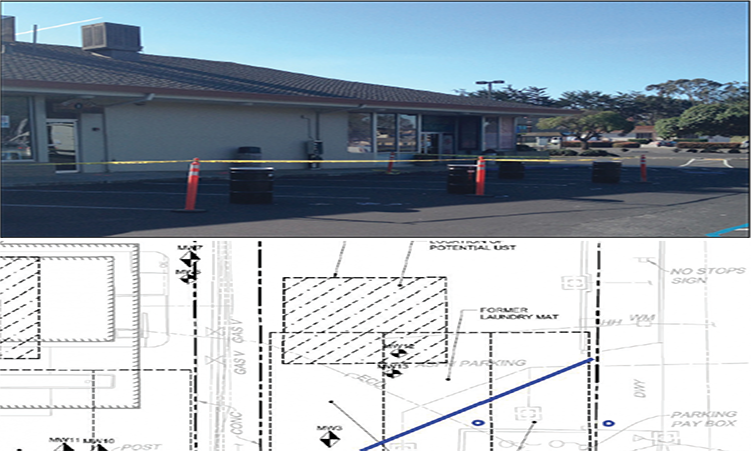
Treatment of mixed chlorinated ethenes and ethanes at an active site, UK
Introduction
REGENESIS was approached to offer an in situ remedial solution to address high levels of mixed chlorinated solvent (TCA and TCE) contamination of the groundwater at a site in northeast Scotland. At the time, an ongoing DPVE system was operating, but was unable to achieve the remediation goal of a 75% reduction in chlorinated solvent mass. Furthermore, a supplementary MIP investigation showed that there was more contamination at depth (>6m) which the DVPE system was not able to reach.
Download pdf2m 42s reading time
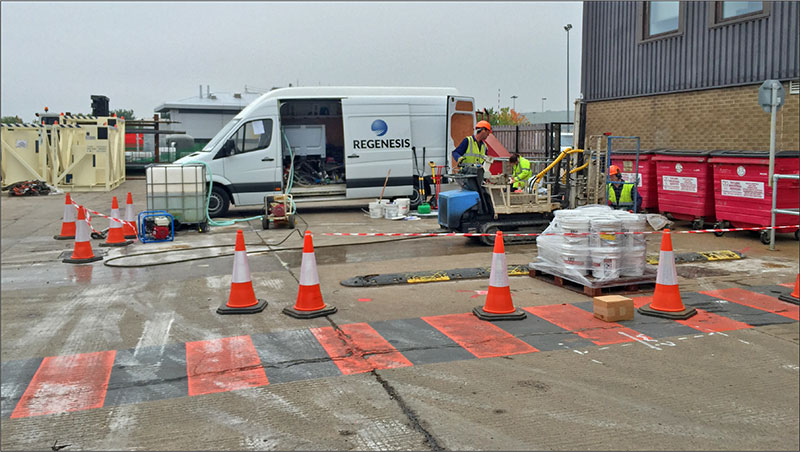
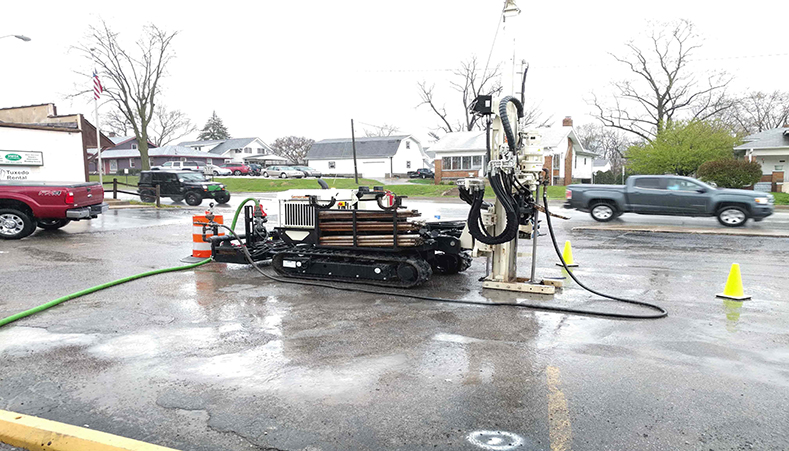
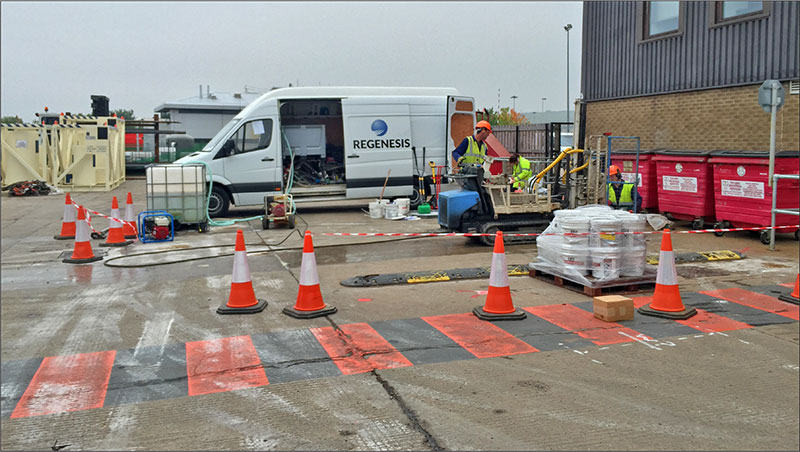 Fig. 1 REGENESIS Remediation Services applying 3DMe and BDI Plus on site
Fig. 1 REGENESIS Remediation Services applying 3DMe and BDI Plus on site
The initial design was based on treatment between 3 – 9m BGL of the aquifer across a 1,200m2 using 3DME and BDI with the preferred method of application being direct push injection. However, during the MIP investigation progression of the rods deeper than 6mBGL was found to be difficult. This raised concerns that (1) direct push injection would not be able to reach 9m BGL and (2) injection of the required dose of 3DMe may not be possible. REGENESIS were therefore asked to undertake a pilot study over a limited area to demonstrate that the works were possible. This was completed successfully and also showed excellent dose response and demonstrated to the site owners that the works (which were completed at night) would not have a deleterious effect on their operations.


Full Scale Application
The pilot trial was conducted over two days (see figure 1) during which the direct push injection rig had no problems getting the injection rod to the required depth of 9m BGL (unlike the MIP). Furthermore, the required volume of 3DMe was accepted by the aquifer with minimal daylighting/surfacing.
Following the MIP and pilot, the fullscale design was tailored to provide the most cost effective approach for the site. 60 direct push injection points were completed over 10 nights, with no disturbance to the site operations.
The direct push injection points were centred on BH 11, a pre-existing well, to ensure we had good baseline data. Both BH11 and the surrounding wells were monitored over 8 months to assess the effect and distribution of 3DMe.
Results
Following the injection works, quarterly validation monitoring was completed. Post injection monitoring showed no inhibition of parent compound degradation due to the mixed halogenated compound plume. 98% and 99% reduction in mean concentration of TCA and TCE respectively.
Full reductive dechlorination was achieved with no build up in daughter products (see fig 2 and 3). The validation curves suggest that both biotic and abiotic degradation occurred.
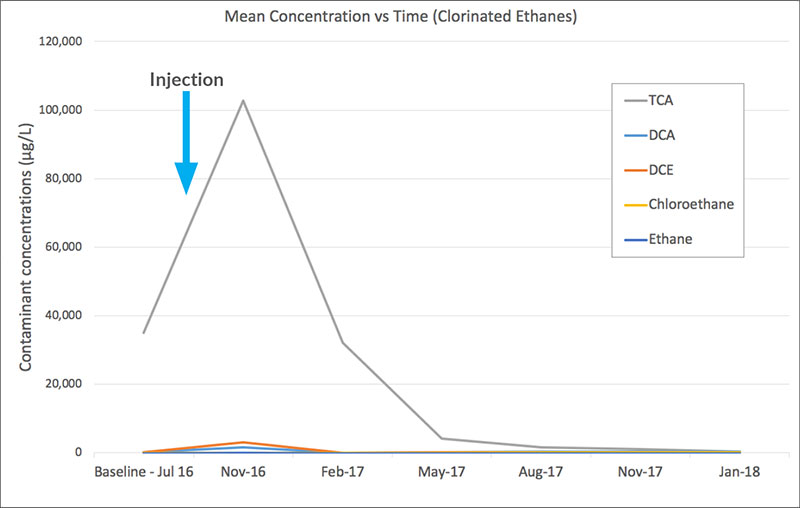
Fig. 2 Mean concentrations of Chlorinated Ethanes over time
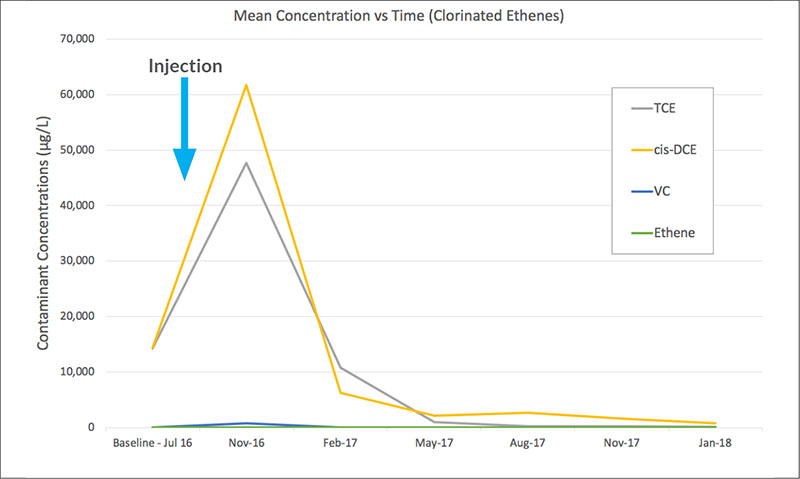
Fig. 3 Mean concentrations of Chlorinated Ethenes over time
Abiotic degradation occurred through the production of reduced iron species by the production of low redox conditions created by the 3DMe.
What’s Special
- A limited pilot study was used to prove the practicality and efficacy of the proposed approach. This area did not require further injection, so added little extra cost to the remediation of the site.
- Bioaugmentation using BDI+ avoided any inhibition of either chlorinated ethenes and ethanes by ensuring that the microbial consortia contained viable counts of dehalogenating bacteria specialising in either contaminant group.
- Very high levels of contamination, suggestive of DNAPL, were reduced to very low concentrations within 18 months.
- No build up of degradation products occurred, showing full reductive dechlorination was achieved and sustained.
- No disturbance of the onsite operations occurred during the limited injection time onsite, with the remediation occurring under the site as it continued to function normally.
- Remediation goals were achieved.
Fig. 4 REGENESIS’s team onsite

Site Goals Achieved Within Two Months
A Former Santa Barbara Manufacturing Facility Treated Using a Combined Remedy Approach
 This case study reviews a contaminated manufacturing site in Santa Barbara, California. A former manufacturing operation had left PCE and TCE contaminant levels above regulatory limits with previous remediation approaches attempted without complete success. Applying a combined remedy approach, Haro Environmental chose to focus on incorporating a design to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations for sustained treatment, and reduce the potential for further downgradient migration of the PCE and TCE contaminants.
This case study reviews a contaminated manufacturing site in Santa Barbara, California. A former manufacturing operation had left PCE and TCE contaminant levels above regulatory limits with previous remediation approaches attempted without complete success. Applying a combined remedy approach, Haro Environmental chose to focus on incorporating a design to rapidly reduce contaminant concentrations for sustained treatment, and reduce the potential for further downgradient migration of the PCE and TCE contaminants.
This case study features the following:
- This site has been an active case since 2007. REGENESIS was able to eliminate the contaminant quickly and effectively using a combined remedy approach.
- After conducting a pre-field remediation test, the injection interval was reduced from 12 feet to 9 feet with a bottom-up approach, reducing the project costs by 30%.
- The combination of PlumeStop, HRC and BDI+ successfully eliminated the contaminants and created conditions for sustained treatment at the site.
5m 22s reading time
Back Diffusion of VOCs from a Fractured Sandstone Aquifer Treated at Former Industrial Facility
Project Highlights
Large-scale pilot tests confirm management of chlorinated VOC back diffusion from fractured bedrock aquifer
- Tests concluded degradation along biotic and abiotic reductive pathways
- Advanced sorbent technology extends treatment longevity to manage to manage long-term back diffusion
2m 20s reading time

Project Summary
Fractured bedrock aquifers can be extremely heterogeneous which not only results in complex dissolved plume behavior, but can also hinder in situ remediation efforts that rely on an injection of amendments to promote microbial activity and abiotic degradation. However, due to the potentially high cost of a pump and treat remedy at a former industrial site in Arkansas, WSP determined that an in situ pilot test with advanced substrates was warranted.
At the Arkansas site, a 2016 pilot study was conducted using a multifunctional amendment formulation. REGENESIS® 3D-Microemulsion®, BDI Plus®, and CRS® were injected to remediate affected groundwater within a fractured sandstone bedrock aquifer impacted by chlorinated solvents. The contaminants at the site included trichloroethene (TCE), 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA), and degradation products. The plume on site underlies several developed properties and threatens a stream located approximately 1,500 feet from the source area. Results of the first pilot study yielded an 82% reduction within 9 months was measured approximately 80 feet from the application location.
A second pilot study was undertaken in 2017 to emplace a sorbent technology with long-lasting treatment capacity (PlumeStop®) on bedrock fracture faces to manage back diffusion from the bedrock primary porosity. This test also included the addition of bioremediation amendments to permanently degrade the sorbed contaminants. The 2017 treatment included PlumeStop and bioremediation amendments. After only one month, an 81% reduction was achieved in samples located 50 feet downgradient.
Preliminary indications of these amendment formulation tests are extremely promising in treating contaminant back diffusion emanating from the fractured bedrock matrix in this aquifer. WSP is confident that favorable performance monitoring results will continue and the full-scale remedy for this complex geologic setting will include REGENESIS products that extend treatment longevity.
Technology Description
PlumeStop® is an innovative groundwater remediation technology designed to address the challenges of excessive time and end-point uncertainty in groundwater remediation.
3-D Microemulsion® is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
HRC® is an engineered, hydrogen release compound designed specifically for enhanced, in situ anaerobic bioremediation of chlorinated compounds in groundwater or highly saturated soils.
BDI Plus® is designed for use at sites where chlorinated contaminants are present and unable to be completely biodegraded via the existing microbial communities.
CRS® is a liquid iron-based reagent for the enhanced biogeochemical in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of chlorinated contaminants.
Former Dry Cleaning Site Makes Way for Community Hospital Following Successful Treatment Using a Combined Remedy Approach
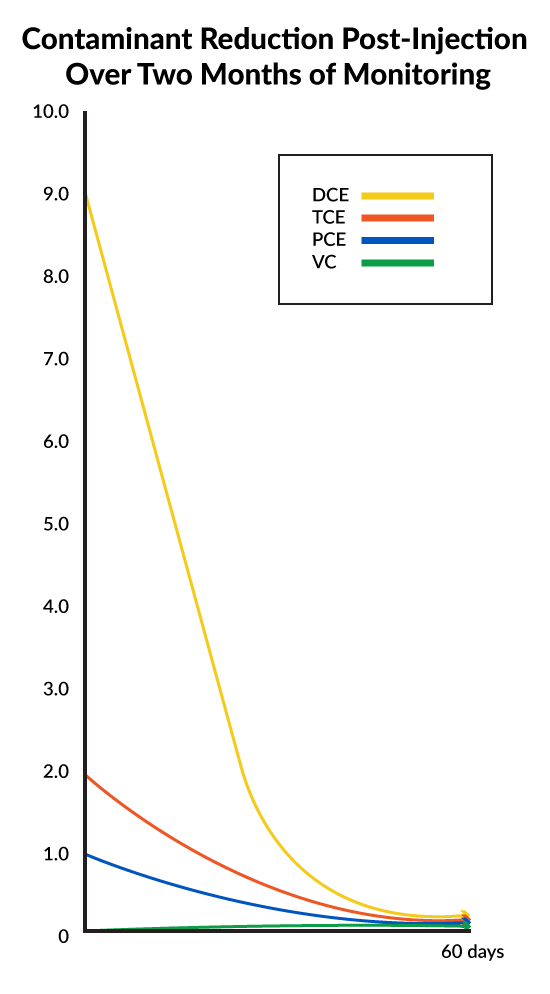
cVOC Contaminants Reduced by 97% After Two Months
Project Highlights
- Two months’ post injection results show contaminants were reduced by 97%
- Combined remediation approach used to successfully keep project on budget and on schedule
- Remediation design and amendments applied provided speed and certainty allowing for project to move forward
1m 55s reading time

Project Summary
A former dry cleaning site in Western New York was targeted for redevelopment to make way for a multidisciplinary, world-class cancer center. Before redevelopment could get underway, the developer needed to address the cVOC levels found on site which exceeded state regulatory standards. The developer engaged Benchmark/Turnkey, a leading environmental firm in the Northeast, to develop a solution to address the contaminant levels found. Benchmark/Turnkey worked with REGENESIS® to design a remedial strategy that included 3D-Microemulsion®, Bio Dechlor Inoculum® Plus, and Chemical Reducing Solution® to reduce the PCE, DCE and TCE contaminants. The design focused on speed and certainty, since the site was tagged for immediate redevelopment. Using a direct push application of the amendments, Benchmark/Turnkey was successful in applying the combined remedial approach on budget and on schedule.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
Bio Dechlor Inoculum Plus (BDI-Plus) is an enriched natural microbial consortium species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Results
Following the injection event, the team monitored the results and at two months found that total cVOC contaminant levels had been reduced by 97%. Based on the progress to date and the concentration of contaminants versus nutrients remaining in the groundwater, Benchmark/Turnkey expects to collect groundwater samples for two intervening semi-annual events then petition the New York Department of Environmental Conservation to discontinue groundwater monitoring.
About the Client
Benchmark Environmental Engineering & Science, PLLC is a licensed professional engineering company that provides comprehensive civil and environmental engineering services. TurnKey Environmental Restoration, LLC is a “sister” company that provides site investigation, remediation and infrastructure construction, and environmental and site management service.
Site Goals Achieved in Two Months Using PlumeStop® at a Santa Barbara Manufacturing Facility
Client avoids additional in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) injections with combined remedy approach using PlumeStop, Bio-Dechlor Inoculum Plus® (BDI Plus) and Hydrogen Release Compound® (HRC) to reach non-detect.Read More
Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination Showing Positive Returns at Indiana Dry Cleaning Site
Project Highlights
- Combined remedies approach using an Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) process successfully remediated an Indiana drycleaning site
- ERD process chosen eliminates need for long-term monitoring
- Contaminant concentrations reduced from thousands of μg/L pre-injection to single digits one month post-injection
2m 38s reading time

Project Summary
While the surrounding Mooresville, Indiana community applauds Crest Cleaners for proactively cleaning up a previously unidentified hazardous mess that was left behind from historic dry cleaning practices, the workhorses remediating the contamination are grinding away below the subsurface. Tiny microorganisms are destroying the PCE in the groundwater and reducing the concentration of the contaminant. It’s all a part of the “Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination,” (ERD) process, which is the primary approach of the Remedial Work Plan (RWP) being implemented by EnviroForensics®.
In addition to the potential for human health risks at the site as a result of soil or groundwater exposure, the contaminant plume in the groundwater represented a potential vapor intrusion risk to an offsite building. The project team debated between two viable options:
- Install, monitor, and maintain a Sub-Slab Depressurization System (SSDS) at the offsite location to mitigate the potentially harmful vapors underneath the building, which would have required years of maintenance and groundwater sampling; or
- Implement an ERD application to reduce the concentration of the groundwater plume, and eliminate potential vapor intrusion issues.
Based on the overall benefit to the community and to reduce stress and aggravation to adjacent property owners that comes with long-term monitoring, the project team chose option two.
Here’s how the remediation at this site worked. Naturally occurring bacteria called Dehalococcoides ethanogenes (DHC) are in the groundwater completing a process called reductive dechlorination where the chlorine atoms are cleaved off and replaced by hydrogen atoms. This process continues until the resulting compound is no longer dangerous. At this site, the process was occurring, but not at a rate that would make the cleanup cost-effective for the client.
In order to complete this cleanup we utilized a process called bioaugmented enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical reduction (ISCR). The process begins by sampling the groundwater across the remediation area for contaminant concentrations and geochemical parameters including DHC populations to determine the dosage of injected materials required in each area of the site. Different areas received modified doses of materials based on the calculations completed by EnviroForensic’s geochemist.
 The ERD agent, 3-D-Microemulsion® (3DMe®) was injected along with Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®), an ISCR augmentation. The ISCR agent delivers a source of ferrous iron, designed to precipitate as reduced iron minerals and provide an additional abiotic pathway for the destruction of PCE. The two work synergistically, increasing the cost effectiveness of the injection. The pre-sampling of DHC revealed that the population of DHC needed to be augmented. 10 gallons of BDI® Plus (DHC enhanced fluid) was injected at each of the 92 injection locations used for the ERD/ISCR. The combination of these three injected materials allows for minimal site disturbance and a high level of effectiveness for the cleanup of drycleaning solvents.
The ERD agent, 3-D-Microemulsion® (3DMe®) was injected along with Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®), an ISCR augmentation. The ISCR agent delivers a source of ferrous iron, designed to precipitate as reduced iron minerals and provide an additional abiotic pathway for the destruction of PCE. The two work synergistically, increasing the cost effectiveness of the injection. The pre-sampling of DHC revealed that the population of DHC needed to be augmented. 10 gallons of BDI® Plus (DHC enhanced fluid) was injected at each of the 92 injection locations used for the ERD/ISCR. The combination of these three injected materials allows for minimal site disturbance and a high level of effectiveness for the cleanup of drycleaning solvents.
An often overlooked byproduct of the ERD process is methane. As a preventative measure, the field staff upgraded the site building SSDS with an intrinsically-safe fan and installed an intrinsically-safe SSDS at the offsite building as an interim measure. Soil gas points were also BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes. Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes. installed between the injection areas and the adjoining properties to the east. Additionally, extra intrinsically-safe fans and piping are ready to be installed.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Results
The results from the first injection event were very promising. Groundwater contaminant concentration went down from thousands of μg/L pre-injection to single digits μg/L one month post-injection. Quarterly groundwater sampling will continue for a year or two to demonstrate that the contaminant plume is retreating or remediated. The ultimate goal of the ERD approach is to reach site closure quickly, and reduce the costs and health risks of this contamination.
Ohio Brownfield Site Receives “No Further Action” Status within One Year of Implementation
Project Highlights
- Combined remedy approach allowed for immediate redevelopment within same year of implementation.
- Efficiencies resulted in vapor intrusion mitigation cost of $3.34 per sq. ft., with no long term operation and maintenance required.
- Cost for groundwater treatment approximately $10 per cubic yard (product + application).
1m 25s reading time

Project Summary
A former industrial magnet manufacturing facility in Ohio received a $2.34 million Clean Ohio Revitalization Fund (CORF) grant through the Ohio Department of Development in 2011. Site investigation activities identified chlorinated VOC’s in groundwater and vapors above the state standards, requiring remediation. Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination, using 3D Micro-Emulsion®, and BDI-Plus® were implemented within the defined 24,000 sq. ft. treatment area via direct push injection.
This work was conducted in the Spring of 2012. In the Fall of 2012, the Geo-Seal Vapor barrier system was installed below a 15,522 sq. ft. apartment complex raised at the site. Utilizing a combined approach of enhanced reductive dechlorination with vapor mitigation addressed the immediate risk of vapor intrusion, in addition to the long term risk of groundwater impacts. By implementing this strategy, the site was allowed to be redeveloped as an apartment complex roughly 6 months following the groundwater treatment. The cost for groundwater treatment was approximately $10/cy (product + application) and Geo-Seal® was $3.34/sq. ft. (product + installation).
Technology Description
BDI Plus is an enriched, natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC) which are capable of completely dechlorinating contaminants during in situ anaerobic bioremediation processes.
3-D Microemulsion is a wide-area distribution, staged release, electron donor emulsion for the optimized enhanced anaerobic biodegradation of chlorinated compounds.
Geo-Seal is a composite system that creates the ideal blend between constructability and chemical resistance by using both high density polyethylene (HDPE) and spray-applied asphalt latex.
Results
Housing developers face many considerations, including approvals for land excavation and required building permits. By implementing a combined remedy approach, consisting of enhanced reductive dechlorination with vapor mitigation, this site was able to qualify for NFA status in less than a year, allowing the developer to begin new construction without further delay.
Non-Detect Levels Reached with Application of PlumeStop® at Former Dry Cleaning Site
Lines of evidence for post-sorption solvent degradationRead More
$150,000 Cost Savings Achieved using Enhanced Anaerobic Bioremediation and Bioaugmentation
Site Closure Pending for Treatment of TCE at Former Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Pilot test moved to full-scale application after rapid decrease in TCE and daughter product contamination
- Cost for ERD injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed-permanganate ISCO injection
- A no further action request has been submitted to the regulatory agency and is being reviewed for closure

Project Summary
During due diligence for a property transfer at a former manufacturing facility in Indiana, TCE impacts in groundwater were discovered downgradient from a former above-ground storage tank (AST). Little to no TCE remained in the sandy soils within the source area but migrated into groundwater resulting in a plume extending off-site. An initial plan was proposed to address the TCE in groundwater via an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) approach using potassium permanganate. The consultant, KERAMIDA, believed this approach was overly aggressive, given the relatively low groundwater concentrations and lack of significant soil impacts. Also, the permanganate ISCO treatment was much more expensive and difficult to implement compared to a biological enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach. At the request of the regulatory agency, a pilot injection using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus was performed in the source area and rapid reduction of TCE was observed within the first three months, accompanied by daughter product (cDCE and VC) production. Based on the results, the regulatory agency approved a full-scale injection one year later. Postinjection monitoring performed for two years following the full-scale injection indicated rapid decreases in TCE concentrations in all of the impacted wells with concurrent increases in daughter product concentrations. Daughter product concentrations also decreased significantly 9 months after 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus injection. At the conclusion of two years of post-injection monitoring, all of the wells in the treatment area were below the regulatory action levels for all compounds. A request for closure is currently being reviewed by the regulatory agency.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA developed a remedial plan that involved ERD and bioaugmentation, using 3-D Microemulsion and BDI Plus. The total cost for the injection was approximately $70,000, compared to more than $250,000 for the proposed permanganate ISCO injection. A total of 6,400 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 48 liters of BDI Plus were injected into 48 points spaced 15 feet apart in a grid pattern throughout the primary impacted area. The injection interval was approximately 9 to 18 feet below grade. The ERD/bioaugmentation approach saved more than $150,000 compared to the permanganate ISCO approach, likely more since the nature of ISCO as a contact-based remedial technology would likely have required multiple injections to achieve remedial goals.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
ERD Remediation Approach Replaces Permanganate Treatment in Low Permeability Soils
3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus Treat PCE Contamination at Former Dry Cleaner
Project Highlights
- Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO)
- ISCO injection proved difficult due to low permeable soils so KERAMIDA developed an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design
- Reductions in PCE/TCE contamination observed in most wells within the injection area; monitoring is ongoing

Project Summary
The site was a former Indianapolis dry cleaner with historical releases of PCE to the subsurface. Previous remedial techniques included soil excavation in the source area, in an off-site, right-of-way area, and an in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) injection using potassium permanganate. These approaches did reduce PCE concentrations in groundwater; however, they remained well above regulatory closure levels in multiple wells. After a almost two years of post-ISCO injection monitoring and evaluation, the consultant, KERAMIDA, recommended an alternative biological, enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach in the area of residual chlorinated impacts.
Remediation Approach
KERAMIDA worked with REGENESIS to develop an ERD/bioaugmentation injection design using 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus. The final design included 20 injection points spaced 15 feet apart on a grid pattern throughout the area of residual PCE/TCE impacts. The injection included a total of 1,200 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion and 18 liters of BDI Plus, distributed evenly over the 20 injection points with an injection interval of 10-13 feet below grade (targeting the impacted sand lens). The low permeability of the impacted sand lens, which proved problematic for the high volume of fluids needed for the permanganate ISCO injection, was a challenge. Since 3-D Microemulsion can be injected with minimal water when necessary, the low fluid volumes required to effect remediation proved to be ideal for this site. In addition, the low cost of the approach compared to other potential options, combined with the long-lasting effects of the remediation products provided a significant cost-to-closure savings. One year of post-ERD implementation (post-injection) monitoring shows PCE/TCE decreases and corresponding daughter product production (cDCE and VC). The persistence of strong anaerobic conditions resulting from the use of 3-D Microemulsion is expected to keep VOC concentrations and daughter products low well into the future.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
About the Consultant
 KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.
KERAMIDA Inc. is an engineering and consulting firm that serves industries, businesses, cities, and governments worldwide. They provide strategy and implementation services in: Sustainability, Green House Gases, Energy, Environmental Compliance, Remediation, Environmental Due Diligence, Brownfield Redevelopment, Plant Decommissioning, Health & Safety, Training, Risk Management, and ISO Management Systems. Established in 1988, KERAMIDA is headquartered in the historic Lockerbie Square district of Indianapolis, Indiana. The firm employs over 70 technical experts and support personnel in offices throughout the U.S., including Chicago, IL; Pittsburgh, PA; New York, NY; Los Angeles, CA, Sacramento, CA. KERAMIDA’s many principals have worked for over 25 years in the sustainability, environmental, health & safety, and remediation arenas, and are recognized leaders in their fields. Their engineers, scientists, and planners are renowned for delivering creative, integrated EHS solutions to a broad range of clients throughout the U.S. and abroad.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español