BTEX Concentrations Decreased to Non-Detect 18 Months Following RegenOx Injection
Project Highlights
- Combined remediation approach treats contaminants that remained following emergency excavation
- RegenOx® and ORC Advanced® selected to eliminate need for dedicated groundwater treatment infrastructure
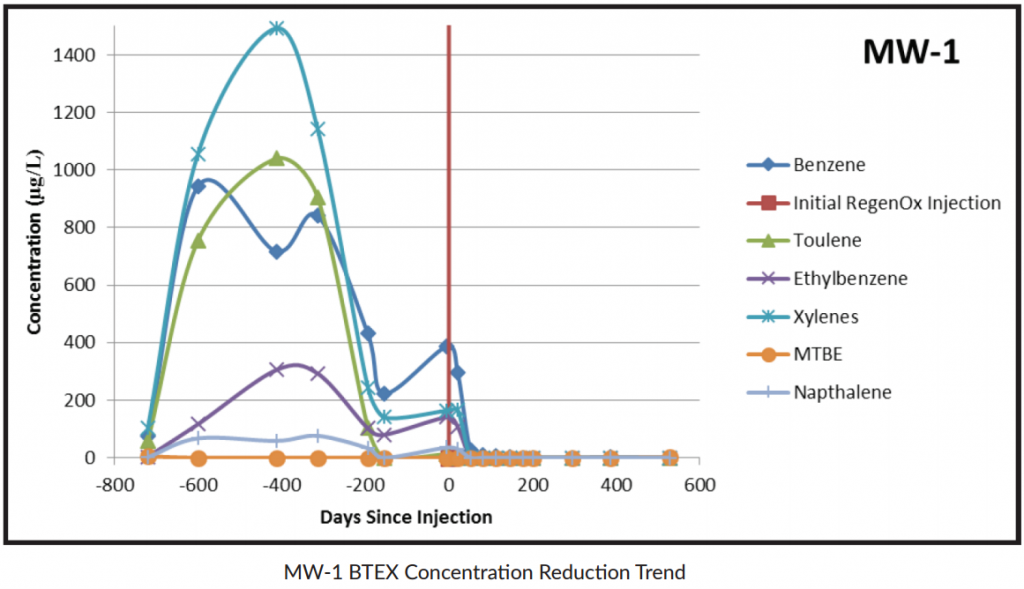
- BTEX levels reduced by 97% to below non-detect levels in the two highest concentration wells
Project Summary
A rural site located in south-central North Carolina required remediation to treat petroleum contamination from an overturned tanker truck. Excavation activities during an emergency response removed much of the contaminant mass, however additional contamination in soil and groundwater remained after the excavation was completed.
In the two highest-concentration wells, total BTEX averaged more than 1,300 μg/L in the four quarterly groundwater monitoring events prior to treatment.
A combined chemical oxidation and aerobic bioremediation treatment was employed to eliminate the need for dedicated groundwater treatment infrastructure at this roadside location to advance the site to regulatory closure.
The products selected were RegenOx, an in situ chemical oxidant, and ORC Advanced, an enhanced aerobic bioremediation product. The treatment covered a 3,900-square-foot area through 30 direct-push injection points in the former spill area.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
ORC Advanced is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
Results
Within 18 months of treatment, the site was under natural attenuation monitoring prior to regulatory closure with five of the six wells already below stringent regulatory requirements.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español
