Combined approach to remediate chlorinated solvents in Cambridge, UK
In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR), Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) and bioaugmentation used on active construction site to allow redevelopment to be completed
Summary
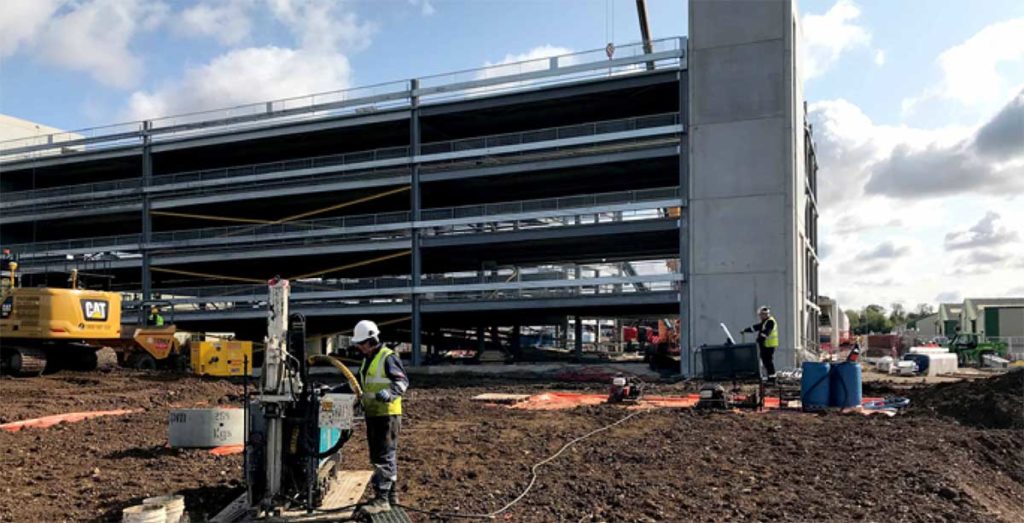
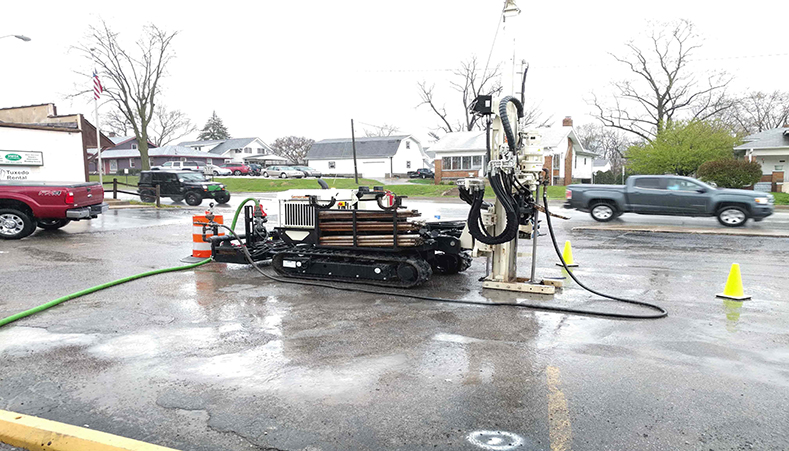
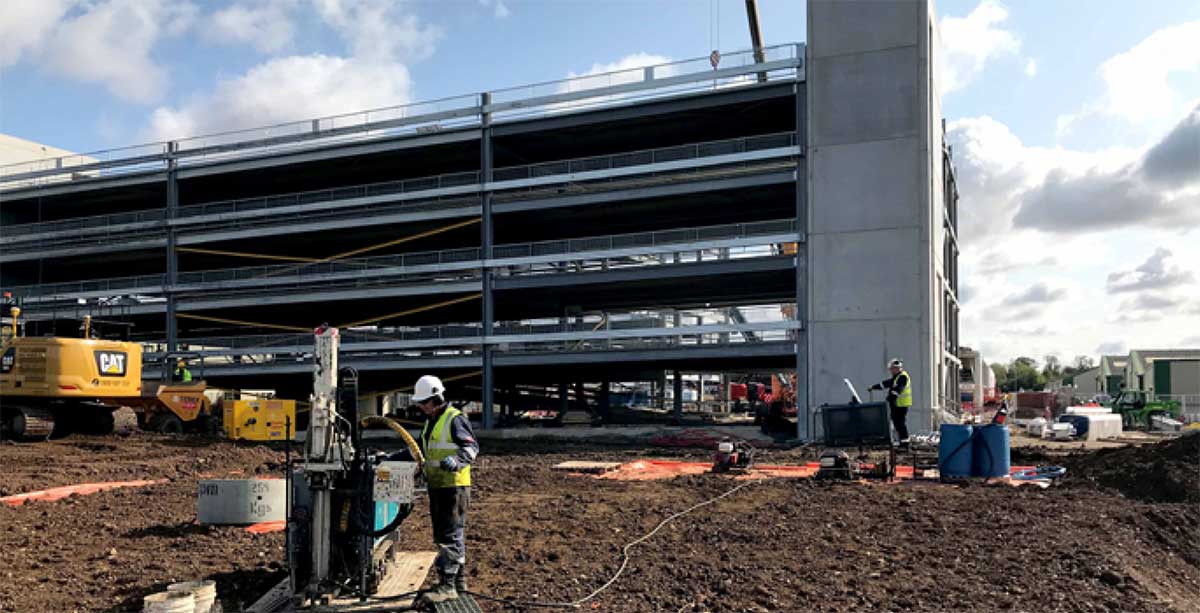 This site is currently undergoing redevelopment from a former industrial estate and trade park, into a business park. The underlying groundwater is impacted with chlorinated solvents from an adjacent industrial site. REGENESIS provided an in situ approach that could provide full reductive dechlorination of the contamination from a single injection, allowing redevelopment to occur during the remediation period.
This site is currently undergoing redevelopment from a former industrial estate and trade park, into a business park. The underlying groundwater is impacted with chlorinated solvents from an adjacent industrial site. REGENESIS provided an in situ approach that could provide full reductive dechlorination of the contamination from a single injection, allowing redevelopment to occur during the remediation period.
1m reading time
Application
It was decided that a combination of In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR) using Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS) and Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) using 3-D Microemulsion (3DME) as well as bioaugmentation with Bio-Dechlor Inoculum Plus (BDI+) would be applied at this site. This combined approach was designed to provide rapid contaminant degradation, minimised daughter product creation and long term treatment from the single injection. The treatment used seven direct push injection points to accurately target the contamination in a heterogeneous gravels, sands and clay.
What’s Special?
- The ISCR, bioaugmentation and biostimulation approach was used to optimise the remedial approach by combining:
- Wide radii of influence to minimise the number of injection points required
- Rapid onset of ERD
- Minimisation of daughter product creation
- Long-term treatment from a single application
- The application took only one day, with remediation occurring in situ, allowing the site development to continue unimpeded.
ZVI Applied To Remediate DoD Superfund Site
Combined Remedy Effectively Treats 1,2-DCA and TCE at Tinker Air Force Base
This case study reviews the remediation of dichloroethane (1,2-DCA) and Trichloroethylene (TCE) using colloidal zero valent iron (ZVI) at Tinker Air Force Base, a major United States Air Force base located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. The remediation included an application of emulsified vegetable oil (EVO), an aqueous suspension of colloidal zero valent iron (MicroZVI Precursor), with small amounts of fertilizer and B12. Typically, zero valent iron cannot be applied through well systems. However, due to the small particle size of the zero valent iron, this application was successfully applied through the existing wells. At 3 years post-injection, the contaminant levels remain near zero with the presence of ethene indicating continuous biodegradation.
This case study features the following:
- Successful application of colloidal zero valent iron through well system
- At 3 years post-injection, the presence of ethene signals active biodegradation
- Aqueous suspension of colloidal zero valent iron effectively reduced contaminant levels
Significant Reduction in VOCs Achieved at Rail Site
 This case study reviews a contaminated rail site in Canada that had released chlorinated solvents in groundwater. WSP conducted a pilot test at the site to assess the applicability of a brand-new technology that optimizes delivery of amendments using hydrocolloids. The pilot test would determine the applicability of a passive treatment barrier using PlumeStop and AquaZVI. A combined remedy approach was chosen because it optimizes the use of colloidal activated carbon and zero valent iron, allowing for the highest treatment efficiency at the lowest possible cost. After conducting the pilot test, data for samples collected within the treatment barrier indicated significant contaminant concentration decreases in groundwater and saturated soil.
This case study reviews a contaminated rail site in Canada that had released chlorinated solvents in groundwater. WSP conducted a pilot test at the site to assess the applicability of a brand-new technology that optimizes delivery of amendments using hydrocolloids. The pilot test would determine the applicability of a passive treatment barrier using PlumeStop and AquaZVI. A combined remedy approach was chosen because it optimizes the use of colloidal activated carbon and zero valent iron, allowing for the highest treatment efficiency at the lowest possible cost. After conducting the pilot test, data for samples collected within the treatment barrier indicated significant contaminant concentration decreases in groundwater and saturated soil.
This case study features the following:
- First application of PlumeStop® and AquaZVI™ globally
- Despite wintery weather conditions at the Rail Site in Northern Quebec, the amendment delivery and distribution was successful
- Over 95% decrease in dissolved and saturated soil VOC concentrations
- Thorough data analysis including ISMs and CSIA confirmed definite contaminant degradation
6m 9s reading time
Back Diffusion of VOCs from a Fractured Sandstone Aquifer Treated at Former Industrial Facility
Project Highlights
Large-scale pilot tests confirm management of chlorinated VOC back diffusion from fractured bedrock aquifer
- Tests concluded degradation along biotic and abiotic reductive pathways
- Advanced sorbent technology extends treatment longevity to manage to manage long-term back diffusion
2m 20s reading time

Project Summary
Fractured bedrock aquifers can be extremely heterogeneous which not only results in complex dissolved plume behavior, but can also hinder in situ remediation efforts that rely on an injection of amendments to promote microbial activity and abiotic degradation. However, due to the potentially high cost of a pump and treat remedy at a former industrial site in Arkansas, WSP determined that an in situ pilot test with advanced substrates was warranted.
At the Arkansas site, a 2016 pilot study was conducted using a multifunctional amendment formulation. REGENESIS® 3D-Microemulsion®, BDI Plus®, and CRS® were injected to remediate affected groundwater within a fractured sandstone bedrock aquifer impacted by chlorinated solvents. The contaminants at the site included trichloroethene (TCE), 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA), and degradation products. The plume on site underlies several developed properties and threatens a stream located approximately 1,500 feet from the source area. Results of the first pilot study yielded an 82% reduction within 9 months was measured approximately 80 feet from the application location.
A second pilot study was undertaken in 2017 to emplace a sorbent technology with long-lasting treatment capacity (PlumeStop®) on bedrock fracture faces to manage back diffusion from the bedrock primary porosity. This test also included the addition of bioremediation amendments to permanently degrade the sorbed contaminants. The 2017 treatment included PlumeStop and bioremediation amendments. After only one month, an 81% reduction was achieved in samples located 50 feet downgradient.
Preliminary indications of these amendment formulation tests are extremely promising in treating contaminant back diffusion emanating from the fractured bedrock matrix in this aquifer. WSP is confident that favorable performance monitoring results will continue and the full-scale remedy for this complex geologic setting will include REGENESIS products that extend treatment longevity.
Technology Description
PlumeStop® is an innovative groundwater remediation technology designed to address the challenges of excessive time and end-point uncertainty in groundwater remediation.
3-D Microemulsion® is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
HRC® is an engineered, hydrogen release compound designed specifically for enhanced, in situ anaerobic bioremediation of chlorinated compounds in groundwater or highly saturated soils.
BDI Plus® is designed for use at sites where chlorinated contaminants are present and unable to be completely biodegraded via the existing microbial communities.
CRS® is a liquid iron-based reagent for the enhanced biogeochemical in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of chlorinated contaminants.
Former Dry Cleaning Site Makes Way for Community Hospital Following Successful Treatment Using a Combined Remedy Approach
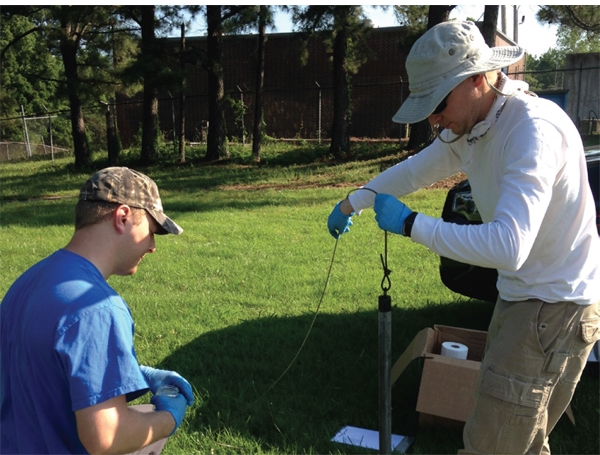
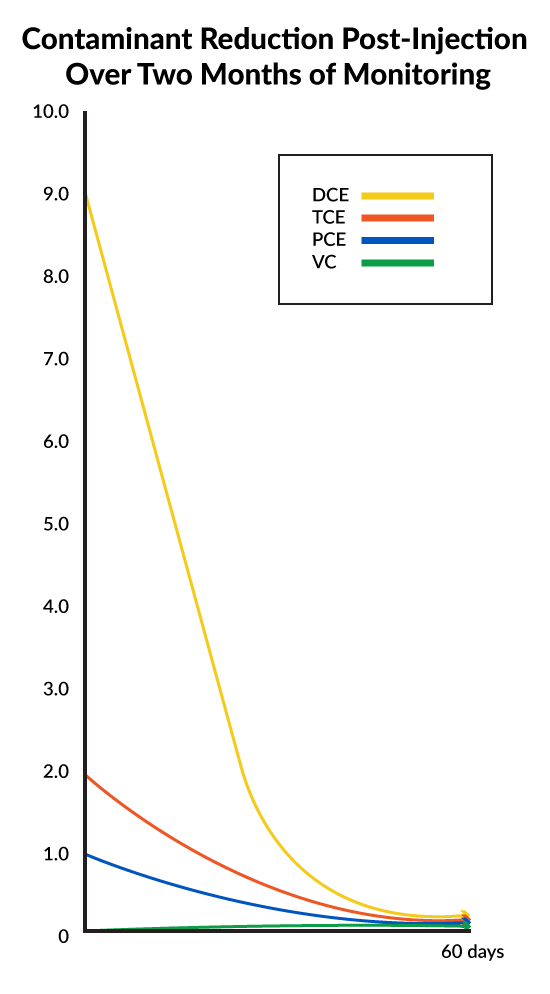
cVOC Contaminants Reduced by 97% After Two Months
Project Highlights
- Two months’ post injection results show contaminants were reduced by 97%
- Combined remediation approach used to successfully keep project on budget and on schedule
- Remediation design and amendments applied provided speed and certainty allowing for project to move forward
1m 55s reading time

Project Summary
A former dry cleaning site in Western New York was targeted for redevelopment to make way for a multidisciplinary, world-class cancer center. Before redevelopment could get underway, the developer needed to address the cVOC levels found on site which exceeded state regulatory standards. The developer engaged Benchmark/Turnkey, a leading environmental firm in the Northeast, to develop a solution to address the contaminant levels found. Benchmark/Turnkey worked with REGENESIS® to design a remedial strategy that included 3D-Microemulsion®, Bio Dechlor Inoculum® Plus, and Chemical Reducing Solution® to reduce the PCE, DCE and TCE contaminants. The design focused on speed and certainty, since the site was tagged for immediate redevelopment. Using a direct push application of the amendments, Benchmark/Turnkey was successful in applying the combined remedial approach on budget and on schedule.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
Bio Dechlor Inoculum Plus (BDI-Plus) is an enriched natural microbial consortium species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Results
Following the injection event, the team monitored the results and at two months found that total cVOC contaminant levels had been reduced by 97%. Based on the progress to date and the concentration of contaminants versus nutrients remaining in the groundwater, Benchmark/Turnkey expects to collect groundwater samples for two intervening semi-annual events then petition the New York Department of Environmental Conservation to discontinue groundwater monitoring.
About the Client
Benchmark Environmental Engineering & Science, PLLC is a licensed professional engineering company that provides comprehensive civil and environmental engineering services. TurnKey Environmental Restoration, LLC is a “sister” company that provides site investigation, remediation and infrastructure construction, and environmental and site management service.
Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination Showing Positive Returns at Indiana Dry Cleaning Site
Project Highlights
- Combined remedies approach using an Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) process successfully remediated an Indiana drycleaning site
- ERD process chosen eliminates need for long-term monitoring
- Contaminant concentrations reduced from thousands of μg/L pre-injection to single digits one month post-injection
2m 38s reading time

Project Summary
While the surrounding Mooresville, Indiana community applauds Crest Cleaners for proactively cleaning up a previously unidentified hazardous mess that was left behind from historic dry cleaning practices, the workhorses remediating the contamination are grinding away below the subsurface. Tiny microorganisms are destroying the PCE in the groundwater and reducing the concentration of the contaminant. It’s all a part of the “Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination,” (ERD) process, which is the primary approach of the Remedial Work Plan (RWP) being implemented by EnviroForensics®.
In addition to the potential for human health risks at the site as a result of soil or groundwater exposure, the contaminant plume in the groundwater represented a potential vapor intrusion risk to an offsite building. The project team debated between two viable options:
- Install, monitor, and maintain a Sub-Slab Depressurization System (SSDS) at the offsite location to mitigate the potentially harmful vapors underneath the building, which would have required years of maintenance and groundwater sampling; or
- Implement an ERD application to reduce the concentration of the groundwater plume, and eliminate potential vapor intrusion issues.
Based on the overall benefit to the community and to reduce stress and aggravation to adjacent property owners that comes with long-term monitoring, the project team chose option two.
Here’s how the remediation at this site worked. Naturally occurring bacteria called Dehalococcoides ethanogenes (DHC) are in the groundwater completing a process called reductive dechlorination where the chlorine atoms are cleaved off and replaced by hydrogen atoms. This process continues until the resulting compound is no longer dangerous. At this site, the process was occurring, but not at a rate that would make the cleanup cost-effective for the client.
In order to complete this cleanup we utilized a process called bioaugmented enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical reduction (ISCR). The process begins by sampling the groundwater across the remediation area for contaminant concentrations and geochemical parameters including DHC populations to determine the dosage of injected materials required in each area of the site. Different areas received modified doses of materials based on the calculations completed by EnviroForensic’s geochemist.
 The ERD agent, 3-D-Microemulsion® (3DMe®) was injected along with Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®), an ISCR augmentation. The ISCR agent delivers a source of ferrous iron, designed to precipitate as reduced iron minerals and provide an additional abiotic pathway for the destruction of PCE. The two work synergistically, increasing the cost effectiveness of the injection. The pre-sampling of DHC revealed that the population of DHC needed to be augmented. 10 gallons of BDI® Plus (DHC enhanced fluid) was injected at each of the 92 injection locations used for the ERD/ISCR. The combination of these three injected materials allows for minimal site disturbance and a high level of effectiveness for the cleanup of drycleaning solvents.
The ERD agent, 3-D-Microemulsion® (3DMe®) was injected along with Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®), an ISCR augmentation. The ISCR agent delivers a source of ferrous iron, designed to precipitate as reduced iron minerals and provide an additional abiotic pathway for the destruction of PCE. The two work synergistically, increasing the cost effectiveness of the injection. The pre-sampling of DHC revealed that the population of DHC needed to be augmented. 10 gallons of BDI® Plus (DHC enhanced fluid) was injected at each of the 92 injection locations used for the ERD/ISCR. The combination of these three injected materials allows for minimal site disturbance and a high level of effectiveness for the cleanup of drycleaning solvents.
An often overlooked byproduct of the ERD process is methane. As a preventative measure, the field staff upgraded the site building SSDS with an intrinsically-safe fan and installed an intrinsically-safe SSDS at the offsite building as an interim measure. Soil gas points were also BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes. Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes. installed between the injection areas and the adjoining properties to the east. Additionally, extra intrinsically-safe fans and piping are ready to be installed.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Chemical Reducing Solution is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Results
The results from the first injection event were very promising. Groundwater contaminant concentration went down from thousands of μg/L pre-injection to single digits μg/L one month post-injection. Quarterly groundwater sampling will continue for a year or two to demonstrate that the contaminant plume is retreating or remediated. The ultimate goal of the ERD approach is to reach site closure quickly, and reduce the costs and health risks of this contamination.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – TCE Plume Treated with 3-D Microemulsion®
Combined Treatment Remedies Reduce Contamination Concentrations at Wisconsin Manufacturing Facility
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to design and implement an in situ enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) remediation plan for this manufacturing site, impacted by trichloroethylene (TCE). The treatment included the use of 3-D Microemulsion® and Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®) as controlled-release electron donors, and BDI® Plus to bioaugment the subsurface. The two treatment areas at this former manufacturing facility covered an area of 35,000 square feet (ft2). A total of 19,200 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, 2,400 lbs. of CRS, and 48 liters of BDI Plus with over 1011 Dehalococcoides (DHC) cells per liter were injected over a period of less than two weeks on site.

Thirty-nine direct-push injection points were advanced between both of the treatment areas. RRS utilized retractable screen tip injection tooling to apply the pH neutral 3-D Microemulsion with CRS and BDI Plus at discrete intervals in the vertical treatment intervals of 5 to 20 feet below ground surface (bgs) and 15 to 30 feet bgs. The RRS trailer and equipment configuration allowed for low pressure application of the remediation chemistry at up to three injection points simultaneously. Remediation chemistry was applied up to 100 feet from the trailer in subfreezing temperatures while RRS personnel monitored flow rates and injection pressures at each application point to optimize distribution and influence of the remediation chemistry.
Combined Remedies Treat Chlorinated Solvents at Gulf Coast Superfund Site
Former Industrial Facility and Landfill Pilot Test Shows Rapid Reduction in PCE, TCE and 1,2 DCE
Project Highlights
- Superfund Site once housed an industrial facility and landfill.
- Rapid reduction needed to avoid off-site migration of daughter products.
- Simultaneous application of Enhanced Aerobic Biodegradation, Bioaugmentation and In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR).

Project Summary
This former industrial property had a landfill that was used in the mid-1900s for disposal of magnesium dross and refractory brick as well as breakout material from electrolytic chlorine cells. As much as 254,000 cubic feet of material were removed from the landfill although a large chlorinated solvent plume remains both from landfill waste below the water table and from industrial operations on-site. A feasibility study for the site was approved in 2012 which evaluated the use of enhanced reductive dechlorination to treat dissolved chlorinated solvents at the site and to prevent off-site migration past the property boundary and beneath a highway. A pilot test to evaluate at least two different biological amendments was conducted and Regenesis supplied 3D Microemulsion, BDI, and CRS for the evaluation. Three aquifers exist at the site, but the pilot test was performed in the first groundwater bearing unit only.
Remediation Approach
After a review of sulfate concentrations, other natural attenuation data, and cVOC concentrations it was determined that the optimal treatment choice would be to test a combination of an electron donor in the form of 3-D Mircoemulsion®, a bioaugmentation culture called Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM® Plus, and the use of Chemical Reducing Solution® (CRS) to prevent any hydrogen sulfide toxicity and to promote a level of beneficial in situ chemical reduction (ISCR). For the pilot test 10 injections points were used to place 800 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, 18 liters of BDI Plus and 400 pounds of CRS. The product was injected over a 10-foot interval.
The goal for this project was to attain as rapid reduction as possible for the site specifically to avoid off-site migration of daughter products such as vinyl chloride. Therefore, it was deemed beneficial to inject all three proposed products at once. The product was injected in March 2014 and results at roughly 1 month post injection are extremely promising. PCE has been reduced from 134 ppb to 1.57 ppb, TCE from 271 ppb to 1.77 ppb, and cic-1,2-DCE from 235 ppb to 4.25 ppb. Vinyl Chloride has shown some increase from non-detect to 13 ppb.
However, Dehalococcoides has increased from non-detect to 7 x 10×5 cells/bead and vinyl chloride reduced from nondetect to 9 x 10×4 cells per bead which strongly correlates to the rapid enhanced reductive dechlorination.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
CRS (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Combined Remedies Treat Chlorinated Solvents at Gulf Coast Superfund Site
Former Industrial Facility and Landfill Pilot Test Shows Rapid Reduction in PCE, TCE and 1,2 DCE
Project Highlights
- Superfund Site once housed an industrial facility and landfill.
- Rapid reduction needed to avoid off-site migration of daughter products.
- Simultaneous application of Enhanced Aerobic Biodegradation, Bioaugmentation and In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR).

Project Summary
This former industrial property had a landfill that was used in the mid-1900s for disposal of magnesium dross and refractory brick as well as breakout material from electrolytic chlorine cells. As much as 254,000 cubic feet of material were removed from the landfill although a large chlorinated solvent plume remains both from landfill waste below the water table and from industrial operations on-site. A feasibility study for the site was approved in 2012 which evaluated the use of enhanced reductive dechlorination to treat dissolved chlorinated solvents at the site and to prevent off-site migration past the property boundary and beneath a highway. A pilot test to evaluate at least two different biological amendments was conducted and Regenesis supplied 3D Microemulsion, BDI, and CRS for the evaluation. Three aquifers exist at the site, but the pilot test was performed in the first groundwater bearing unit only.
Remediation Approach
After a review of sulfate concentrations, other natural attenuation data, and cVOC concentrations it was determined that the optimal treatment choice would be to test a combination of an electron donor in the form of 3-D Mircoemulsion®, a bioaugmentation culture called Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM® Plus, and the use of Chemical Reducing Solution® (CRS) to prevent any hydrogen sulfide toxicity and to promote a level of beneficial in situ chemical reduction (ISCR). For the pilot test 10 injections points were used to place 800 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, 18 liters of BDI Plus and 400 pounds of CRS. The product was injected over a 10-foot interval.
The goal for this project was to attain as rapid reduction as possible for the site specifically to avoid off-site migration of daughter products such as vinyl chloride. Therefore, it was deemed beneficial to inject all three proposed products at once. The product was injected in March 2014 and results at roughly 1 month post injection are extremely promising. PCE has been reduced from 134 ppb to 1.57 ppb, TCE from 271 ppb to 1.77 ppb, and cic-1,2-DCE from 235 ppb to 4.25 ppb. Vinyl Chloride has shown some increase from non-detect to 13 ppb.
However, Dehalococcoides has increased from non-detect to 7 x 10×5 cells/bead and vinyl chloride reduced from non-detect to 9 x 10×4 cells per bead which strongly correlates to the rapid enhanced reductive dechlorination.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
CRS (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Combined Remedies Used at Former Chemical Company in Illinois, USA
cVOCs in Bedrock Treated at Active Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) used combined technologies to work toward the shutdown of a pump and treat (P&T) system.
- Previous Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) technology applications did not achieve COC reductions.
- Advanced ERD, Bioaugmentation and ISCR remedies were combined and applied into weathered bedrock.
- The project required RRS to be PICS certified. PICS is a contractor prequalification services used many large E&C and fortune 500 companies.

Project Summary
The site is home to an active chemical manufacturing facility with historic spills of cVOCs. Within the contamination impact zones, a groundwater P&T system is being used to mitigate off-site migration of cVOCs in the groundwater. The consultant was seeking ways to turn off the P&T system by treating the plume in-situ. They had previously used an ERD technology without fully achieving primary COC reductions. RRS designed and implemented a pilot study for the site.
Remediation Approach
The pilot study was designed to test Regenesis’ combined remedy approach which incorporated ERD using 3-D Microemulsion, Bioaugmentation with BDI Plus and ISCR with CRS. RRS applied the integrated technologies through direct-push borings. The 2,500-square-foot treatment zone included 10-foot vertical injections into silty sand and clay over weathered dolomite bedrock.
Technology Description
- 3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory–emulsified product.
- HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).
- Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
- CRS® (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español










