Sustainability in remediation
All across the globe, contaminated soil and groundwater creates a risk to the environment and human health. The challenge is how to remediate such widespread pollution problems without exacerbating another pressing global issue: climate change.
REGENESIS provides sustainable in situ remediation solutions. Our technologies enable contaminated land professionals to minimise the environmental impacts of their projects and reduce the carbon footprint of their clients’ supply chain.
How do we compare?
Explore the sustainability comparison studies and awards below.
Sustainability Case Study
PFAS
We asked Ramboll’s Circular Solutions and Climate Specialist team to undertake a comprehensive sustainability study comparing our approach to pump & treat.
This focused on an international airport where a PlumeStop® barrier is being used to remediate PFAS contamination. The study includes crade-to-grave Life Cycle Analysis, Life Cycle Cost Analysis and a Tier 2 sustainability assessment. The results are clear:

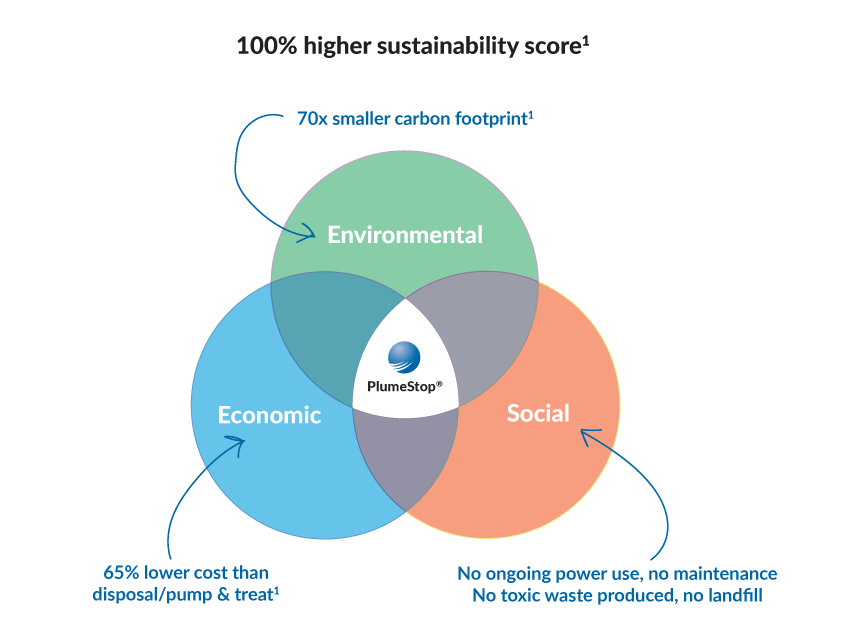
1 Sustainability of in situ and ex situ remediation of PFAS contaminated groundwater (15.05.2023); Ramboll; using ‘cradle to grave’ carbon footprint analysis, full product-level Life Cycle Analysis, Life Cycle Cost Analysis and Sustainability assessment using Ramboll’s SURE model (Tier 2 assessment in line with ISO, ASTM standards and SuRF-UK guidance)
Sustainability Case Study
Chlorinated Solvents
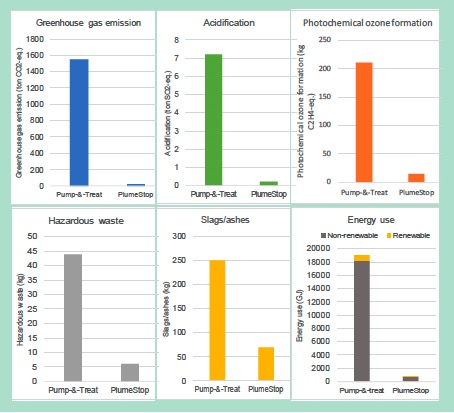
The Danish Environmental Protection Agency published a report analysing the sustainability of an in situ PlumeStop treatment of a chlorinated solvent plume using Life Cycle Analysis and a Tier 2 sustainability assessment. The approach was then compared to a potential pump-and-treat system and shown to be much more sustainable across all parameters.
Read the report to learn why PlumeStop came out as the most favourable remediation option.
Sustainability Case Study
Petroleum Hydrocarbons
This case study describes the voluntary remediation of an impacted operational petrol filling station in the UK where high levels of dissolved phase contamination was shown to be migrating beyond the site boundary.
Environmental consultancy SLR Consulting concluded that the most sustainable remedial design for the site would be the installation of an injectable permeable reactive barrier (IPRB) using PetroFix®. Compared to a source excavation approach, the project prevented up to 55 wagon loads of soil disposal. Substantial energy savings were also made when compared with operating a groundwater treatment plant.

Sustainability Awards and Listings
- Climate Change Business Journal® Business Achievement Awards 2024 (USA), Category: Technology Merit – Colloidal Activated Carbon -Winner
- Environment Analyst’s Sustainability Awards 2024 (USA), Category: Remediation Project of the Year – Highly Commended
- Fast Company’s World Changing Ideas 2024 Awards (Global), Category: Enduring Impact – PlumeStop technology – Winner
- TIME’s Best Inventions of 2024 List (Global), Category: Sustainability – Absorbing PFAS Polution, SourceStop – Listed

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español
