 What is Naphthalene?
What is Naphthalene?
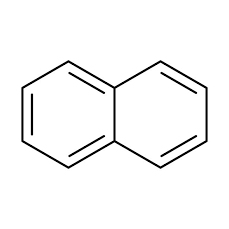
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula C ₁₀H ₈. It is the simplest poly-cyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and appears as a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass.
Uses
Naphthalene is used in the production of phthalic anhydride; it is also used in mothballs.Other uses of naphthalene include carbamate insecticides, surface active agents and resins, as a dye intermediate, as a synthetic tanning agent, as a moth repellent, and in miscellaneous organic chemicals.
Sources & Potential Exposure
Individuals may be exposed to naphthalene through the use of mothballs. Workers may be occupationally exposed to naphthalene during its manufacture and use, especially in coal tar production, wood preserving, tanning, or ink and dye production. Naphthalene is released to the air from the burning of coal and oil and from the use of mothballs. Coal tar production, wood preserving, and other industries release small amounts. Typical air concentrations of naphthalene in cities are about 0.18 parts per billion (ppb). Naphthalene has also been detected in tobacco smoke.Acute (shortterm) exposure of humans to naphthalene by inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact is associated with hemolytic anemia, damage to the liver, and neurological damage. Cataracts have also been reported in workers acutely exposed to naphthalene by inhalation and ingestion. Chronic (long-term) exposure of workers and rodents to naphthalene has been reported to cause cataracts and damage to the retina. Hemolytic anemia has been reported in infants born to mothers who “sniffed” and ingested naphthalene (as mothballs) during pregnancy.
Federal Regulations
EPA has classified naphthalene as a Group C, possible human carcinogen.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español
