PlumeStop Application Pilot Study: Former Dry Cleaner Site, USA
Approach
A beta-test pilot evaluation of PlumeStop™ performance was conduced on chlorinated solvent groundwater contamination at a former dry cleaner site. PlumeStop was applied in conjunction with the slow-release electron donor, HRC® and the microbial bioaugmentation dechlorinator inoculum, BDI® for the treatment of residual PCE (550 μg/L). The test was conducted around a single well. Conditions prior to the test were aerobic (ORP +254 mV; DO 44%). Multiple parameters were monitored from groundwater samples to explore lines or evidence of solvent fate / degradation.
2m 27s reading time
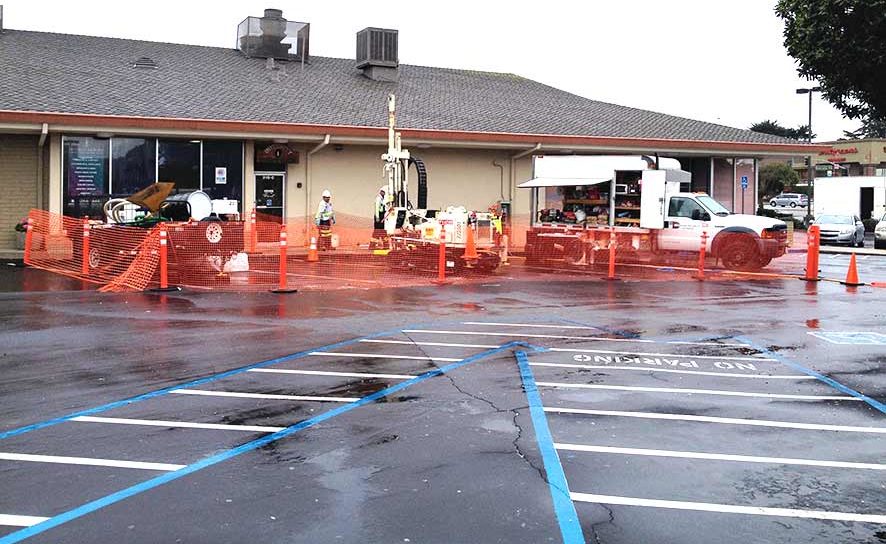

Results
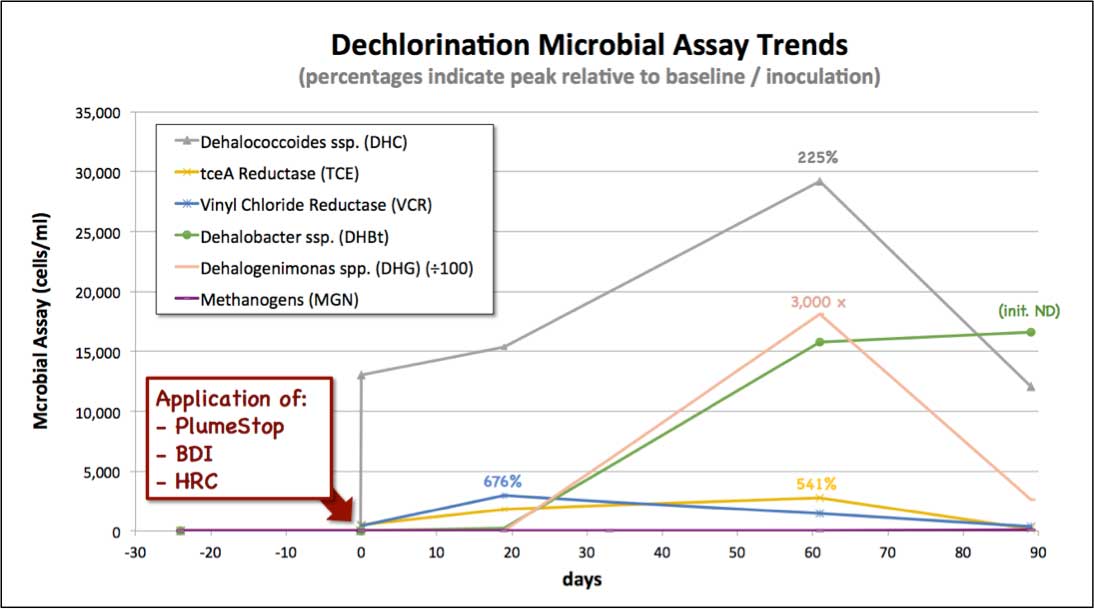
Post-treatment solvent concentrations in groundwater were reduced by over 99% to non-detect (<5μg/L) by the first sampling round (19 days). Microbial quantitative array data revealed marked increases in reductive dechlorinator species from baseline conditions in the months following reagent application (several hundred percent or more). (Baseline taken as immediately post-inoculation for species included in BDI). Moreover, functional enzymes for dechlorination of PCE through to ethene similarly increased over the same period (i.e. including specific genes for the degradation of TCE, DCE and vinyl chloride). Through this time, groundwater concentrations of PCE and daughter products remained below detection limits (>15 months post treatment).
Electron donor status and redox potential post-application quickly stabilised at near-optimal conditions ( 150mV +/- 30 mV), with rapid decreases in competing electron acceptors observed within the first sampling intervals, albeit with some interplay with available iron, possibly reflecting an electron shuttle dynamic with iron naturally present within the formation. The redox remained below methanogen activity thresholds – methanogen numbers did not share the trends observed in dehalorespirers, and in fact were detected above quantitation thresholds (2 – 30 cells /ml) in one sampling event only, at significantly lower cell counts than Dehalococcoides (94 vs. 12,200 cells/ml).
Discussion
The continued expansion and proliferation of an active dechlorinating microflora in the months following inoculation are indicative of solvent biodegradation through this time. That no solvent was present above detection limits in groundwater through the same period would indicate the degradation to be proceeding ostensibly from the sorbed phase (i.e. PlumeStop/water interface). This would be consistent with the PlumeStop bio-matrix hypothesis. It is also of note that the dechlorinator numbers and activity peaked at approximately sixty days and declined thereafter. Although the data set is limited, this trend would be consistent with the presumed depletion of the solvent through degradation, the starting concentration having been only 550 μg/L.
Conclusion
These data provide lines of evidence for post-sorption degradation of the target solvents on the PlumeStop, and would further indicate that methanogenic conditions are not necessary for complete reductive dechlorination activity through to ethene. Moreover, all data were obtainable from groundwater samples presenting a straightforward means of performance tracking via wells using the lines of evidence approach.
What’s Special
- Depletion of groundwater solvent concentrations to non-detect within 19 days
- All Contaminants of Concern (PCE and daughter products) are remaining below detection limits 15 months post application (and counting)
- Multiple lines of evidence for post-sorption solvent degradation
- All data obtainable from groundwater samples alone
- No generation of methane / competition from methanogens
Combined Technologies Replace Pump and Treat System
Manufacturing Facility Remediated Using Bioremediation, Bioaugmentation and ISCR
Project Highlights
- Combined technologies of bioremediation and ISCR were used to treat the PCE
- The remediation design replaced a costly legacy pump and treat system
- More than $200,000 per year saved by shuting down pump and treat system
- RRS’ injection strategy allows for the coapplication of BDI Plus, 3D-Microemulsion and CRS during the same mobilization event

Project Summary
Historic activities at an active manufacturing facility contaminated a sand aquifer with chlorinated solvents (primarily perchloroethene, PCE). Previous remediation activities included an extensive pump and treat system as well as other in situ activities. The cost of operating the pump and treat system was such that the client looked for a more cost-eff ective remediation approach. Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) combined bioremediation/in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) approach proved to be cost-effective as a replacement technology for the pump and treat system, saving the client more than $200,000 per year. This remediation solution was installed both inside and outside of the manufacturing facility during winter in sub-zero temperatures.
Remediation Approach
Four treatment rows of a total 48 injection points were used to apply the product with a treatment area of 5-30 feet below ground surface.
The following in situ remediation technologies were used:
- 19,300 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion FE®
- 48 liters of Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus®
- 2,400 pounds of Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®)

Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion FE is an engineered electron donor material that off ers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profi le, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsifi ed product. When injected into the subsurface, this stimulates bioremediation of the pollutant by the process of biologically enhanced reductive dechlorination. Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing a high density of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium, when added to the subsurface augments the naturally occurring population of microbes that carry out the desired reductive dechlorination process. CRS (Chemical Reducing Solution) is a soluble iron substrate designed to easily distribute to an aquifer and stimulate that serves to stimulate the abiotic in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español

