In Situ Chemical Oxidation of Chlorinated Solvents Using Persulfox™ At An Industrial Site
Overview:
Chlorinated compounds were discovered in shallow groundwater at a former industrial site in Attleboro, Massachusetts. With total VOC concentrations as high as 85,000 ug/L in groundwater, a rapid and aggressive remediation approach was required. In Situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) using PersulfOxTM – catalyzed persulfate was selected to treat a portion of the impacted area which was approximately 35’ long x 35’ wide x 15’ deep and primarily comprised of sand. Three prescribed injections of ISCO using PersulfOx were performed over a 7- month period.
- PersulfOx is a persulfate based ISCO reagent that promotes rapid and sustained in situ oxidation of a wide-range of organic contaminants.
- This patented technology utilizes a unique catalytic surface on which oxidants and contaminants react in a process known as “surface mediated oxidation.”
- PersulfOx also contains built-in activation which eliminates complex and potentially hazardous chemical addition required to achieve traditional persulfate activation.
- From a health and safety aspect, the use of PersulfOx alone is safer than traditional activation methods such as heat, chelated metals, hydrogen peroxide or base.
- If warranted, PersulfOx can also be activated through traditional means to achieve site remediation goals.
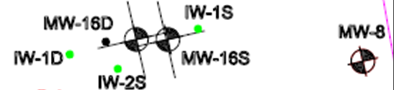
Figure 1. Injection wells and monitoring wells
A 10% solution of PersulfOx in water was mixed and injected into a 10-foot treatment thickness using 3 injection wells within the vicinity of monitoring wells MW-16D, MW-16S and MW-8 (Fig.1).
Results:
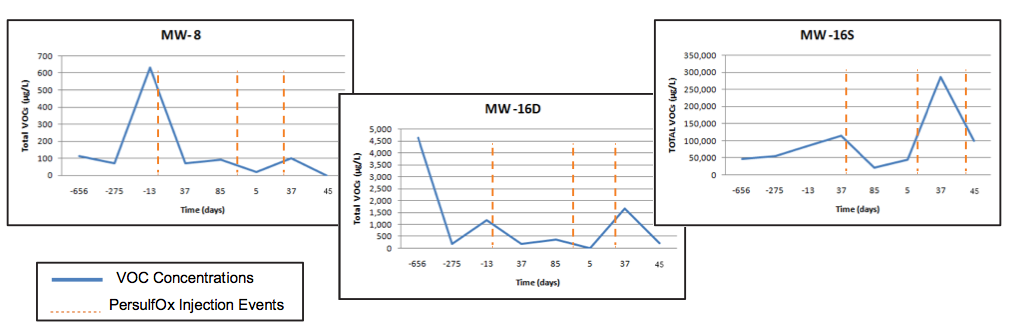
After each PersulfOx application, an anticipated increase and subsequent decrease in VOCs (resulting from subsurface disturbance and contaminant desorption) was observed. After the 3 prescribed applications of PersulfOx, 2 of the treatment zone wells, MW-16D and MW-8, measured significant VOC removal, 81% and 99% respectively. Treatment zone well MW-16S (the most highly impacted—starting at 85,000 ug/L) showed a significant increase in VOCs after the first 2 injections (indicative of the liberation of soil bound mass). After the third application of PersulfOx, VOC concentrations in MW-16S were clearly decreasing (see figures below).
Petroleum Hydrocarbon and Chlorinated Solvent Treatment Using PersulfOx™ at a Former Service Station
Overview
Petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated compounds were discovered in groundwater at a former gasoline service station/auto-repair facility. This redevelopment site, located in Bronx County, New York, previously housed an underground storage tank (UST) used for gasoline storage. Following the discovery of groundwater contamination in excess of NYSDEC groundwater protection standards, the UST and soils were removed to bedrock at a depth of 11 feet. Further monitoring revealed toluene and benzene contamination as well as tetrachloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethene (TCE) impacts from parts cleaning associated with the on-site auto-repair shop. Remedial action was required to restore site groundwater and make way for redevelopment and construction of a new building. In Situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) using PersulfOxTM was chosen as the remediation approach.
- PersulfOx is a persulfate based ISCO reagent that promotes rapid and sustained in situ oxidation of a wide-range of organic contaminants.
- This patented technology utilizes a unique catalytic surface on which oxidants and contaminants react in a process known as “surface mediated oxidation.”
- PersulfOx also contains built-in activation which eliminates complex and potentially hazardous chemical addition required to achieve traditional persulfate activation.
- From a health and safety aspect, the use of PersulfOx alone is safer than traditional activation methods such as heat, chelated metals, hydrogen peroxide or base.
- If warranted, PersulfOx can also be activated through traditional means to achieve site remediation goals.
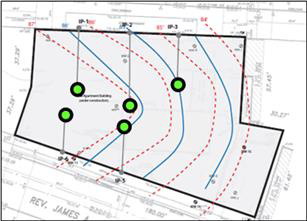
The ISCO treatment system consisted of a series of pipes extending below the basement level of the existing slab for the specific purpose of delivering PersulfOx directly onto the bedrock surface. The pipes terminated into dispersion pits scraped into the bedrock allowing PersulfOx to pool and enter the fractures (Figure 1). The ISCO delivery system design allowed for multiple reagent applications as often as required to complete the remediation process.
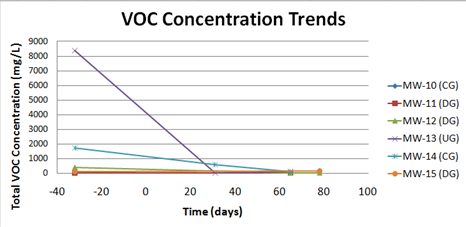
Current trends in the available monitoring well data indicate significant reductions in total VOCs (Figure 2).
Combined Technologies Replace Pump and Treat System
Manufacturing Facility Remediated Using Bioremediation, Bioaugmentation and ISCR
Project Highlights
- Combined technologies of bioremediation and ISCR were used to treat the PCE
- The remediation design replaced a costly legacy pump and treat system
- More than $200,000 per year saved by shuting down pump and treat system
- RRS’ injection strategy allows for the coapplication of BDI Plus, 3D-Microemulsion and CRS during the same mobilization event

Project Summary
Historic activities at an active manufacturing facility contaminated a sand aquifer with chlorinated solvents (primarily perchloroethene, PCE). Previous remediation activities included an extensive pump and treat system as well as other in situ activities. The cost of operating the pump and treat system was such that the client looked for a more cost-eff ective remediation approach. Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) combined bioremediation/in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) approach proved to be cost-effective as a replacement technology for the pump and treat system, saving the client more than $200,000 per year. This remediation solution was installed both inside and outside of the manufacturing facility during winter in sub-zero temperatures.
Remediation Approach
Four treatment rows of a total 48 injection points were used to apply the product with a treatment area of 5-30 feet below ground surface.
The following in situ remediation technologies were used:
- 19,300 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion FE®
- 48 liters of Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus®
- 2,400 pounds of Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®)

Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion FE is an engineered electron donor material that off ers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profi le, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsifi ed product. When injected into the subsurface, this stimulates bioremediation of the pollutant by the process of biologically enhanced reductive dechlorination. Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing a high density of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium, when added to the subsurface augments the naturally occurring population of microbes that carry out the desired reductive dechlorination process. CRS (Chemical Reducing Solution) is a soluble iron substrate designed to easily distribute to an aquifer and stimulate that serves to stimulate the abiotic in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants.
Chlorinated Solvent Concentrations Reduced >100x within Six Months
Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination Used to Treat Former Dry Cleaner in South Carolina Coastal Plain
Project Highlights
- Small groundwater recovery system in place to provide hydraulic control.
- Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) treatment selected to achieve site closure more quickly.
- High PCE concentrations reduced by more than 100x within 6 months and remain <5 ug/L two years post-injection.
- Follow-up treatments enhanced initial injection and contributed to continued dechlorination.

Project Summary
The site, located in the Coastal Plain of South Carolina, was impacted from former dry cleaning operations. A small groundwater recovery system had historically been used to provide hydraulic control, but the site owner wanted to move the site toward closure more quickly. Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) with 3-D Microemulsion® was selected based on cost, ease-of-use and expected remediation performance. After the initial injection, PCE concentrations decreased by more than 100x within 6 months of application and remain below 5 ug/L two years after the initial injection.
Remediation Approach
The core of the plume was characterized by concentrations of 14-18 mg/L PCE at baseline plus the full suite of chlorinated ethene daughter products. An initial application of 3-D Microemulsion occurred in June 2011 over a 7,750-square-foot area in the surficial aquifer from 3-25 feet below ground surface. The injections were completed using direct-push equipment into temporary borings on 13-20 foot centers. Based on the success of the initial injection, a follow-up injection was completed in September 2013 over a much smaller footprint (2,200 square feet) to fill in treatment gaps near the upgradient edge of the initial treatment area and to supplement the 3-D Microemulsion in the core of the plume. The follow-up treatment has built on the initial treatment and is contributing to continued depletion of the chlorinated solvents.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Turn-Key PCE Plume Remediation on at Michigan Superfund Site
Former Manufacturing Facility Treated with 437,000 Pounds of PersulfOx® in 18 Days
Project Highlights
- PersulfOx was selected over other persulfate activation methods because of its inherent health and safety benefits and easy-of-use.
- An aggressive application schedule was implemented to satisfy stakeholders – 37,800 lbs (15,500 gallons) of PersulfOx were injected in a single day.
- On-site diagnostics conducted by RRS confirmed PersulfOx distribution throughout the targeted treatment area.
- The project was completed ahead of schedule and on budget.
- The site was left with minimal impact to the PGA Championship Golf Course.

Project Summary
A former manufacturing facility in Western Michigan was redeveloped into an active golf course. The USEPA took over responsibility for cleanup of the chlorinated solvents that remained. Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted by a leading consulting fi rm to implement a remediation design to address the chlorinated VOC plume with concentrations as high as 3,000 ppb. PersulfOx was selected over other persulfate activation methods such as hydrogen peroxide or alkaline activate on because the built-in catalyst minimized hazardous materials handling allowing for a safer and easier application. This was especially important because of the treatment areas close proximity to a sensitive receptor (river). Despite persistent freezing temperatures, RRS was able to finish this project ahead of the projected schedule. The RRS team faced a unique challenge on this site as it is a PGA Championship Golf Course which required extreme caution while injecting on the course. Strategic injection point placement, equipment staging, and surface protection via mats were just a few of the techniques implemented by the team

Remediation Approach
The 18-day injection event included 437,000 pounds of PersulfOx which was applied through 129 injection points in a grid pattern 5-30 feet below ground surface. The team used two direct-push injection machines to apply PersulfOx into eight points injection simultaneously.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate componentand generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español

