Regenesis Remediation Services™ – TCE-Impacted Soil Treated with RegenOx®
In Situ Chemical Oxidation Significantly Reduces Contamination Concentrations at Former Manufacturing Facility Site
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to design and perform in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) via soil mixing to remediate trichloroethylene (TCE) impacted soils at a former manufacturing site in Hamilton, Ohio. RegenOx® was selected as the primary remediation technology based on site conditions, and the treatment area focused on soilbound TCE contamination averaging 86 mg/kg in the sandy-silt to clay-rich unsaturated soils. The remediation objective was to reduce TCE levels in the soil to below the maximum concentration for Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP) of 0.5 mg/L, to allow for subsequent off-site disposal.

The impacted soils were treated in-place by a hydraulic excavator with a specialized mixing attachment. RegenOx was evenly dispersed throughout the contaminated soil, then thoroughly mixed using the excavator attachment. Once mixing was complete, the soils were hydrated with a RegenOx solution, to maximize oxidant loading to achieve aggressive remediation goals. As a result of the soil mixing procedures, a 99% reduction in soil concentrations was achieved. RRS remediated approximately 670 cubic yards of TCE-impacted soil on this real estate redevelopment project. Soil mixing was performed primarily from 4 feet to 8 feet below ground surface (bgs) over an area of approximately 4,500 square feet. Construction activities were able to proceed on schedule due to RRS’s well managed application and proper use of the RegenOx chemistry.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – TCE Impacted Soil Treated with RegenOx®
Soil Mixing Using In Situ Chemical Oxidation Reduces Contamination Concentrations at Former Manufacturing Facility
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was asked to design and implement a pilot test as well as a full scale design for a soil mixing project using in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) technology. The specific goal of the remediation plan was to reduce trichloroethylene (TCE) levels to less than .5 ppm, to meet standards for off-site removal as non-hazardous waste. The design included the use of RegenOx® Part A and B as an oxidant in a pug mill system. The TCE at this former manufacturing facility was present from two (2) feet below ground surface (bgs) down to eleven feet bgs in certain areas.

A total of 27,950 pounds of RegenOx Part A and 7,260 lbs of RegenOx Part B were applied over 39 discrete treatment cells during the course of the remediation project. Using an excavator, the top two feet of soil was removed and stored separately, after which the contaminated soil could be excavated and treated with RegenOx Part A and B in a pug mill system. Using RegenOx as an oxidizer, TCE on site was remediated using oxidation to dechlorinate TCE to dichloroethene (DCE), vinyl chloride (VC), and finally to ethene, a benign end product. Two years later, soil samples came back clean and the soil could be trucked off site as non-hazardous waste.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – PCE Treated with RegenOx®
Soil Mixing Using In Situ Chemical Oxidation Reduces Contamination Concentrations at Former Dry Cleaning Facility
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was hired for this large-scale soil mixing project to treat tetrachloroethylene (PCE) in shallow surface soils. The application used in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) technology to oxidize residual chlorinated solvents at this former dry cleaner site. The goal was to reduce chlorinated volatile organic compounds (cVOCs), particularly PCE, from >20 ppm to less than 5 ppb. The design of the project was divided into a grid with twelve sections, each 25 feet (ft.) by 21.5 ft., and 5 ft. deep.

Using RegenOx® remediation chemistry and an excavator to complete the soil mixing, the impacted soils were removed by an excavator and a proportional amount of RegenOx was evenly dispersed throughout the excavated soil, then thoroughly mixed using the excavator.
Once mixing was complete, the soils were placed back into the treatment cell while being hydrated with a RegenOx solution made up of RegenOx, water and hydrogen peroxide. By optimizing the contact between the soil, contaminants, and RegenOx, powerful desorption effects strip PCE off of the soil matrix and onto the RegenOx catalytic surface. This catalytic surface contributes to localized free-radical generation, leading to focused and efficient contaminant destruction via soil mixing. After eight days of the completion of the project, 98-100% reductions were achieved in the twelve sections of the grid.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – PCE Plume Treated with RegenOx®
In Situ Chemical Oxidation Reduces Contamination Concentrations at a Former Dry Cleaner Site
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to design and perform in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) via soil mixing to remediate tetrachloroethylene (PCE) impacted soil at a former dry cleaner site located in Cook County, Illinois. RegenOx® was chosen as the primary remediation technology for the chemical oxidation. The treatment area focused on soilbound PCE contamination around 1,170 mg/kg in the clay-rich unsaturated soils. The soil remediation objective was to reduce PCE levels below the 240 mg/kg soil saturation limit established by the Illinois EPA.

The impacted soils were removed by a mini trackhoe excavator and placed inside a vacant unit adjacent to a treatment cell where the soil mixing was performed. A proportional amount of RegenOx was evenly dispersed throughout the excavated, contaminated soil, then thoroughly mixed using the excavator. Once mixing was complete, the soils were placed back into
the treatment cell while being hydrated with a RegenOx solution.
By optimizing the contact between the soil, contaminants, and RegenOx, powerful desorption effects strip PCE off of the soil matrix and onto the RegenOx catalytic surface. This catalytic surface contributes to localized free-radical generation, leading to focused and efficient contaminant destruction. Approximately 242 cubic yards of soil bound contaminant mass was successfully treated at this site. Soil mixing was performed from surface grade to approximately 10 feet below grade.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – LNAPL Recovery at an Active Gas Station
Combined Treatment Remedies Reduce Contamination Concentrations at Michigan Service Station
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to remediate a residual LNAPL and dissolved-phase petroleum plume from historic gasoline and diesel fuel releases at an active service station. RegenOx PetroCleanze™ (PetroCleanze) was chosen as the primary remediation technology to facilitate the recovery of residual LNAPL and chemically oxidize contaminants without negatively impacting sensitive infrastructure.

The design called for three (3) application events using PetroCleanze, with Oxygen Release Compound (ORC®) Advanced applied during the final application event in a down-gradient plume cut- off barrier, to promote the enhanced aerobic biodegradation of dissolved-phase petroleum hydrocarbons. Eight (8) injection/extraction wells and 28 direct-push technology (DPT) injection points were used to apply the remediation reagents in the silty-sand aquifer and smear zone. Vacuum extraction was conducted between PetroCleanze applications to recover residual freephase petroleum hydrocarbons liberated from the soils. Reagent distribution monitoring confirmed PetroCleanze was present throughout the targeted source area during each application event.
Prior to the first PetroCleanze application event, no measurable free product was observed at this site since 2006. Less than twenty-four hours after the first PetroCleanze application event, LNAPL up to three inches thick was observed in four of the eight wells. After completing the third application and extraction event, LNAPL was not observed in any wells on site, and BTEX concentrations in groundwater were showing reductions for the first time since the fuel releases first occurred. A total of 2,160 pounds of RegenOx PetroCleanze and 1,120 lbs. of ORC Advanced were injected.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – LNAPL Recovery & In Situ Chemical Oxidation
Combined Treatment Remedies Reduce Contamination Concentrations at a Former Service Station
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to remediate a dissolved-phase and residual LNAPL petroleum hydrocarbon plume resulting from historic petroleum fuel releases at a former service station. RegenOx® PetroCleanze™ (PetroCleanze) was chosen as the primary remediation technology in addition to Oxygen Release Compound (ORC®) Advanced, to facilitate recovery of residual LNAPL and chemically oxidize contaminants without negatively impacting sensitive infrastructure. ORC Advanced was applied during the second PetroCleanze application to promote the enhanced aerobic bioremediation of dissolved phase petroleum hydrocarbons.

Eighteen direct-push injection points were used to apply the reagents in the silty sand aquifer and saturated soil over the course of two application events. Vacuum extraction was conducted after each PetroCleanze application to recover residual free-phase petroleum hydrocarbons liberated from the soils. Reagent distribution monitoring during the application events confirmed PetroCleanze was present across the targeted source area. Remediation chemistry was applied via direct-push injection points with a bottom-up approach from 5 to 15 feet below ground surface (bgs). A total of 4,470 pounds (lbs.) of RegenOx PetroCleanze and 720 lbs. of ORC Advanced were injected throughout the course of the two applications.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – LNAPL Recovery with RegenOx®
Remediation of Residual LNAPL and a Dissolved-Phase Plume at a Former Gasoline Service Station
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to remediate a residual LNAPL and dissolved phase petroleum plume from a historic fuel release at this former gasoline service station. RegenOx PetroCleanze™ (PetroCleanze) was chosen as the primary remediation technology to facilitate recovery of residual LNAPL and chemically oxidize contaminants without negatively impacting sensitive infrastructure.

Twenty-six (26) direct-push injection points were used during each of the four (4) application events to apply the remediation chemistry in the sandysilt aquifer and smear zone soils. Vacuum extraction was conducted after each PetroCleanze application to recover residual free-phase petroleum hydrocarbons liberated from the soils. Reagent distribution monitoring confirmed PetroCleanze was present across the targeted source area during each application event. Direct-push injection points were advanced using a bottom-up approach between 25 and 20 feet below ground surface (bgs). The injection interval focused on the highest concentrations of contaminants identified in the upper saturated soils and smear zone soils. A total of 13,230 pounds of PetroCleanze were injected via DPT injection points over the course of the project with low pressures and moderate flow rates.
RegenOx® Injected Into Frozen Permafrost at Alaska Site
Seasonal Access and Remote Location Require Unique Remediation Plan at Service Station
Project Highlights
- Sensitive ecosystem and limited seasonal accessibility required a unique remediation plan design.
- RegenOx® injected into frozen permafrost.
- Overall remediation plan requires three applications while site is accessible in summer months.

Project Summary
Located in Deadhorse, Alaska, this service station site was contaminated through multiple releases from the diesel and gasoline tanks. When this lease site was originally bid, it was required to be constructed with a minimum of 5 feet of gravel on the pads to protect the tundra. This lease requirement remains today.
The remote location on the North Slope of Alaska made it challenging to design, plan, and implement a remediation plan considering the temperatures were just above freezing. The area can only be accessed seasonally for monitoring/application and shipping products to the site proved to be a challenge. Located in a very sensitive native ecosystem (tundra/permafrost), in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was chosen as the remediation approach to avoid enlarging the plume.
Overall treatment goal for the project is to reduce hydrocarbon concentrations in approximately 365 cubic yards of source area soil to below cleanup levels. Treatment will be conducted in multiple phases and this project summary will summarize steps taken within the first year to address one-third of the exceedance area.
Remediation Approach
Surface soil to down to one-foot below ground surface was removed and stockpiled before subsurface soil from (1-5 feet below ground surface) was treated via in situ soil mixing using RegenOx®. Based on the effectiveness of Year 1 treatment; the plan is to use the same treatment method on remaining soil in subsequent years.
For the 125 cubic yards (or 1/3 of contaminated soil at the site), a total of 3,430 pounds of RegenOx (2,500 pounds of RegenOx Part A and 930 pounds of RegenOx Part B) were applied to treat BTEX, TPH, and naphthalene concentrations. Due to the sensitive and remote nature of the site, the application was staggered and the methodology was ultimately modified to prevent oversaturation and reduce the risk of plume migration. The Part B was mixed with a small amount of water and then applied and mechanically mixed thoroughly into the treatment area, followed by the Part A being applied dry and then well-mixed over the same area.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – TCE Plume Treated with Combined Remedies
Wisconsin Manufacturing Facility Remediated with RegenOx®, 3-D Microemulsion ®
A stainless steel tube manufacturing facility and their environmental consultant, Symbiont, selected Regenesis as a team member to assist in the design and implementation an in situ chemical oxidation and ERD remediation plan. The goal was to reduce trichloroethene (TCE) in source area groundwater over a 1.5 acre site from as high as 110,000ug/L to less than 10,000 ug/L using RegenOx, then transition to ERD. RegenOx® was applied through injection wells over three to five applications from 11/2007 to 6/2008. Five month later, ERD was started using 3-D Microemulsion® in this sandy surficial aquifer.

Chemical Oxidation of VOCs – Ex Situ Soil Treatment
Objective
This pilot scale study designed and undertaken by RemedX compared chlorinated hydrocarbon (CHC) destruction by three chemical oxidant additions: solid permanganate, permanganate solution and RegenOx™ under identical treatment conditions. Treatment effectiveness of the additions were compared with each other and with an oxidant-free (water only) control to quantify physical losses such as volatilization during soil mixing. The results from this pilot study will be used to evaluate the feasibility of a full scale ex situ soil treatment application.
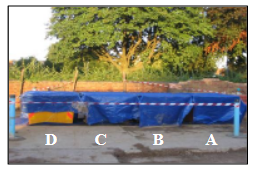
1.SOIL HOMOGENIZATION
An excavator mixed the bulk soil.

2. SOIL SPLIT INTO 4 SKIPS
The bulk soil was split and labelled by oxidant treatment.
Baseline Sampling
Baseline samples were obtained with a hand auger at 0.15 m depth and field PID readings were taken to confirm homogenization. For each skip, 2 composite samples of 5 prior samples were analyzed for Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds (sVOCs), Soil Moisture, Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and grain size. The baseline sampling indicated the soil homogenization process had been effective.

Oxidant Delivery and Soil Mixing
In Skip A, permanganate powder was added and mixed with the excavator. In Skip B, permanganate solution was sprayed and mixed with the excavator. In Skip C, RegenOx™ oxidant powder (Part A) and RegenOx™ activator gel (Part B) were added by hand and then mixed with the excavator. Skip D was the untreated control.

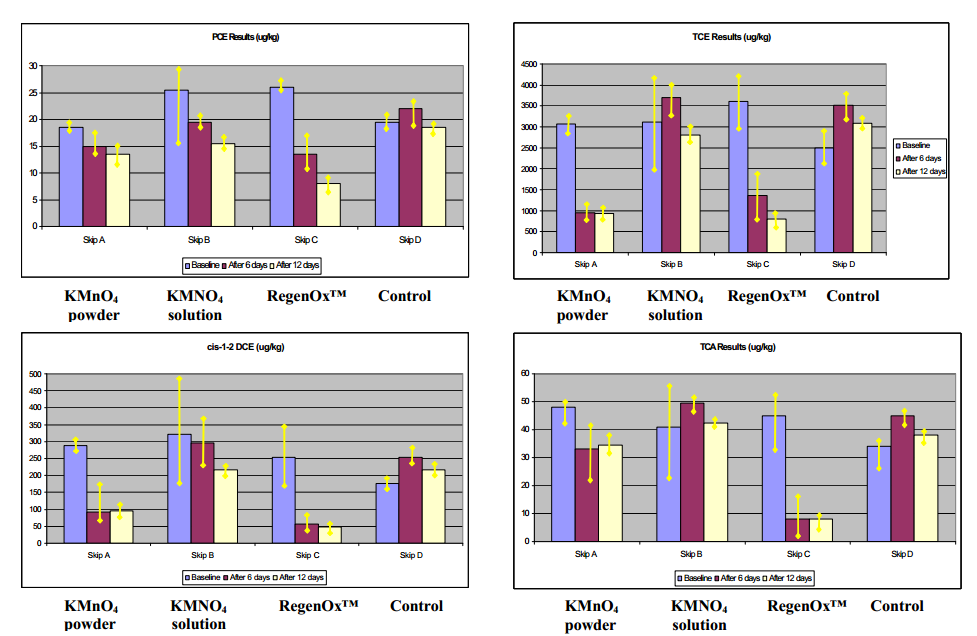
Results
Little or no reduction of any contaminant was observed in either the permanganate solution treatment or the control over the 12 day test period. In contrast, significant reductions in trichloroethene (TCE) and cis-1,2 dichloroethene (DCE) were measured in Skips A (permanganate power) and Skip C (RegenOx™). Significant reductions of perchloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethane (TCA) were also observed in Skip C (RegenOx™) as compared with the other treatments. This was most marked for TCA where an 80% reduction was observed in the RegenOx™ treatment whilst other treatments did not differ significantly from the control (no treatment). The likely reason for unsatisfactory results in Skip B (permanganate solution) was the limited amount of oxidant delivered due to the high moisture content of the soil. The results showed no significant changes in total organic carbon (TOC) and moisture in any of the samples, regardless of treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
- RegenOx™ can be effectively used for ex situsoil treatment with less material handling problems than liquid permanganate solution.
- Both Skip A (powdered permanganate) and Skip C (RegenOx™) showed good reductions of TCE and DCE.
- RegenOx™ treated a wider range of CHCs than permanganate, with statistically better results for DCE, PCE
- and TCA and evidence of on-going contaminant reduction through the test period.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español




