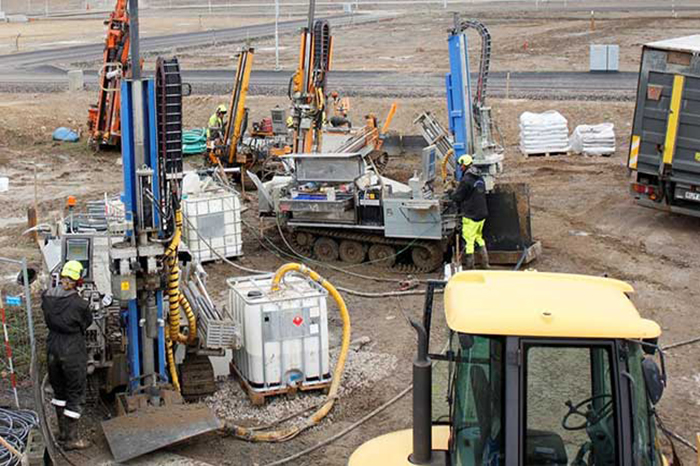
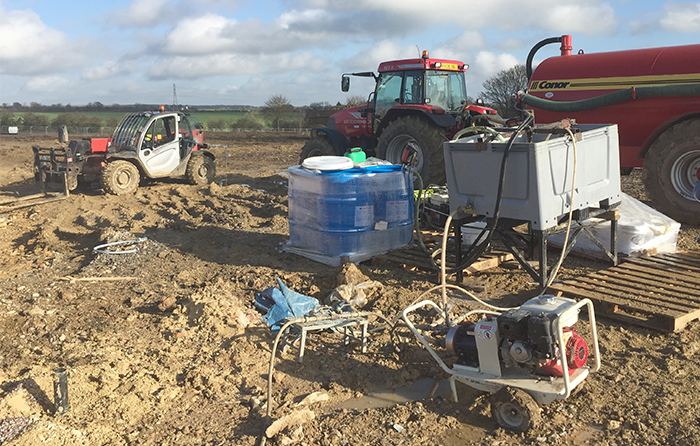
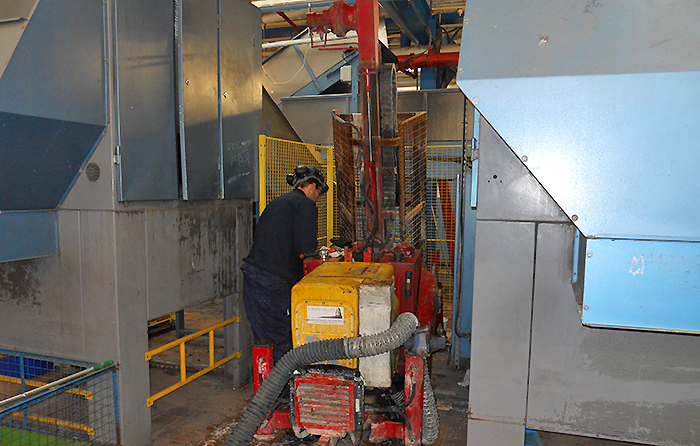
Residential Redevelopment of Former Industrial Site, Helsingborg Sweden
Enhanced reductive dechlorination treats high concentrations of chlorinated solvents (TCE) in varying permeabilities at a former manufacturing facility. Read More
Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium in Bedrock at Former Saw Mill
Bedrock chrome VI contamination treated to non-detect levels in 2 months, expediting regulatory sign-off and unlocking the site for redevelopmentRead More
In Situ Remediation of PCE and DNAPL at Active Industrial Drycleaners
A highly sustainable form of remediation with estimated savings likely to exceed £500,000. Read More
$150,000 Cost Savings Achieved using Enhanced Anaerobic Bioremediation and Bioaugmentation
Site Closure Pending for Treatment of TCE at Former Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Pilot test moved to full-scale application after rapid decrease in TCE and daughter product contamination
- Cost for ERD injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed-permanganate ISCO injection
- A no further action request has been submitted to the regulatory agency and is being reviewed for closure

Project Summary
During due diligence for a property transfer at a former manufacturing facility in Indiana, TCE impacts in groundwater were discovered downgradient from a former above-ground storage tank (AST). Little to no TCE remained in the sandy soils within the source area but migrated into groundwater resulting in a plume extending off-site. An initial plan was proposed to address the TCE in groundwater via an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) approach using potassium permanganate. The consultant, KERAMIDA, believed this approach was overly aggressive, given the relatively low groundwater concentrations and lack of significant soil impacts. Also, the permanganate ISCO treatment was much more expensive and difficult to implement compared to a biological enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach. At the request of the regulatory agency, a pilot injection using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus was performed in the source area and rapid reduction of TCE was observed within the first three months, accompanied by daughter product (cDCE and VC) production. Based on the results, the regulatory agency approved a full-scale injection one year later. Postinjection monitoring performed for two years following the full-scale injection indicated rapid decreases in TCE concentrations in all of the impacted wells with concurrent increases in daughter product concentrations. Daughter product concentrations also decreased significantly 9 months after 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus injection. At the conclusion of two years of post-injection monitoring, all of the wells in the treatment area were below the regulatory action levels for all compounds. A request for closure is currently being reviewed by the regulatory agency.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA developed a remedial plan that involved ERD and bioaugmentation, using 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus. The total cost for the injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed permanganate ISCO injection. A total of 6,400 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 48 liters of BDI Plus were injected into 48 points spaced 15 feet apart in a grid pattern throughout the primary impacted area. The injection interval was approximately 9 to 18 feet below grade. The ERD/bioaugmentation approach saved more than $150,000 compared to the permanganate ISCO approach, likely more since the nature of ISCO as a contact-based remedial technology would likely have required multiple injections to achieve remedial goals.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
ERD Remediation Approach Replaces Permanganate Treatment in Low Permeability Soils
3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus Treat PCE Contamination at Former Dry Cleaner
Project Highlights
- Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO)
- ISCO injection proved difficult due to low permeable soils so KERAMIDA developed an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design
- Reductions in PCE/TCE contamination observed in most wells within the injection area; monitoring is ongoing

Project Summary
The site was a former Indianapolis dry cleaner with historical releases of PCE to the subsurface. Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation in the source area, in an off-site, right-of-way area, and an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) injection using potassium permanganate. These approaches did reduce PCE concentrations in groundwater; however, they remained well above regulatory closure levels in multiple wells. After a almost two years of post-ISCO injection monitoring and evaluation, the consultant, KERAMIDA, recommended an alternative biological, enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach in the area of residual chlorinated impacts.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA worked with REGENESIS to develop an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus. The final design included 20 injection points spaced 15 feet apart on a grid pattern throughout the area of residual PCE/TCE impacts. The injection included a total of 1,200 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 18 liters of BDI Plus, distributed evenly over the 20 injection points with an injection interval of 10-13 feet below grade (targeting the impacted sand lens). The low permeability of the impacted sand lens, which proved problematic for the high volume of fluids needed for the permanganate ISCO injection, was a challenge. Since 3-D Microemulsion can be injected with minimal water when necessary, the low fluid volumes required to effect remediation proved to be ideal for this site. In addition, the low cost of the approach compared to other potential options, combined with the long-lasting effects of the remediation products provided a significant cost-to-closure savings. One year of post-ERD implementation (post-injection) monitoring shows PCE/TCE decreases and corresponding daughter product production (cDCE and VC). The persistence of strong anaerobic conditions resulting from the use of 3-D Microemulsion is expected to keep VOC concentrations and daughter products low well into the future.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
Former Taxi Maintenance Site Successfully Treated with Enhanced Anaerobic Biodegradation and Bioaugmentation
TCE/ 1,2-DCE Plume Reduced Using BDI Plus®, 3-D Microemulsion® and HRC® Allows for Development of Elementary School
Project Highlights
- Combined introduction of HRC® hydrogen release compounds and BDI Plus® bioaugmentation cultures resulted in reduction in chlorinated solvent concentrations, meeting site goals
- Successful remediation permitted redevelopment of the site into an elementary school

Project Summary
A former taxi maintenence facility located in Los Angeles County, California was used as a garage and maintenance facility containing seven underground storage tanks (USTs), four hydraulic hoists, an elevator, a clarifier, and a spray paint booth. Environmental assessment related to the planned redevelopment of the garage and nearby commercial properties and residences revealed contamination of the soil and groundwater beneath the site with trichloroethene (TCE) and 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE) due to release from the former USTs and paint shop areas.
Under the jurisdiction of the California Department of Toxic Substance Control, an enhanced anaerobic biodegradation approach in conjunction with bioaugmentation was developed to remediate the chlorinated solvent contamination. This approach combined the introduction of the dechlorinating microcosm BDI Plus® with the application of supporting hydrogen release compounds 3-D Microemulsion® and HRC Primer®. Following treatment of the site, reduction in TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations have been observed after four quarters of postremediation monitoring. Microbial data supports the benefits of the bioaugmentation effort by showing a steep increase in dehalococcoides populations, which increased by nearly four orders of magnitude. In addition, all geochemical parameters are in range for a reductive state.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
HRC Primer is derivative of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound product and is designed to provide a controlled but fast release of hydrogen to assist in initiating anaerobic biodegradation.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI Plus) is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Results
Reduction of TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations by enhanced anaerobic biodegradation and bioaugmentation facilitated the redevelopment of a former taxi garage and maintenance facility. Following a reduction in contaminant concentrations, the site was redeveloped to an elementary school.
RegenOx® and 3-D Microemulsion® Injections Treat VOC Impacted Soils
PCE Contamination at Former Dry Cleaning Site in Northern California Remediated
Project Highlights
- PCE soil concentrations of up to 16,095 ug/kg in the hot spot area
- After initial ISCO application, ERD was used to continue VOC concentration reduction
- Latest sampling event reported concentrations below clean-up target levels
- No further remediation needed on-site
Project Summary
In 2007, VOCs including (PCE) and related compounds including (TCE), (cis-DCE), and vinyl chloride (VC) were detected in soil and groundwater samples collected at a site in Northern California. A comprehensive field investigation conducted under the Regional Water Quality Control Board identified a distinct VOC-impacted soil area behind the former dry cleaner. Site characterization work identified the presence of VOCs including PCE with soil concentrations of up to 16,095 ug/kg in the hot spot area. A combined technology remediation approach was

implemented on-site including injections of RegenOx®, 3-D Microemulsion® and HRC® Primer. At the most recent sampling event, approximately 2.5 years post-application, the maximum detected concentrations of PCE and related VOCs was 420 ug/kg and all soil sample results were below the Soil Cleanup Levels. These data suggest that the combination of in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) with RegenOx, followed by enhanced reductive dechlorination with 3-D Microemulsion has been highly effective in reducing VOC concentrations in soil.
Remediation Approach
Three rounds of ISCO injections with RegenOx were applied on-site to treat the vadose zone soils. After the first round of injection, PCE was detected in soil samples collected in this area at maximum concentrations of 2,000 ug/kg, which, while substantially lower than initial concentrations indicated a need for further treatment. Enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) was performed by injecting 3-D Microemulsion and HRC Primer into vadose zone soil to treat PCE and related daughter products. The products were injected into 33 borings in the hot spot area with the treatment interval between 3 feet and 17 feet below ground surface. The most recent soil samples indicated a VOC concentration reduction to below the Regional Water Board’s soil to groundwater leaching ESLs (upon which the Site Cleanup Levels listed in the Site Cleanup Order were based). As a result, residual VOC concentrations in soil in the hot spot area do not appear to present a significant source for leaching to underlying groundwater. Continued groundwater monitoring being performed. No further remediation is required in this area.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
3-D Microemulsion factory emulsified is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release
profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory–emulsified product.
HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).
Hexavalent Chromium Remediation at Former Saw Mill
Summary
REGENESIS were retained to carry out the remediation design and site application works to treat groundwater impacted with hexavalent chromium (Cr VI) on the site of a former saw mill in the United Kingdom, Europe. Metals Remediation Compound® (MRC) and 3-D Microemulsion® (3DMe) were applied into the groundwater to provide rapid reduction and immobilisation of the CrVI present. Groundwater samples collected 2 months after application were analysed for CrVI , returning non-detect results.

Treatment
Due to the ground conditions of weathered limestone, treatment was carried out via pre-installed treatment wells at 5 m spacing in the source area and 6 m in the barrier. MRC and 3DMe were co-applied into these wells to target the source area of contamination and to install a reactive barrier at the down-gradient edge of the site to protect a nearby watercourse. MRC and 3DMe provide a powerful combination of wide distribution and strong reducing and immobilising properties.
What’s Special?
- REGENESIS’ injection team completed the site works ahead of schedule to allow the groundwork contractor to prepare the site for housing development.
- The use of MRC and 3DMe allowed for wide spacing of the injection wells and therefore lower drilling costs.
- The treatment approach achieved rapid reductions from up to 15,000 μg/L of Cr(VI) to non-detect within two months, expediting regulatory sign-off and unlocking the site for redevelopment
Technology Descriptions
Metals Remediation Compound (MRC) removes metals such as dissolved Cr(VI) from groundwater via in situ immobilisation (precipitation and/or sorption to soil particles).
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product..
Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination with Bioaugmentation Treats Source Area, Stops Plume Migration
Combined Remedy Source Treatment Applied at Florida Dry Cleaner
Project Highlights
- Aggressive source treatment to deplete the high-concentration PCE mass
- Plume treatment with a permeable reactive barrier to cut off the plume
- Low-impact direct-push injections in both areas

Project Summary
A former dry cleaner in an urban setting in central Florida was contaminated with a PCE plume that extended nearly 1,000 feet downgradient from the source. An extensive treatability test involving multiple emulsified vegetable oils and other electron donor technologies indicated that 3-D Microemulsion® would perform best at the site. An enhanced anaerobic bioremediation treatment was implemented in two areas – the source area near the dry cleaner and an area approximately 500 feet downgradient. A total of 13,900 gallons of 3-D Microemulsion was injected into 30 direct push points in the two areas. In addition, 97 liters of Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI® Plus) bioaugmentation culture was injected to accelerate treatment results.
Remediation Approach
The injections were performed near the former dry cleaner to deplete the source mass and expedite a transition into natural attenuation monitoring. A plume treatment was implemented as a permeable reactive barrier approximately 500 feet downgradient to help mitigate the risk of additional downgradient migration. Injections were completed using direct-push technology.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor technology that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile pH-neutral chemistry, and unique subsurface distribution properties.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is a natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Cost-Effective Remediation Plan Implemented at Active Texas Dry Cleaner
3-D Microemulsion® Reduces Chlorinated Solvent Contamination to Clean-Up Standards
Project Highlights
- Dual-phase extraction used to treat high level PCE in the source area.
- Enhanced Anaerobic Bioremediation selected as a cost-effective approach to treating migrating contamination.
- Majority of contamination reduced to clean-up standards; two low-level VC areas remain above desired limits.
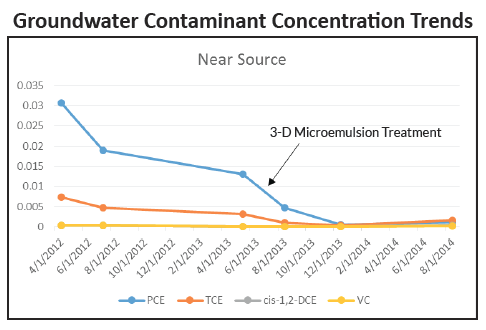
Project Summary
Dry cleaning operations resulted in a PCE release at a Texas dry cleaner. PCE concentrations at high at 95 mg/L were observed on-site. Aggressive clean-up measures were used in the form of dual-phase extraction of DNAPL and solvents in the source area. This resulted in nearly a two order-of-magnitude reduction in PCE concentrations in certain source wells. The second clean-up phase included expanding the system to treat contamination that had migrated out of the source area into the periphery of the groundwater plume.
Remediation Approach
Due to a limited budget for remediation, a cost-effective anaerobic bioremediation approach was selected due to the desire for a long-lasting solution that could also achieve low concentrations. 3-D Microemulsion and HRC Primer were injected along the migration centerline of the plume extending from just outside the source area to the toe of the plume. A second smaller treatment event was conducted in the vicinity of the former source area.
One year post-injection all solvent concentrations have dropped below clean-up standards with the exception of two low-level contamination areas. Recent treatment of the source area is starting to result in similar trends although there is not enough data yet to track remediation progress of the second injection event.
However, biostimulation alone through the addition of 3-D Microemulsion and HRC Primer appears to be very effective. Ongoing monitoring will occur followed by initiation of closure monitoring once all critical wells reach target levels.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español









