 What is Xylene?
What is Xylene?
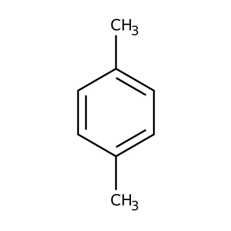
Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon widely used in industry and medical technology as a solvent. It is a colorless, sweet-smelling liquid or gas occurring naturally in petroleum, coal and wood tar, and is so named because it is found in crude wood spirit.
Uses
Mixed xylenes are used in the production of ethylbenzene, as solvents in products such as paints and coatings, and are blended into gasoline.
Sources and Potential Exposure
Commercial or mixed xylene usually contains about 40-65% m-xylene and up to 20% each of o-xylene and p-xylene and ethylbenzene. Xylenes are released into the atmosphere as fugitive emissions from industrial sources, from auto exhaust, and through volatilization from their use as solvents. Acute (shortterm) inhalation exposure to mixed xylenes in humans results in irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, gastrointestinal effects, eye irritation, and neurological effects. Chronic (long-term) inhalation exposure of humans to mixed xylenes results primarily in central nervous system (CNS) effects, such as headache, dizziness, fatigue, tremors, and incoordination; respiratory, cardiovascular, and kidney effects have also been reported. Mixed xylenes are distributed throughout the environment; they have been detected in air, rainwater, soils, surface water, sediments, drinking water, and aquatic organisms. Xylenes are released into the atmosphere as fugitive emissions from industrial sources, from auto exhaust, and through volatilization from their use as solvents.
Federal Regulations
EPA has classified mixed xylenes as a Group D, not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español
