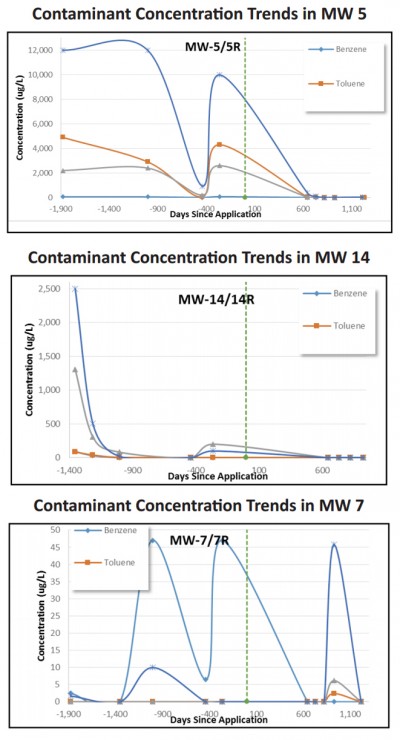
During backfill activities, ORC Advanced Pellets were added to provide a long-term source of oxygen to promote aerobic biodegradation of residual, dissolved-phase petroleum constituents remaining in the excavation area. A total of 520 pounds of ORC Advanced Pellets were applied to the saturated zone of the excavation. Both MW-7R and MW-14R have seen BTEX, TRPH, and MTBE reduced to stringent groundwater quality standards for Florida (Groundwater Contaminant Target Levels, or GCTLs). In MW-5R, Total Residual Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TRPH), MTBE, benzene, and ethylbenzene have been reduced to below GCTLs. Toluene and xylenes concentrations remain slightly above GCTLs but have declined by more than 99% related to both constituents.
Technology Description
Advanced Formula Oxygen Release Compound (ORC Advanced®) is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration
Single PersulfOx® Treatment Reduces MTBE Concentrations by 50 Percent
Project Highlights
- Both PersulfOx and NaOH activated persulfate used on-site to test effectiveness
- Single injection event of PersulfOx resulted in 50% reduction of MTBE
- Backfilled gravel excavation used as a treatment cell for contaminant mass migrating from an inaccessible dispenser canopy toward the property boundary

Project Summary
A gas station in the Washington DC metro area was contaminated with BTEX and MTBE following a release from a dispenser island. High concentrations of MTBE (160 ppm) diffused into the native silty clay and beyond the property boundary. Two persulfate chemistries utilized at the site to evaluate treatment longevity. Persulfate test kits demonstrated that PersulfOx remained active for six months. The PersulfOx® injections were performed within a downgradient former excavation which was backfilled with gravel to intercept the contaminants. The single injection event of PersulfOx resulted in 50% reduction of MTBE. Treatments in the former excavation have also reduced MTBE concentrations at the property boundary.
Remediation Approach
The PersulfOx injection was performed into three injection wells that were located in an excavation that was backfilled with gravel. This gravel backfilled excavation used as a treatment cell for contaminants originating from under the dispenser canopy (upgradient). The goal was to oxidize contaminant mass as it moves through the former excavation toward the property boundary. The native soils consisted of silty clay, which have a low hydraulic conductivity and do not accept injection volumes easily. This approach treats the petroleum bleed-off from the dispenser canopy before it moves downgradient and eventually off-site. The purpose of the project was designed to evaluate performance data where PersulfOx and NaOH activated persulfate were compared for contaminant reduction trends, longevity, and ease of application.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solventtype contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Residential Property Treated for TPHd Concentrations in Groundwater
Project Highlights
- Excavation and remediation injections performed in a tight residential setting with intense local community involvement.
- Treatment included shoring/excavation, soil handling and off-site disposal, in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO), bioremediation and sewer replacement.
- Groundwater sampling post-remediation indicates an overall decrease in TPHd concentrations and monitoring is ongoing.

Project Summary
An underground heating oil storage tank contaminated the groundwater below a residential property in Northern California. The two-story home, located near a downtown beach community, had a 100-gallon heating oil tank that was removed in 1994. Site investigation and groundwater monitoring activities were conducted since the removal, when apparent petroleum hydrocarbon impacts were identified. TPHd concentrations of 3,300 ug/L were detected on-site.
Remediation proved to be difficult considering the location of the residential property. The home was surrounded by other residences on three of its corners, with a bed and breakfast and swimming school located to the northwest of the property. A tight injection approach was required so the neighboring properties were not disturbed.
Remediation Approach
To meet the objective mass reduction of residual TPHd in both soil and groundwater, the remedial approach combined excavation/shoring and removal of TPHd impacted soils. It also included ISCO using RegenOx® and bioremediation using Oxygen Release Compound (ORC Advanced®). Approximately 233 cubic yards of soil were removed. A total of 2,350 pounds of RegenOx Part A and 1,320 pounds of Regenox Part B, along with 716 pounds of ORC Advanced® in slurry form, was injected into the subsurface via 16 direct-push injections.
Technology Description
ORC Advanced is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
ORC® Advanced Pellets Utilized as Part of Combined Remedy Approach at Ohio Brownfield’s Project
Project Highlights
- Ohio VAP Certified Professional specified ORC® Advanced Pellets in Remedial Action Plan for purpose of obtaining grant through the Clean Ohio Revitalization Fund (CORF).
- $1.98 million in brownfield’s funding was granted through CORF as a result of Proposed Remedial Action Plan.
- Approximately 18,000 pounds of ORC® Advanced Pellets were applied to the base of 5 former underground storage tank excavation sites to address residual TPH and PAH impacts in groundwater

Project Summary
The site, a former cordage and twine factory in Ohio, was closed in 2004 after 125 years of operation. The city and developer secured $1.98 million in brownfield’s funding through the Clean Ohio Revitalization Fund (CORF). These funds were secured for demolition and remediation activities at the site included but not limited to asbestos removal, underground storage tank removal, and contaminated soil excavation and demolition activities.
Remediation Approach
Approximately 18,000 pounds of ORC Advanced Pellets were specified by the Ohio VAP Certified Professional responsible for this project. Per the CORF remedial plan the pellets were applied to the base of 5 former underground storage tankexcavation sites. As part of this combined remedy approach (excavation + biodegradation), ORC Advanced Pellets were included to promote enhanced aerobic biodegradation of residual TPH and PAH impacts in water for a period of 9-12 months.
Technology Description
ORC Advanced® Pellets (ORC-A Pellets) are a pelletized version of REGENESIS’ widely-used ORC Advanced and are designed specifically for direct application into excavations, tank pits and trenches. This pelletized, dry application material minimizes airborne dust while eliminating the need for specialized equipment and spray water required for powder-slurry applications. ORC Advanced Pellets are approximately 3-10 mm in size.
PersulfOx® Rapidly Treats TBA Contamination
Project Summary
Site operations at this manufacturing facility located in New Jersey caused groundwater to be impacted with tert-butyl alcohol (TBA). Previous attempts at site remediation using alkaline activated persulfate had not met performance goals. PersulfOx was subsequently applied in an area of significant TBA contamination resulting in orders of magnitude reductions within just three weeks’ time.
Alkaline Activated Persulfate – Unsuccessful
An initial attempt at remediation using alkaline activated persulfate included a full-scale injection of persulfate and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This approach was deemed unsuccessful, as sampling after one week showed pH to be below the range required for persulfate activation, leaving significant untreated TBA in site groundwater. Additionally, the large volume of NaOH required for this approach raised concerns of impacting nearby storm sewers.
Remediation Approach
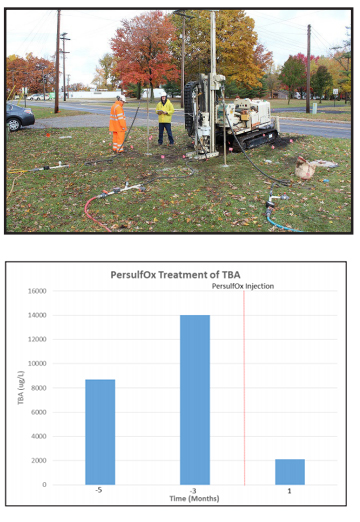
The treatment approach included a grid of six injection points placed 15-feet apart into the sandy aquifer. Each point received >1,800 pounds of PersulfOx across of 5-foot thickness.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Results
Following the PersulfOx application, site monitoring indicated a significant reduction in TBA contamination in the target zone. TBA concentrations were reduced from >14,000 ug/L to 2,100 ug/L with a single injection of PersulfOx in only three weeks’ time.
Combined Technologies Treat High TBA Levels
Site Closure Pending at Active California Retail Petroleum Service Station
Project Highlights
- A range of various remediation approaches were applied at the site over a span of 20 years.
- Enhanced Aerobic Biodegradation (EAB) remediation approach replaces soil excavation plan at site.
- Site closure pending.
Project Summary
An active service station in Southern California was contaminated with high levels of TBA and TPH-g. Various active remediation approaches took place on-site for nearly 20 years including excavation of the underground storage tanks and dispensers, soil vapor extraction and groundwater pump and treat. Although the active remediation reduced concentrations at the source, contamination levels remained high. Regenesis became involved with the site in 2011 and after two applications of enhanced aerobic biodegradation using ORC® Advanced and RegenOx®, site closure is pending.
Remediation Approach
In 1995, the underground storage tanks and dispensers were excavated and 257 tons of contaminated soil was removed. From 2003 to 2009, dissolved oxygen injection was applied into seven injection wells and in 2009, over 6,000 gallons of water was extracted from one well. In November 2011, Regenesis became involved in the project and proposed a combined remedies approach.
The remedy implemented at the site from November 2011 through November 2012 included introduction of a controlledrelease molecular oxygen into the subsurface water to promote bio-degradation of the fuel hydrocarbons. The implementation of the remedy was completed in two phases with the initial injection activities being completed in November 2011. A second injection event was completed at the site in November 2012. Approximately a total of 6,000 pounds of ORC Advanced and 480 pounds of RegeneOx were applied on-site.
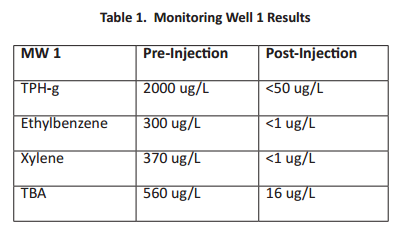
Contaminant concentrations were analyzed in the most recent monitoring events and compared to pre-injection concentrations. Results for performance monitoring well MW 1 were the most significant as all contaminant concentrations decreased to below regulatory limits (Table 1). Closure has been requested and is currently pending.
Technology Description
Advanced Formula Oxygen Release Compound (ORC Advanced®) is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxyhydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
Combined Remedies Replace Costly Mechanical Remediation Systems
RegenOx® and ORC® Advanced Treat MTBE/TBA at Five Active California Service Stations
Project Highlights
- In Situ chemical oxidation (ISCO), enhanced aerobic biodegradation replaced costly mechanical remediation systems.
- Underground infrastructure required extra precaution when applying remediation reagents on each site.
- Site closure or review of site closure at all five service stations

Project Summary
Five sites in Orange County, CA were selected for remediation using ISCO and enhanced aerobic biodegradation. All of the selected sites were gasoline service stations that were contaminated with low levels of hydrocarbons methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) and elevated levels of the MTBE biodegradation daughter product tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA). The initial remediation approach consisted of soil vapor extraction, air sparging and dual phase extraction; however, contaminant concentrations remained elevated, impeding regulatory closure.
The decision was made to transition from mechanical-based remediation systems using a combination of ISCO and enhanced aerobic biodegradation to achieve site closure criteria with various regulatory agencies.
Remediation Approach
Initial mass reduction was achieved using mechanical systems, however concentrations remained too high for regulatory closure. The goal was to reduce the remaining levels of petroleum hydrocarbons, MTBE and TBA using RegenOx and ORC Advanced. The service station included up to three direct-push injection applications of the reagents into areas where underground infrastructure was present on each site. RegenOx and ORC Advanced are both highly compatible with subsurface infrastructure so it was more of a challenge from a physical injection vantage. O&M strategy required monitoring of REDOX and microbial shifts. All five sites have been closed or under review for closure under the local regulatory agencies.
Advanced Formula Oxygen Release Compound (ORC Advanced®) is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxyhydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español