$150,000 Cost Savings Achieved using Enhanced Anaerobic Bioremediation and Bioaugmentation
Site Closure Pending for Treatment of TCE at Former Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Pilot test moved to full-scale application after rapid decrease in TCE and daughter product contamination
- Cost for ERD injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed-permanganate ISCO injection
- A no further action request has been submitted to the regulatory agency and is being reviewed for closure

Project Summary
During due diligence for a property transfer at a former manufacturing facility in Indiana, TCE impacts in groundwater were discovered downgradient from a former above-ground storage tank (AST). Little to no TCE remained in the sandy soils within the source area but migrated into groundwater resulting in a plume extending off-site. An initial plan was proposed to address the TCE in groundwater via an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) approach using potassium permanganate. The consultant, KERAMIDA, believed this approach was overly aggressive, given the relatively low groundwater concentrations and lack of significant soil impacts. Also, the permanganate ISCO treatment was much more expensive and difficult to implement compared to a biological enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach. At the request of the regulatory agency, a pilot injection using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus was performed in the source area and rapid reduction of TCE was observed within the first three months, accompanied by daughter product (cDCE and VC) production. Based on the results, the regulatory agency approved a full-scale injection one year later. Postinjection monitoring performed for two years following the full-scale injection indicated rapid decreases in TCE concentrations in all of the impacted wells with concurrent increases in daughter product concentrations. Daughter product concentrations also decreased significantly 9 months after 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus injection. At the conclusion of two years of post-injection monitoring, all of the wells in the treatment area were below the regulatory action levels for all compounds. A request for closure is currently being reviewed by the regulatory agency.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA developed a remedial plan that involved ERD and bioaugmentation, using 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus. The total cost for the injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed permanganate ISCO injection. A total of 6,400 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 48 liters of BDI Plus were injected into 48 points spaced 15 feet apart in a grid pattern throughout the primary impacted area. The injection interval was approximately 9 to 18 feet below grade. The ERD/bioaugmentation approach saved more than $150,000 compared to the permanganate ISCO approach, likely more since the nature of ISCO as a contact-based remedial technology would likely have required multiple injections to achieve remedial goals.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
ERD Remediation Approach Replaces Permanganate Treatment in Low Permeability Soils
3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus Treat PCE Contamination at Former Dry Cleaner
Project Highlights
- Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO)
- ISCO injection proved difficult due to low permeable soils so KERAMIDA developed an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design
- Reductions in PCE/TCE contamination observed in most wells within the injection area; monitoring is ongoing

Project Summary
The site was a former Indianapolis dry cleaner with historical releases of PCE to the subsurface. Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation in the source area, in an off-site, right-of-way area, and an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) injection using potassium permanganate. These approaches did reduce PCE concentrations in groundwater; however, they remained well above regulatory closure levels in multiple wells. After a almost two years of post-ISCO injection monitoring and evaluation, the consultant, KERAMIDA, recommended an alternative biological, enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach in the area of residual chlorinated impacts.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA worked with REGENESIS to develop an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus. The final design included 20 injection points spaced 15 feet apart on a grid pattern throughout the area of residual PCE/TCE impacts. The injection included a total of 1,200 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 18 liters of BDI Plus, distributed evenly over the 20 injection points with an injection interval of 10-13 feet below grade (targeting the impacted sand lens). The low permeability of the impacted sand lens, which proved problematic for the high volume of fluids needed for the permanganate ISCO injection, was a challenge. Since 3-D Microemulsion can be injected with minimal water when necessary, the low fluid volumes required to effect remediation proved to be ideal for this site. In addition, the low cost of the approach compared to other potential options, combined with the long-lasting effects of the remediation products provided a significant cost-to-closure savings. One year of post-ERD implementation (post-injection) monitoring shows PCE/TCE decreases and corresponding daughter product production (cDCE and VC). The persistence of strong anaerobic conditions resulting from the use of 3-D Microemulsion is expected to keep VOC concentrations and daughter products low well into the future.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
$1 Million Dollar Savings for Insurance Funded Remediation Project through Use of In Situ Chemical Oxidation and Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination
Combined Remedies Treat PCE Contamination at Active Dry Cleaner
Project Highlights
- Combined Remedies Approach (ISCO & ERD) implemented in unison near and below active dry cleaning facility.
- Sustained reduction of contaminants below clean-up levels observed 20 months after initial application.
- ISCO & ERD approach approximately $1,000,000 less expensive than proposed dual-phase extraction system option.
Project Summary
An active dry cleaner site located within a multi-use commercial development strip mall was impacted with high levels of PCE vapors. A subsequent investigation revealed groundwater impacts below the building and outside the building in a former filter storage area.
The original remediation plan involved a dual-phase extraction system with an estimated cost of approximately $1.3 million. An alternative approach consisting of in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) coupled with enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) was proposed by KERAMIDA and ultimately selected by the funding source. To date, the ISCO/ERD approach has cost less than $200,000, including 2 years of monitoring and multiple indoor air/sub-slab vapor sampling events. $50,000 – $75,000 in additional remediation/monitoring is anticipated to achieve closure, resulting in an estimated total savings of $1,000,000 for this project being funded by insurance companies.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA developed a remediation work plan consisting of an ISCO injection into the permeable fill material directly beneath the floor of the dry cleaning space (Source Area), combined with a plume-wide ERD injection.
Injection points for both RegenOx® and 3-D Microemulsion® were installed inside the dry cleaner because there was insufficient clearance for the drilling equipment. The remainder of the ERD injection points outside the building were advanced using direct push technologies.
After approximately six months of post-injection monitoring, the data suggested insufficient bacteria were present to promote accelerated reductive dechloriation. Consequently, the bioaugmentation substrate BDI Plus was applied within the ERD treatment area. Graph to the right shows results from key well within this area.
As indicated above, the bioaugmentation substrate rapidly reduced the daughter products generated as a result of the initial electron donor injection. Two years of groundwater monitoring has been performed since the initial injection and CVOC concentrations in all of the wells, except one source-area well, are below the onsite remedial standard (groundwater migration to indoor airscreening level). In addition, two downgradient wells just outside the treatment area have slightly elevated TCE and VC concentrations.
A small supplemental injection is currently planned for the source area (to further reduce the VC concentration to below the screening level) and around the two off-site wells to reduce the minor cVOC concentrations to below residential levels so that deed restrictions are not required.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
After approximately six months of post-injection monitoring, the data suggested insufficient bacteria were present to promote accelerated reductive dechloriation. Consequently, the bioaugmentation substrate BDI Plus was applied within the ERD treatment area. Graph to the right shows results from key well within this area.
As indicated above, the bioaugmentation substrate rapidly reduced the daughter products generated as a result of the initial electron donor injection. Two years of groundwater monitoring has been performed since the initial injection and CVOC concentrations in all of the wells, except one source-area well, are below the onsite remedial standard (groundwater migration to indoor airscreening level). In addition, two downgradient wells just outside the treatment area have slightly elevated TCE and VC concentrations.
A small supplemental injection is currently planned for the source area (to further reduce the VC concentration to below the screening level) and around the two off-site wells to reduce the minor cVOC concentrations to below residential levels so that deed restrictions are not required.
About the Consultant

KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
Combined Remedies Approach (Dual Phase Extraction, ISCO and ERD) Lead to Rapid Results on a Guaranteed Cost to Closure Project in Indiana
3- D Microemulsion, BDI Plus and RegenOx Reduce cVOC Concentrations
Project Highlights
- Guaranteed cost to closure project.
- ISCO coupled with dual-phase extraction was successful in reducing cVOC concentrations within the core source area.
- Plume-wide ERD injection resulted in meeting remedial goals within 18-20 months.
- Combined remedy approach (ISCO & ERD) accelerated the time to closure allowing project to be completed within budget
Project Summary
A plating plant in Batesville, Indiana was contaminated with chlorinated VOCs. A subsequent investigation identified a plume of TCE extending from the building approximately 250 feet down gradient (off-site and onto private property across a street).

Remediation Approach
The initial remedial approach involved installation and operation of a dual-phase extraction (DPE) system throughout most of the plume area (26 extraction wells), which operated for approximately 1 ½ years. Approximately one year after the DPE system installation, a core area in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) injection of RegenOx® was performed by KERAMIDA and Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS). ISCO combined with further operation of the DPE system was effective in additional reductions of cVOC concentrations in the groundwater. Upon conclusion of these efforts, the DPE system was shut down to allow for enhanced reductive dechlorination process to take place.
A successful enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) pilot test with 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus was performed around two off-site wells at the leading edge of the plume. Based on the success of this test, an ERD injection was performed in a newly-identified source area with outstanding results in the first six months. Consequently, the DPE system remained shut down and a full-scale ERD injection was performed in the core area of the plume.
Approximately 9 months after the full scale injections, a very small supplemental injection was performed in the off-site area where the pilot study was done and another in an area where no injection was performed. One year after the full-scale ERD injection, cVOC concentrations are below the target cleanup levels in all wells with the exception of two slightly elevated VC concentrations, which are expected to decrease shortly.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – PersulfOx® Treats Petroleum Hydrocarbons
In Situ Chemical Oxidation and Enhanced Aerobic Biodegradation Remediate Underground Storage Tank Site
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to design and implement an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) treatment plan to remediate a diesel gas plume from a former leaking underground storage tank (UST) on a residential farm property. The defined treatment area comprised approximately 5,280 square feet (ft2), and the treatment of the gas plume included three application events using

PersulfOx®, with the final application immediately followed by an application with Oxygen Release Compound Advanced (ORC® Advanced). A total of 5,840.6 pounds of PersulfOx and 2,589 pounds of ORC Advanced were injected during the course of the project.
Utilizing PersulfOx remediation chemistry to distribute throughout the subsurface, 91 direct-push injection technology (DPT) injection points were advanced every 100 ft2 over the course of three application events. ORC-A was applied in 53 discrete DPT injection points approximately every 100 ft2. RRS utilized both expendable points and retractable screen-tip injection tooling to apply the PersulfOx and ORC Advanced at discrete intervals across the vertical treatment interval from 8 to 12 feet and 8 to 16 feet below ground surface (bgs) within the sandy saturated soils. Low pressures and moderate application rates were utilized to apply the remediation chemistry at up to four (4) injection point locations simultaneously. RRS personnel performed real-time reagent distribution diagnostics to optimize the distribution of the material.
ISCO/ERD Treat PCE Contamination at Indiana Dry Cleaner
Remediation Plan Addresses Concentrations Below Facility and Downgradient
Project Highlights
- PersulfOx utilized subslab near the source to inhibit vapor issues within the building.
- Combined remediation plan addressed impacts both below the building and downgradient of the facility.
- PCE contamination was nearly depleted and TCE levels below 10 ppb were observed.
- The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.

Project Summary
A release of PCE from a former dry cleaning operation in Indianapolis resulted in groundwater contamination below the facility and downgradient. Contamination impacts were also observed in shallow fill below the concrete slab. Along with the groundwater/soil contamination, vapor intrusion was also detected within the facility and adjacent spaces in the strip mall. A combination of enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was used for remedial action. Analytical results obtained indicate nearly complete reduction of PCE and less than 10 ppb of TCE in all wells. Currently, elevated VC concentrations in two wells were observed but reductions are expected as the ERD process is completed.
Remediation Approach
PersulfOx® Catalyzed Persulfate was injected below the floor slab of the dry cleaner to inhibit vapor production within the facility and adjacent spaces. 3-D Microemulsion® and Bio-Dechlor INNOCULUM® Plus were injected into the uppermost water-bearing area below the dry cleaner and into two areas downgradient on either side of the building. Supplemental ERD injections were applied in two areas approximately 9 months after the initial injection to address minor sand stringers that were contributing to continued contamination impacts. The supplemental injection resulted in immediate elimination of PCE/TCE and a rapid production of VC. The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Combined Remedies Treatment Results in a $650,000 Cost Savings for End User
Project Highlights
- By implementing this strategy with a clear path to closure, KERAMIDA saved their client approximately $650,000 versus the alternative containment plan. KERAMIDA’s sophisticated and aggressive remedial approach matched the technologies (ISCO, ISCR, ERD) to the technical challenges at the site.
- PCE was virtually eliminated in most other impacted wells, and continued evidence of reductive dechlorination is ongoing.
- Project currently in the monitoring phase to establish plume stability for closure.

Project Summary
A PCE spill from a 55 gallon drum in the late 1980s contaminated a manufacturing site in Indiana. Contaminated soil was excavated in the spill area and a pump and treat interceptor system was installed downgradient of the plume. The system continued to operate intermittently throughout the 1990s. A previous consultant had submitted a remediation work plan proposing the use of a permeable reactive barrier. However, the plan was rejected because the intended goal was remedial closure, not containment. KERAMIDA proposed a combined in-situ chemical oxidation (ISCO)/enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach focusing on the spill area (source) and the downgradient, on-site plume, with a small injection off-site. The remediation plan was approved and the injection was completed in November 2013. KERAMIDA’s cost to closure is likely to be achieved for less than $500,000 – saving $650,000-800,000 over the life of the project. (The rejected remediation plan from the previous consultant had an estimated cost of $1.3 million with no plan for closure.)
Remediation Approach
The combined remedies treatment included an initial application of PersulfOx® Catalyzed Persulfate in the source area with subsequent applications of 3D Microemulsion® (3DME), BioDechlor INNOCULUM® Plus (BDI-Plus) and Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®). In addition, 3DME and BDI-Plus were applied in two downgradient areas of the plume. Groundwater monitoring performed in the eight months since injection indicates dramatic reductions in PCE concentrations. Within the source area, an initial PCE concentration of approximately 70,000 ppb was reduced to 278 ppb (with a corresponding increase in cis-1,2-DCE, which is currently being degraded). PCE was virtually eliminated in most other impacted wells and evidence of reductive dechlorination is ongoing.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
CRS is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
PlumeStop® Applied to Former Electronics Facility in Indiana Achieves 99.9% Reduction in 2 Months
Project Highlights
- 92% reduction within two weeks
- 99.9% reduction in two months
- Combined remedy approach reduced mixed VOC plume to non-detect within nine months (<5μg/L)
- No rebound in over 18 months of site monitoring
Project Summary
An evaluation of PlumeStop performance was conducted on a section of a mixed chlorinated solvent plume (cVOC) comprising trichloroethene (TCE – 1,390 μg/L) and 1,1,1-trichlorotethane (TCA, 3,550 μg/L) at a former electronics facility in Indiana. PlumeStop was applied in conjunction with the controlled-release electron donor, Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC®). Post-treatment solvent concentrations in groundwater were reduced in two weeks by 92% at the first sampling round. Concentrations were reduced by 99% by the second sampling round (one month) and 99.9% by the third sampling round (two months). No cVOCs were detected above analytical thresholds (<5μg/L) after three months. Source area treatment activities are being monitored for closure and the results are being evaluated as a potential larger scale plume treatment option.
Remediation Approach
PlumeStop was applied perpendicularly to the groundwater flow using 10 direct-push injections around a central monitoring point. Approximately 180 pounds of HRC was applied into three injection points.
REGENESIS Solution Applied
PlumeStop is an innovative in situ remediation technology designed to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations, stop migrating plumes, eliminate contaminant rebound, achieve stringent clean-up standards and treat back-diffusing contaminants. PlumeStop provides a unique colloidal biomatrix platform which rapidly sorbs contaminants out of the dissolved-phase. Once contaminants are concentrated within the PlumeStop biomatrix, they can be completely biodegraded in place using compatible REGENESIS bioremediation products.
HRC is a controlled release, electron donor material, that when hydrated, is specifically designed to produce a controlled release of soluble lactate. The newly available lactic acid is highly efficient for the production of dissolved hydrogen to fuel anaerobic biodegradation processes in soil and groundwater.
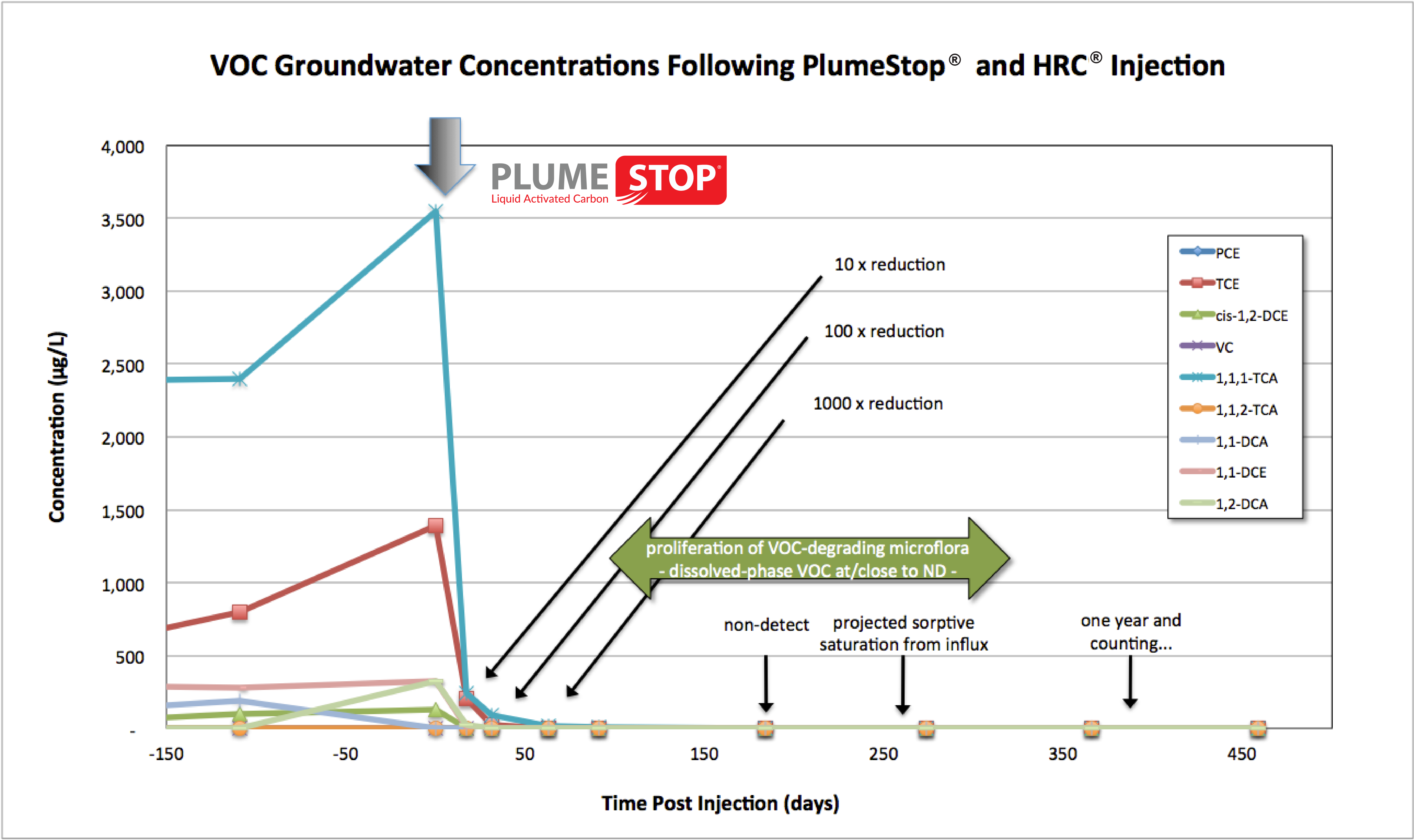
Results
Using a combined remedy approach, the application of PlumeStop and HRC successfully reduced contaminant levels to non-detect and positioned PlumeStop as a viable solution for larger scale projects.
Long-Term Chlorinated Solvent Treatment using a Controlled-Release Microemulsion
PROJECT SUMMARY
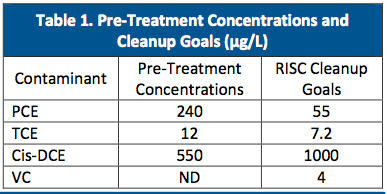
- Dry cleaning operations resulted in a chlorinated solvent plume with concentrations as high as 700 micrograms per liter (μg/L) in chlorinated solvents
- Typical Midwestern geology: Silty clay with intermittent sand stringers underlain by a clay till confining layer
- Contaminants of concern within the silty clay aquifer included tetrachloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethene (TCE) (see Table 1)
- High sulfate environment (~100 mg/L) – potential inhibitor for successful remediation
- Cleanup goals were based on the Industrial Risk Integrated System of Closure (RISC) levels
- Enhanced anaerobic bioremediation of chlorinated solvents in groundwater using 3-D Microemulsion (3DMe)®
- $195,000 (Costs include 3DMe® material, injection, field oversight, 2 yrs post injection monitoring, project management and report writing)
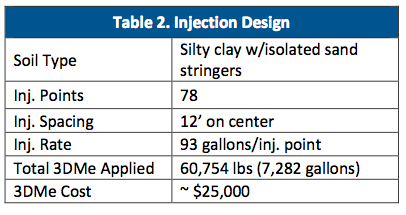
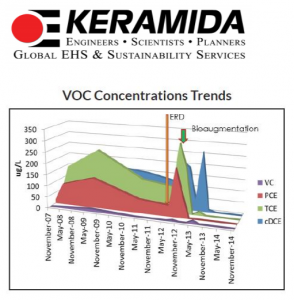
RESULTS
- The 3DMe application overcame high sulfate levels and resulted in a reducing environment lasting almost 2 years
- Sampling at 22 months post-3DMe indicated sustained low levels of ORP (-136mV) and DO (1.3mg/L)
- Reduction of chlorinated solvents by 83% to 98% in all impacted wells
- Site is pending closure from regulatory agency
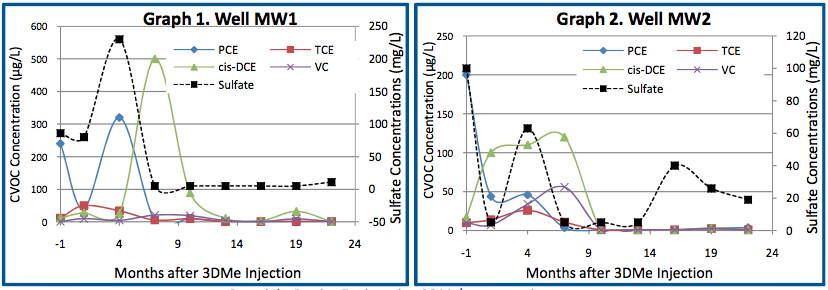
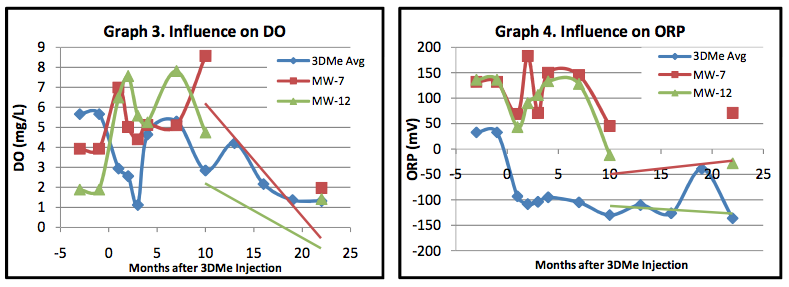
ELECTRON DONOR INFLUENCE
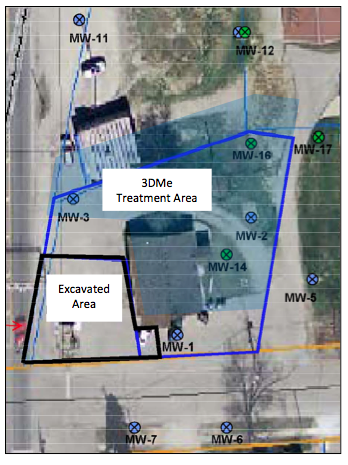
Analytical parameters including oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), dissolved oxygen (DO) and total organic acids (TOAs) were monitored to verify the influence of the electron donor post-injection. The monitoring wells likely influenced by 3DMe (MW1-3, MW5, MW14-17) were analyzed on average and compared to background wells MW7 and MW12.
Within the 3DMe influence area:
- On average, ORP reduced to -100mV and DO levels declined to ~2mg/L (Graphs 3 and 4)
- Concentrations of TOAs were detected at >1,000 mg/L during the first 10 months of
monitoring
Surgical Site Closure – 30 Sites in Indiana Receive Closure using ORC
CASE SUMMARY
Surgical Site Closure
The “Surgical Site Closure” strategy was developed by Mr. Steve Sittler, an employee of KERAMIDA in Indianapolis, Indiana. The method is an innovative remedial strategy designed to intelligently integrate natural attenuation, risk-based cleanup goals and focused source removal/treatment to cost-effectively remediate contaminated areas. This approach is best applied at sites where released materials are amenable to biodegradation and where long-term, natural attenuation-type strategies are not suitable for reasons of property transfer or potential off-site liability. This strategy was performed at 30 sites in Indiana for a major oil company.
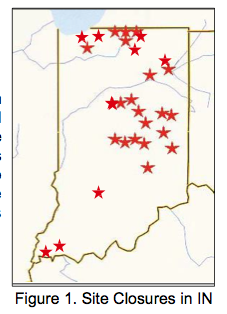
Service Stations/Bulk Storage Terminals – Indiana
From 1998-2008, a total of 30 service station/bulk storage terminal sites were targeted for Surgical Site Closure in Indiana. The subsurface matrix consisted of unconsolidated sediments ranging from low-permeability silty clays with sand stringers to sand and gravel formations. The contaminants of concern were primarily gasoline and diesel fuel. A combination of source removal via excavation coupled with enhanced in situ bioremediation using Oxygen Release Compound (ORC®) was performed at most sites.
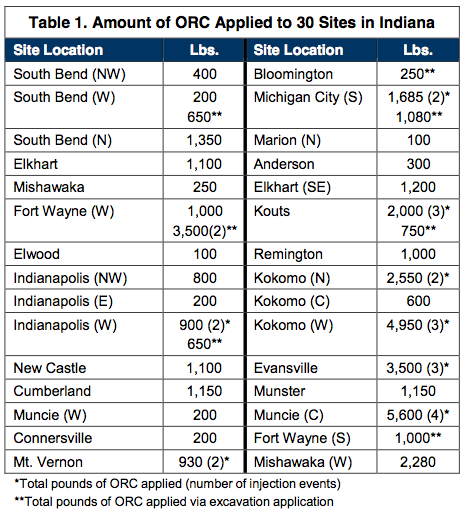
REMEDIATION APPROACH
The remediation approach included focused soil excavation of the source area and/or ORC direct-push injection. At some sites ORC was applied to the base of the excavation prior to backfilling. Shortly afterwards, a direct-push injection of ORC was completed over the remainder of the plume. The amount of ORC needed at each site location was determined using various site characteristics including contaminant concentration, seepage velocity, and treatment area.
The majority of the sites were successfully treated using only one injection of ORC; however, a handful of sites received multiple applications. Most of these sites indicated that high levels of BTEX were present prior to treatment (>1,000ppb to <50,000ppb) and required additional applications to sustain aerobic bioremediation.
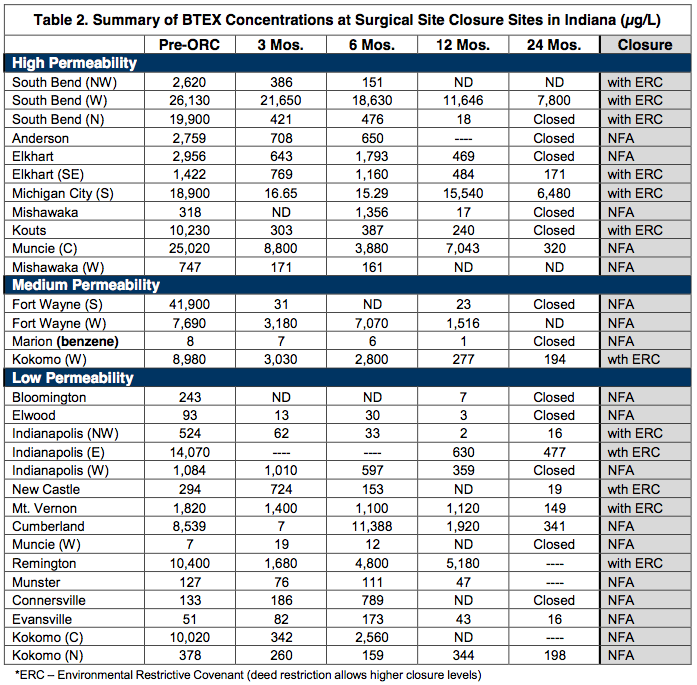
ABOUT THE CONSULTANT
![]() KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
CONCLUSION
The Surgical Site Closure method was successful in reaching site closure at 30 petroleum-impacted sites over a nine-year period. The average time to reach site closure was ~3 years and the average cost to implement the remedial strategy was ~$70,000. Cost analyses indicated that a traditional remediation approach would have ranged from at least $100,000 to potentially $1 million. Actual implementation costs for the Surgical Site Closure approach ranged from approximately $25,000 to $75,000 plus monitoring costs.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español







