Achieve rapid and effective immobilization of PFAS in source areas, to prevent further contaminant movement into groundwater and drive enhanced natural attenuation of the plume.
Protect downgradient receptors and avoid ongoing and uncertain costs with this highly flexible in situ solution.
Treatment Mechanisms
-
Leachability reduction
-
Infiltration prevention
-
Creation of subsurface filter within vadose zone
-
Sorption and retardation of PFAS in groundwater and capillary fringe
Benefits of In Situ Source Treatment
Rapid Risk Reduction
- Protects human health
- Protects the environment

Cost Savings
- Avoid excavation and disposal cost
- Avoid high, ongoing and uncertain costs from pump and treat
- No operational cost

Accurate & Flexible
- Targets vadose and saturated zone source areas
- Site-specific design
- Combine with in situ plume treatment for guaranteed risk elimination

Sustainable Solution
- No waste created
- No hazardous waste disposal required
- No ongoing operational activities and energy use
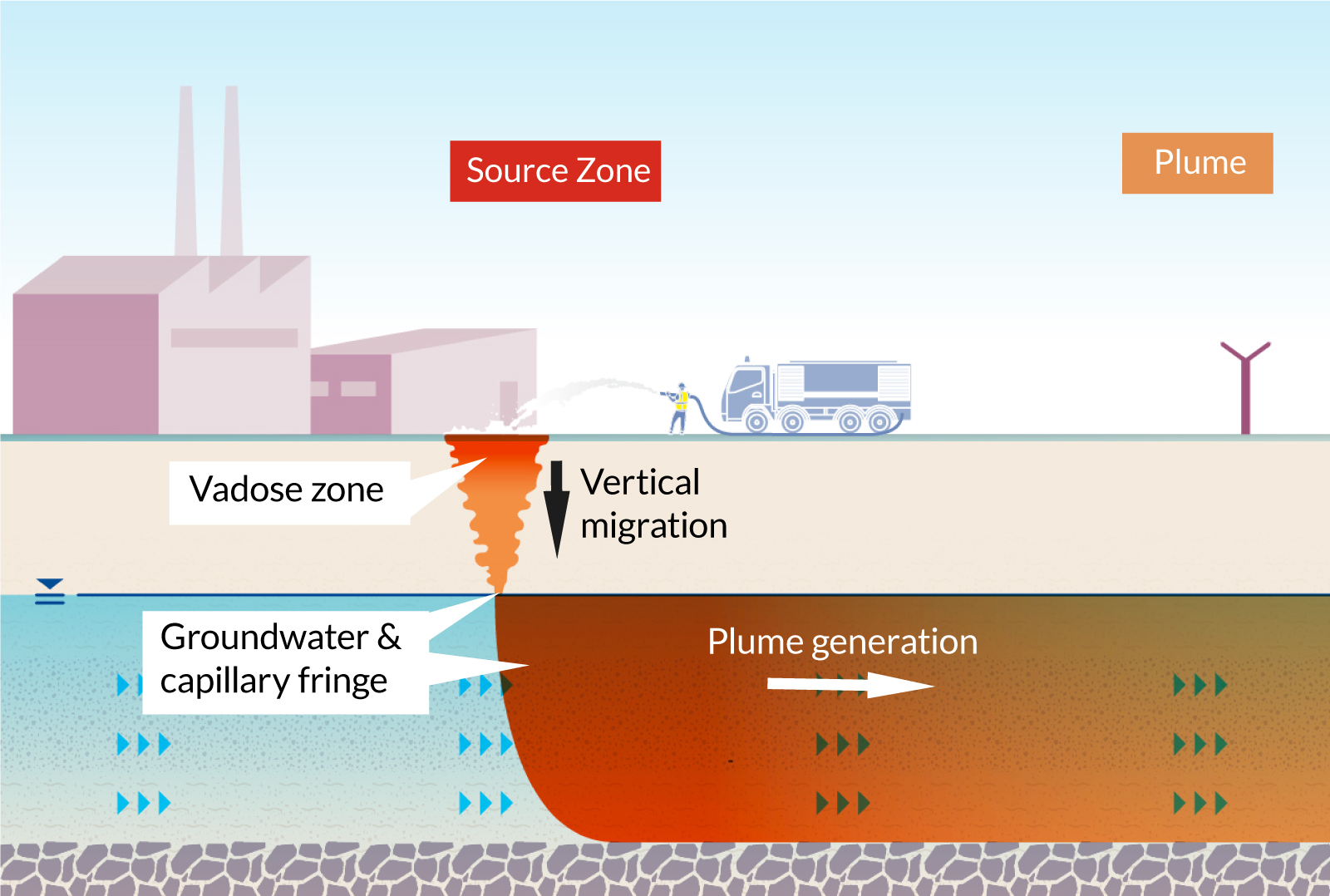
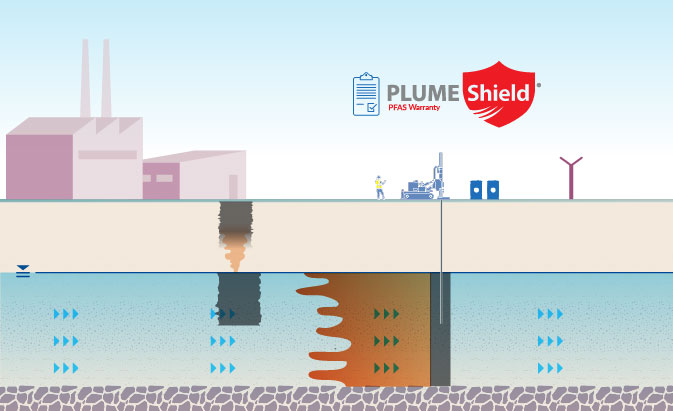
Soil Source Treatment
REGENESIS provides an in situ sequestration and stabilization service for PFAS impacted soils in the source area. This is completed by mixing a site-specific blend of amendments into the target soils. This dramatically reduces the leachability of PFAS attached to the soils and minimizes precipitation infiltration.
SourceStop™ colloidal activated carbon (CAC) is used to penetrate into the underlying soils and coat vertical flow-paths to capture any residual contamination.
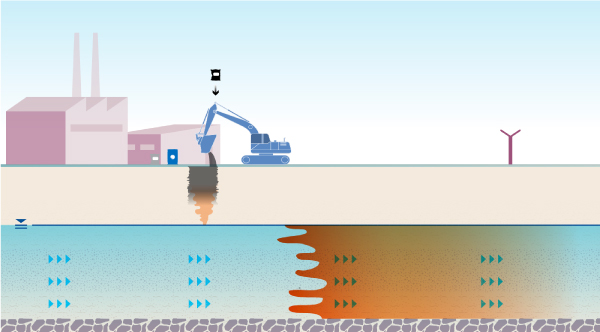
How to complete in situ PFAS source area treatment on your site

1. A soil sample is taken and tested in our laboratory using a blend of amendments including activated carbon, clays and SourceStop.

2. A specific design is created for the site and the best application method is determined

3. The site-specific blend is applied to the site soils and injected into the groundwater

4. Source area contamination is immobilized and the downgradient plume attenuates, configured for the target site.
Groundwater Source Treatment
SourceStop™ is injected under low pressure into the source zone groundwater and capillary fringe. This converts to subsurface into a purifying filter which rapidly removes high levels of PFAS from the groundwater through sorption.
About The Technology
SourceStop is a new remediation technology, engineered to enable in situ application within the vadose zone, capillary fringe and phreatic zone to treat PFAS. The combination of liquid format and micron-scale particle size optimizes treatment through:
-
Uniform soil coating
-
Penetration into low-permeability soils
-
Rapid and highly efficient sorption
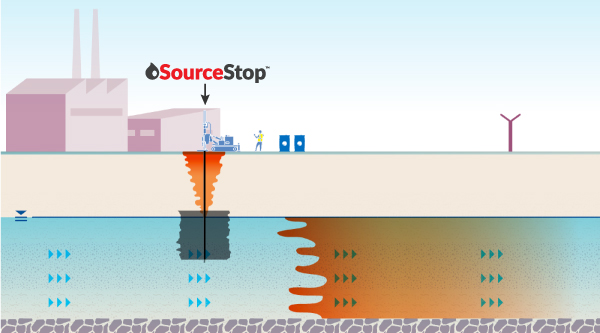

Combine with Plume Treatment & Warranty
If groundwater remedial targets are to be met in a short timeframe, then source treatment is easily combined with a downgradient PlumeStop® barrier to immediately eliminate risk.
The barrier can be provided with a PlumeShield™ warranty to provide certainty and peace of mind.
Resources
Technical Bulletin 1
Soil Stabilization – Optimizing Activated Carbon-Based Adsorbents for Immobilizing PFAS in Source Zones
Technical Bulletin 2
SourceStop – A High Concentration Colloidal Activated Carbon Product for Immobilizing PFAS at the Source
Enhanced Natural Attenuation of PFAS
Learn about the precedent of ENA in remediation and the direction PFAS regulation is taking
LONG LASTING
Long-term source and plume treatment
50% Lower Upfront Cost
Our applications can reduce upfront costs by 50%
90% Lower Treatment Cost
A typical application can reduce total costs by 90%
PFAS TREATMENT BENEFITS
Spill-location soils can discharge PFAS into the groundwater for decades. By using a blend of amendments and SourceStop™, further leaching of contamination is minimised, creating the enhanced attenuation of the downgradient plume below actionable levels.
While the plume is attenuating, offsite liability can be immediately removed and downgradient receptors protected through treatment of the groundwater using a PlumeStop® barrier. The PlumeStop barrier can be supplied with a warranty to guarantee performance.


 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español





