In Situ Remedy Addresses PFAS Risk at Superfund Site
 This case study reviews remedial programs undertaken at the Solvents Recovery Service of New England (SRSNE), where soil and groundwater were contaminated with VOCs and PFAS contaminants. The site was placed on the National Priorities List in 1983 and by 1991, all activities stopped as the site ceased operations. Since shutting down, the site has benefited from significant remediation efforts. In 2018, an innovative remedial approach incorporated natural attenuation with the use of PlumeStop® to work with an existing sheet pile structure to limit the mobility of the plume and effectively treat contaminant concentrations. PlumeStop quickly reduced PFOS/PFOA levels and in combination with AquaZVI® eliminated VOC contaminant concentrations. It is estimated that the PRP group involved will save $400,000 annually with the shut down of the pump and treat system on site.
This case study reviews remedial programs undertaken at the Solvents Recovery Service of New England (SRSNE), where soil and groundwater were contaminated with VOCs and PFAS contaminants. The site was placed on the National Priorities List in 1983 and by 1991, all activities stopped as the site ceased operations. Since shutting down, the site has benefited from significant remediation efforts. In 2018, an innovative remedial approach incorporated natural attenuation with the use of PlumeStop® to work with an existing sheet pile structure to limit the mobility of the plume and effectively treat contaminant concentrations. PlumeStop quickly reduced PFOS/PFOA levels and in combination with AquaZVI® eliminated VOC contaminant concentrations. It is estimated that the PRP group involved will save $400,000 annually with the shut down of the pump and treat system on site.
This case study features the following:
- Estimated savings of $400,000 annually as a result of halting pump and treat operations
- PlumeStop quickly reduced PFOS/PFOA levels and in combination with AquaZVI eliminated VOC contaminant concentrations
- Extension of the popular Rails to Trails route now runs through the property, as a result of successful remediation efforts
8m 56s reading time
PlumeStop® and ORC Advanced® Applications Achieve Successful Results in 24 Hours
4m 35s reading time
Project Highlights
- Successful rapid reduction of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminant concentrations in soil and groundwater completed within approximately 24 hours.
- In Situ injection application of PlumeStop® Liquid Activated Carbon and ORC Advanced technologies assist REGENESIS strategic partner in bringing closure to facility identified as Leaking Underground Storage Tank (LUST) site
- Petroleum hydrocarbon concentrations (PHCs) in groundwater and soil reduced below Washington Department of Ecology’s (Ecology) Model Toxics Control Act (MTCA)
Project Summary
An active gasoline station in Bothell, Washington was listed as a hazardous Leaking Underground Storage Tank (LUST) site by the State of Washington Department of Ecology (Ecology) after two subsurface investigations detected petroleum hydrocarbon-impacted soil and groundwater. Entering into the state’s Voluntary Cleanup Program (VCP) in 2001, the site continuously failed to meet regulatory requirements defined in the Model Toxics Control Act (MTCA), despite years of cleanup efforts using a soil vapor extraction (SVE) system and an air sparge (AS) system to remove contaminant concentrations from beneath the site. Charged with remediation, Antea Group partnered with REGENESIS to implement a solution, which included in situ injection applications using PlumeStop and ORC Advanced technologies.
Technology Applied
PlumeStop – an innovative groundwater remediation technology designed to address the challenges of excessive time and end-point uncertainty in groundwater remediation. PlumeStop is composed of very fine particles of activated carbon (1-2µm) suspended in water through the use of unique organic polymer dispersion chemistry. Once in the subsurface, the material behaves as a colloidal biomatrix binding to the aquifer matrix, rapidly removing contaminants from groundwater, and expediting permanent contaminant biodegradation.
ORC Advanced (ORC-A) – an engineered, oxygen-release compound designed specifically for enhanced, in situ aerobic bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater and saturated soils that, upon contact with groundwater, produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen (17% by weight) for periods of up to 12 months in a single application, accelerating aerobic biodegradation processes up to 100 times faster than natural degradation rates.
Background
Despite the installation of three groundwater monitoring wells (MW-1 through MW-3) in 2002 and five additional monitoring wells (MW-4 through MW-8) in 2003, concentrations of total petroleum hydrocarbons in TPH-g and BTEX in the western portion of the site exceeded the Model Toxics Control Act (MTCA) Method A cleanup levels. In 2004, a soil vapor extraction (SVE) system and an air-sparge (AS) system were installed and by 2005 an estimated 2,076 pounds of total volatile hydrocarbons (TVH) were extracted, with concentrations falling below MTCA Method A cleanup levels for two consecutive quarters. Laboratory analysis of groundwater samples collected during the following two quarters, however, indicated that hydrocarbon compounds in groundwater had increased in several monitoring wells.
Challenge
The AS system was restarted in October, 2005 and operated on an approximate 2-week-on and 2-week-off cycle through February, 2009, when it was shut down based on non-detectable hydrocarbon concentrations in all but one groundwater monitoring well, MW-3. As a remediation strategy to address TPH-g and benzene impacts that remained in well MW-3, sulfate injection was proposed. However, due to high sulfate concentrations observed in the down-gradient monitoring well, MW-9, the sulfate injections were suspended in November of 2012 and evaluations of other chemical injection methods were proposed.
REGENESIS Remediation Services (RRS) recommended PlumeStop injection and completed two soil borings for design verification testing in November, 2015. Soils on-site were primarily sand and gravel, with two, 4-6” clayey silt layers—one at approximately five feet and the other at 10.5 feet below ground surface (bgs). Based on field screening with photoionization (PID), contamination appeared to be concentrated at the 8-9 feet depth interval, a point at which soil increasingly hardens. With results of a laboratory analysis, RRS modified the design, adjusting the vertical treatment interval from 5-12 feet below ground surface to 7-11 feet, with the concentrations and quantities of PlumeStop and ORC-A remaining unchanged.
Solution
REGENESIS Remediation Services (RRS) injected approximately 200 gallons of PlumeStop 6,000 ppm solution into on-site wells IW-1 and SVE-1 December, 2015. Using strategically placed point locations to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations, Direct Push Technology (DPT) was employed to advance injection points throughout the treatment zone at each respective injection point location. The following day, the solution was increased to 12,000 ppm, for a total of 835 gallons of PlumeStop solution (as applied with water) injected within the targeted treatment interval to deliver the full volume of remediation chemistry and complete the application on schedule.
A total of nine (9) PlumeStop DPT injection points were cleared to 5 feet below ground surface pre-injection, and during the course of the injection seven (7) point locations were advanced to a depth of 11 feet below ground surface and retracted to a depth of 7 feet below ground surface using 1.50 inch outer diameter (O.D) Geoprobe® injection rods with retractable screen tooling.
Additionally, 120 pounds of ORC-A were applied at approximately 30% solution (w/w) in cleared boreholes via a backfilling method, which involved drilling to the target depth, retracting the rods and pouring the ORC-A slurry down open boreholes to approximately 5 feet below ground surface in order to properly abandon points.
Results
During the course of the injection and at the end of the application, increases in groundwater levels were observed in monitoring wells MW-3 and MW-9 in the treatment area. Additionally, increases in ORP (oxidation reduction potential) were observed in MW-2, MW-3, MW-6, MW-7, MW-8, and MW-9. Increases in dissolved oxygen were also noted post-injection in MW-2, MW-3, MW-6, MW-7, MW-8, and MW-9.
The successful and rapid reduction of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminant concentrations in soil and groundwater was achieved within approximately 24 hours, despite difficulty injecting the material via direct-push injection points. With field modifications, RRS was able to not only mitigate surfacing issues by switching to injection via injection well application but also observe the desired distribution of the remediation chemistry in the subsurface.
In the same way the State of Washington Department of Ecology continues to take steps and implement tools that will streamline the cleanup process even further, REGENESIS recognizes the critical need for cost-effective, sustainable and environmentally sound remediation solutions. Whether pioneering new in situ technologies in the lab or rolling up its sleeves in the field to ensure a successful project outcome, REGENESIS remains committed to advancing the remediation industry for the benefit of its partners as well as for the future of the world at large.
How PlumeStop® Brings Sites to Permanent Closure
PlumeStop rapidly removes contaminants from groundwater and stimulates their permanent degradation. This exciting, turn-key solution offers several key benefits for addressing brownfield site treatment, including:
- Rapid reduction of dissolved-phase plumes
- Distribution of widely under low injection pressures
- Achievement of stringent groundwater clean-up standards
- Providing a long-term means of addressing matrix back–diffusion
- Elimination of excessive time and end-point uncertainty associated with groundwater remediation
PlumeStop is composed of very fine particles of activated carbon (1-2µm), suspended in water through the use of unique organic polymer dispersion chemistry. Once in the subsurface, the material behaves as a colloidal biomatrix, binding to the aquifer matrix, rapidly removing contaminants from groundwater, and expediting permanent contaminant biodegradation. This unique remediation technology accomplishes treatment with the use of highly dispersible, fast-acting, sorption-based technology which captures and concentrates dissolved-phase contaminants within its matrix-like structure. When contaminants are sorbed onto the regenerative matrix, biodegradation processes achieve complete remediation at an accelerated rate, leading to successful site treatment.
Former Taxi Maintenance Site Successfully Treated with Enhance d Anaerobic Biodegradation and Bioaugmentation
Project Highlights
- Combined introduction of HRC® hydrogen release compounds and BDI Plus® bioaugmentation cultures resulted in reduction in chlorinated solvent concentrations, meeting site goals
- Successful remediation permitted redevelopment of the site into an elementary school
Project Summary
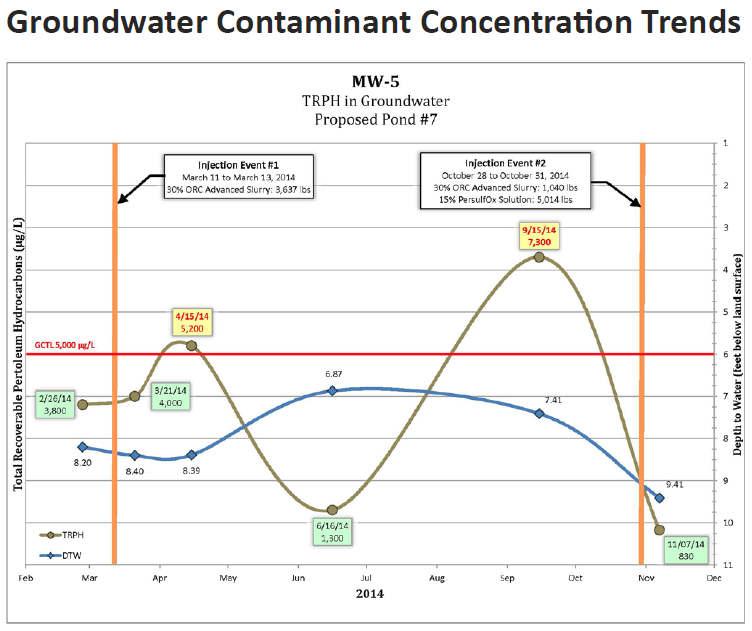
A former taxi maintenence facility located in Los Angeles, California was used as a garage and maintenance facility containing seven underground storage tanks (USTs), four hydraulic hoists, an elevator, a clarifier, and a spray paint booth. Environmental assessment related to the planned redevelopment of the garage and nearby commercial properties and residences revealed contamination of the soil and groundwater beneath the site with trichloroethene (TCE) and 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE) due to release from the former USTs and paint shop areas.
Under the jurisdiction of the California Department of Toxic Substance Control, an enhanced anaerobic biodegradation approach in conjunction with bioaugmentation was developed to remediate the chlorinated solvent contamination. This approach combined the introduction of the dechlorinating microcosm BDI Plus® with the application of supporting hydrogen release compounds 3-D Microemulsion® and HRC Primer®. Following treatment of the site, reduction in TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations have been observed after four quarters of postremediation monitoring. Microbial data supports the benefits of the bioaugmentation effort by showing a steep increase in dehalococcoides populations, which increased by nearly four orders of magnitude. In addition, all geochemical parameters are in range for a reductive state.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
HRC Primer is derivative of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound product and is designed to provide a controlled but fast release of hydrogen to assist in initiating anaerobic biodegradation.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI Plus) is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Results
Reduction of TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations by enhanced anaerobic biodegradation and bioaugmentation facilitated the redevelopment of a former taxi garage and maintenance facility. Following a reduction in contaminant concentrations, the site was redeveloped to an elementary school.
45s reading time
Historic Site On Track To Reach Remediation Goals
 This case study reviews a site in the Ohio River Valley where historic industrial operations over the last 100 years at a manufacturing facility have resulted in PCE and TCE impacts to 7,500 square feet of shallow groundwater. To move the redevelopment of this site forward, groundwater VOC sample results must meet the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for four consecutive quarters. Download the case study to learn about the combined remedy using PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI+ to address the contaminants.
This case study reviews a site in the Ohio River Valley where historic industrial operations over the last 100 years at a manufacturing facility have resulted in PCE and TCE impacts to 7,500 square feet of shallow groundwater. To move the redevelopment of this site forward, groundwater VOC sample results must meet the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for four consecutive quarters. Download the case study to learn about the combined remedy using PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI+ to address the contaminants.
This case study features the following:
- Creative combined remedy approach addressed accumulated contaminants from over 100 years of manufacturing operations
- Innovative application approach using 1.5” diameter wells effectively accommodated low ceiling and tight spaces, allowing for successful reagent injection
- 180 days post-injection, all VOCs were measured at greatly reduced concentrations and geochemical conditions remain ideal for biodegradatio
2m 40s reading time
Remediation Goals Achieved with Combined Remedy Approach
Soil Mixing and ISCO Approach Achieves Arizona DEQ Closure Levels
 This case study reviews an active Underground Storage Tank (UST) case with the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ), where the site needed to meet ADEQ closure levels quickly in order to seek risk-based closure as part of a property transaction. After performing remedial assessment activities, the consulting firm Antea Group selected a combined remedy approach from REGENESIS, which included soil mixing using RegenOx® and H2O2 in the source zone and ISCO injections using PersulfOx® in the core plume. The solution from REGENESIS achieved ADEQ Closure levels for the site and now Antea Group is seeking a risk-based closure.
This case study reviews an active Underground Storage Tank (UST) case with the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ), where the site needed to meet ADEQ closure levels quickly in order to seek risk-based closure as part of a property transaction. After performing remedial assessment activities, the consulting firm Antea Group selected a combined remedy approach from REGENESIS, which included soil mixing using RegenOx® and H2O2 in the source zone and ISCO injections using PersulfOx® in the core plume. The solution from REGENESIS achieved ADEQ Closure levels for the site and now Antea Group is seeking a risk-based closure.
This case study features the following:
- Significant contaminant reductions achieved in both the source area and core plume
- 8-10 weeks of time saved compared to alternative approaches
- $500,000 saved in project costs compared to alternative Electrical Resistance Heating (ERH) approach being considered
Advanced Remedial Technologies Restore Neighborhood
Former Michigan Industrial Site Treated Using Combined Remedy Approach
This case study reviews a former plating facility in southwest Michigan that had released chlorinated volatile organic compounds (cVOCs) into shallow groundwater, resulting in a ¼-mile long contaminant plume. In response, the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality (MDEQ) and the environmental firm, DLZ, implemented a combined remedy which included mitigating vapor intrusion in the residential basements and treating the groundwater plume with a novel, multi-phase in situ bioremediation approach.
- Application of combined REGENESIS technologies to biodegrade contaminants, prevent further plume migration, and protect occupants from the threat of vapor intrusion.
- Reduction of the total cVOC plume extent by 95% and reduced mass by 99.8%.
- Positive results indicating the degradation process is ongoing and processing.
8m 54s reading time
Site Goals Achieved Within Two Months
A Former Santa Barbara Manufacturing Facility Treated Using a Combined Remedy Approach
 This case study reviews a contaminated manufacturing site in Santa Barbara, California. A former manufacturing operation had left PCE and TCE contaminant levels above regulatory limits with previous remediation approaches attempted without complete success. Applying a combined remedy approach, Haro Environmental chose to focus on incorporating a design to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations for sustained treatment, and reduce the potential for further downgradient migration of the PCE and TCE contaminants.
This case study reviews a contaminated manufacturing site in Santa Barbara, California. A former manufacturing operation had left PCE and TCE contaminant levels above regulatory limits with previous remediation approaches attempted without complete success. Applying a combined remedy approach, Haro Environmental chose to focus on incorporating a design to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations for sustained treatment, and reduce the potential for further downgradient migration of the PCE and TCE contaminants.
This case study features the following:
- This site has been an active case since 2007. REGENESIS was able to eliminate the contaminant quickly and effectively using a combined remedy approach.
- After conducting a pre-field remediation test, the injection interval was reduced from 12 feet to 9 feet with a bottom-up approach, reducing the project costs by 30%.
- The combination of PlumeStop, HRC and BDI+ successfully eliminated the contaminants and created conditions for sustained treatment at the site.
5m 22s reading time
Combined Remedy Chosen for FDEP Innovative Technologies Program
Large Dilute BTEX Plume Succesfully Treated To Meet Concentration Milestones
 A former gas station site in Taylor County Florida had undergone prior remedial efforts over the years. The Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP), through its Innovative Technologies Program, engaged the environmental consulting firm, Advanced Environmental Technologies LLC (AET) to design an alternative combined remedial approach employing PlumeStop®, RegenOx® and ORC Advanced®, to sorb, degrade, and destroy the existing petroleum contaminant plume. Prior to full-scale implementation, treatment of this site began with a thorough Design Verification Testing (DVT).
A former gas station site in Taylor County Florida had undergone prior remedial efforts over the years. The Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP), through its Innovative Technologies Program, engaged the environmental consulting firm, Advanced Environmental Technologies LLC (AET) to design an alternative combined remedial approach employing PlumeStop®, RegenOx® and ORC Advanced®, to sorb, degrade, and destroy the existing petroleum contaminant plume. Prior to full-scale implementation, treatment of this site began with a thorough Design Verification Testing (DVT).
This case study features the following:
- An in situ combined remedy approach that was chosen as the most technically-feasible and cost-effective strategy in a competitive bid scenario for the Florida Department of Environmental Protection’s Innovative Technologies Program
- High level of site complexity – flowable fill layer present over the treatment area, difficult geology (i.e., clays and limestone), and close proximity to structures, utilities and a roadway
- Use of PlumeStop, RegenOx, and ORC Advanced to successfully address a large BTEX plume
RegenOx Application Quickly and Efficiently Lowered Diesel Range Organics (DRO) to Below ADEC Requirements
Project Highlights
- Two applications of RegenOx® reduced contaminants to a level below the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation (ADEC) standards to protect against migration to groundwater
- Completed in 8 weeks, restoring agriculture viability
- Soil was safely and efficiently cleaned preventing fuel from contaminating a nearby sensitive receptor

Project Summary
A Hydaburg site in Alaska, owned by Alaska Power and Telephone, previously housed diesel fuel generators and is now being converted into a hydro-electric plant. The land was contaminated by a diesel fuel spill requiring remediation. Approximately 1,000 cubic yards of soil were impacted and the starting concentrations of DRO were approximately 1 500 ppm. The goal was to reduce concentrations to below the ADEC standard of 230 ppm.
Due to the cold weather encountered during this project and the sensitive infrastructure in the area, it was important that the technology work effectively in less than ideal conditions. Also, the technology could not be corrosive nor generate excess heat. RegenOx, produces minimal heat and pressure, is non-corrosive, and works well at any temperature above freezing making it ideal for this project. Additionally, RegenOx is a chemical oxidant which quickly and effectively destroys a range of contaminants-in this case, DRO. The soil was screened with a trommel and RegenOx was mixed in a cement truck before being sprayed onto the soil. RegenOx was applied twice, with the applications spaced a week apart. This site required 20 lbs of RegenOx per cubic yard, in total 20,000 lbs.
Technology Description
RegenOx is a percarbonate-based in situ chemical oxidation technology that rapidly destroys petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated contaminants through powerful chemical reactions. It directly oxidizes contaminants while a catalytic component generates oxidizing free radicals to destroy the target compounds.
Results
After two applications of RegenOx, the concentrations of DRO went from 1,500 ppm to below 125 ppm, satisfying the ADEC requirement of below 230 ppm, within 8 weeks. After the remediation treatment, the soil was spread out, grass was planted and is now growing at the Hydaburg site, attesting to the renewed health of the soil.
Innovative Combined Amendment Approach Successfully Applied to Treat PHC Levels
Project Highlights
- Site previously treated with a series of RegenOx® and ORC Advanced® amendments significantly reduces plume concentrations. Remaining hot spot was then treated with turn-key injection application of PersulfOx® and ORC Advanced technologies bringing closure to facility
- Successful turn-key treatment of offsite hot spot completed within five days

Project Summary
An active gas station, identified by the State of Washington Department of Ecology as one of five LUST sites within one mile of Vancouver’s three groundwater monitoring wells, had entered into the state’s Voluntary Cleanup Program (VCP) in 2006 subsequent to shutdown of the onsite air-sparge/vapor extraction (AS/VE) system. This system had historically been employed at the site to supply oxygen for remedial purposes and address subsurface contamination that was first discovered beneath the dispenser islands in 1993. While prior applications of RegeneOx and ORC Advanced were effective in mitigating onsite contamination, PHC levels remained above MTCA criteria offsite hindering achievement of regulatory closure.
Antea® Group—the environmental consulting firm charged with remediation—partnered with REGENESIS® to implement a remedial strategy and technical design, which included the turn-key injection application of PersulfOx and ORC Advanced technologies to address petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) using an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) and enhanced aerobic remediation approach. The hot spot injection application included one event of PersulfOx coapplied with ORC Advanced, using direct push technology (DPT) injection points throughout the 3200 sq. ft. treatment area through 40 DPT injection points.
Technology Description
RegenOx – An injectable two-part advanced in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) reagent that combines a solid sodium percarbonate-based alkaline oxidant (Part A) with a liquid mixture of sodium silicates, silica gel and ferrous sulfate (Part B), resulting in a powerful technology that treats and destroys a wide range of target contaminants including both petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated compounds.
PersulfOx – An advanced ISCO reagent and all-in-one product with a built-in patented catalyst destroys organic contaminants found in groundwater and soil through abiotic chemical oxidation reactions.
ORC Advanced – An engineered, oxygen-release compound designed specifically for enhanced, in situ aerobic bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater and saturated soils. ORC Advanced produces a controlled release of molecular oxygen accelerating aerobic biodegradation processes up to 100 times f aster than natural degradation rates.
Results
For the final application event, following five on-site working days, REGENESIS completed the hot spot application process during which 9,753 lbs. of PersulfOx and 2,240 lbs. of ORC Advanced were applied to the designated treatment area. First quarter sampling results post-application showed concentrations below MTCA criteria. Following three quarters of monitoring, remediation of this site will be complete.
About the Client
Antea Group is an international engineering and environmental consulting firm specializing in full-service solutions in the fields of environment, infrastructure, urban planning and water. With more than 3,000 employees in over 100 offices around the world, Antea Group serves clients ranging from global energy companies and manufacturers to national governments and local municipalities.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español











