Combined Remedies Treat Chlorinated Solvents at Gulf Coast Superfund Site
Former Industrial Facility and Landfill Pilot Test Shows Rapid Reduction in PCE, TCE and 1,2 DCE
Project Highlights
- Superfund Site once housed an industrial facility and landfill.
- Rapid reduction needed to avoid off-site migration of daughter products.
- Simultaneous application of Enhanced Aerobic Biodegradation, Bioaugmentation and In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR).

Project Summary
This former industrial property had a landfill that was used in the mid-1900s for disposal of magnesium dross and refractory brick as well as breakout material from electrolytic chlorine cells. As much as 254,000 cubic feet of material were removed from the landfill although a large chlorinated solvent plume remains both from landfill waste below the water table and from industrial operations on-site. A feasibility study for the site was approved in 2012 which evaluated the use of enhanced reductive dechlorination to treat dissolved chlorinated solvents at the site and to prevent off-site migration past the property boundary and beneath a highway. A pilot test to evaluate at least two different biological amendments was conducted and Regenesis supplied 3D Microemulsion, BDI, and CRS for the evaluation. Three aquifers exist at the site, but the pilot test was performed in the first groundwater bearing unit only.
Remediation Approach
After a review of sulfate concentrations, other natural attenuation data, and cVOC concentrations it was determined that the optimal treatment choice would be to test a combination of an electron donor in the form of 3-D Mircoemulsion®, a bioaugmentation culture called Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM® Plus, and the use of Chemical Reducing Solution® (CRS) to prevent any hydrogen sulfide toxicity and to promote a level of beneficial in situ chemical reduction (ISCR). For the pilot test 10 injections points were used to place 800 pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, 18 liters of BDI Plus and 400 pounds of CRS. The product was injected over a 10-foot interval.
The goal for this project was to attain as rapid reduction as possible for the site specifically to avoid off-site migration of daughter products such as vinyl chloride. Therefore, it was deemed beneficial to inject all three proposed products at once. The product was injected in March 2014 and results at roughly 1 month post injection are extremely promising. PCE has been reduced from 134 ppb to 1.57 ppb, TCE from 271 ppb to 1.77 ppb, and cic-1,2-DCE from 235 ppb to 4.25 ppb. Vinyl Chloride has shown some increase from non-detect to 13 ppb.
However, Dehalococcoides has increased from non-detect to 7 x 10×5 cells/bead and vinyl chloride reduced from nondetect to 9 x 10×4 cells per bead which strongly correlates to the rapid enhanced reductive dechlorination.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
BDI Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
CRS (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Former Service Station Treated on Native American Reservation Land
Combined Remedies Used to Remediate BTEX Contamination
Project Highlights
- Enhanced Aerobic Bioremediation and In Situ Chemical Oxidation used to treat high BTEX levels on-site
- Previous remediation activities included soil excavation but contamination persisted
- One application area located in lot used for beef cattle on reservation land and special approvals were required
- Project was state-funded by Pollution Liability Insurance Agency (PILA) of Washington but regulated by Region 10 EPA resulting in extensive coordination between both agencies

Project Summary
This Wapato, Washington site was a former gas station with historical releases dating back to at least 1995. It is located on a Native American Reservation so the site is regulated through Region 10 of the EPA.
The initial remedial activities consisted of excavation of source area soil but contamination remained. Considering the persistent contamination, the goal of the site was to reduce the remaining concentrations to meet regulatory goals.
Remediation Approach
A combied remedies strategy was devised for this site, including in situ treatment in three separate areas. Two areas were treated with both PersulfOx® and ORC® Advanced.
The third area was an empty lot that was used for ranging beef cattle. The client had concerns about how the treatment might affect the cattle, so only ORC Advanced was applied to this area because it is both insoluable and non-toxic. Because the entire site was located on reservation land it required special approvals by the tribal irrigation office before the injections could occur. A total area of 4,100-square-feet was treated for high levels of BTEX. Monitoring is ongoing.
Technology Description
ORC Advanced is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator
PersulfOx® ISCO Remediation Reduces BTEX F1 & F2 Concentrations at Alberta Municipal Affairs Site
ISCO Solution Results in Cost Savings and Treatment Area Reduction at Former Service Station
Project Highlights
- In Situ Chemical Oxidation (ISCO) used as a cost-effective alternative to excavation remediation methods
- In Situ treatment using direct push resulted in reduction in treatment area
- ISCO solution met time and budget goals

Project Summary
BTEX contaminated soil was found at an Alberta Municipal Affairs (AMA) site. The former service station located in Central Alberta, Canada had left a petroleum leak creating a smear zone with F1 and F2 concentrations at the source of the plume. Since the AMA site had limited funding and time constraints, a persulfate-based ISCO solution using PersulfOx was recommended to significantly reduce high petroleum concentrations in the soil and groundwater. This site marked the first time the engineering firm working with REGENESIS had employed an ISCO solution, having used excavation remediation methods as their recommended approach in the past. An expedited remediation plan was created and included multiple rounds of PersulfOx injections to treat the site.
Remediation Approach
PersulfOx was applied in seven existing monitoring wells. Working with the engineering firm, using direct-push injection of PersulfOx, REGENESIS strategically focused the application around two of the existing monitoring wells. Due to the saturated soil type and an increased risk for surfacing, precise application-volume monitoring was required. After the first round of two applications was completed, overall contaminant concentrations decreased.
REGENESIS Solution Applied
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Results
The REGENESIS ISCO plan incorporating direct-push injections of PersulOx significantly reduced the level of BTEX contaminant concentrations following the first round of application. The PersulfOx solution effectively addressed the plume in the saturated smear zone, while meeting the goals of the project, as well as the client’s time and budget constraints.
Former Paint Manufacturing Facility Treated for MIBK, BTEX
RRS Implements Cost-Effective, Turn-Key Remediation in Low-Permeability Soils
Project Highlights
- Soil and groundwater impacted with both BTEX and MIBK.
- Low-permeability soil was of a concern to the client, however very little surfacing was witnessed post-injection.
- Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) finished the project in half the time and nearly half the cost of competing firms.

Project Summary
Site operations at a former paint manufacturing facility in Northern California caused soil and groundwater to be impacted with MIBK and BTEX compounds. The site was under an order for clean-up through the regional water quality board and the treatment was designed to use in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) to reduce contaminant mass in the source area before transitioning to MNA.
Remediation Approach
Comprised of what the consultant described as “San Francisco Bay Muds” or essentially clay soil with sand stringers, the site had challenging geologic conditions. At first, the client was apprehensive about the ability to inject PersulfOx® into the tight soils without surfacing. However, a turn-key approach was devised during the design of this project, with an emphasis on minimizing product application costs and addressing any possible surfacing issues. A total of 29,644 pounds of PersulfOx was applied by RRS in two applications, through a total of 58 directpush points and 2 injection wells at the site. The product was applied at a 20% solution for a total injection volume of 15,691 gallons.
The injections were completed in half the time and nearly half the cost of what other injection contractor firms proposed. The capabilities of the RRS team, trailer and ability to manifold and inject into four points at one time resulted in significant time and cost savings for the client. Monitoring is ongoing.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solventtype contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
RRS is a dedicated team of scientists and engineers whose primary function is to provide environmental engineering and consulting firms with specialized groundwater and soil remediation planning, design, verification and application services.
In Situ Chemical Oxidation Treats High TPH Concentrations
Over 114,000 Pounds of PersulfOx® Applied to Illinois Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- High levels of TPH and TCE were detected on-site after a suspected cutting oil/degreasing solvent spill.
- Remediation mandated after oil sheen observed in river adjacent to manufacturing facility.
- In Situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) paired with excavation to remediate site.
- Tight treatment deadline met through the use of PersulfOx in 2,204-pound SuperSacks, which were delivered within a few days’ notice.

Project Summary
An Illinois metal fabrication manufacturing facility has been in operation since the early 1900s and is still active today. The use of cutting oils and degreasing solvents lead to high levels of TPH and TCE on-site. The state of Illinois cited the facility for a violation when an oil sheen was observed seeping from the property into an adjacent waterbody. A mechanical oil recovery system was installed and absorbent booms were used to mitigate the oil from reaching the river. ISCO was selected as the remediation approach to address the contamination below the active facility through a series of applications. Additionally, the TCE area was treated with PersulfOx® via injection wells and a soil mixing application.
Remediation Approach
Prior to the start of remediation activities, the primary consultant was removed from the project and a new firm was brought in. The remediation firm placed a tight deadline (a couple of months) to complete the full scope of activities. REGENESIS was able to assist with keeping the project on-deadline through the delivery of 2,204-pound PersulfOx SuperSacks, which were delivered within a few days’ notice. The consultant had a series of injection wells installed inside and outside of the building. PersulfOx was injected into these wells during three applications over a three-month period. Additionally, the TCE area was treated with PersulfOx through a soil mixing application using an excavator. The final step of the remediation plan is to treat the TPH-impacted soils outside the building through excavation, and Oxygen Release Compound (ORC®) Advanced Pellets will be used as a long-term oxygen source for enhanced bioremediation of the residual TPH.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
ORC Advanced Pellets are a pelletized version of REGENESIS’ widely used ORC Advanced and are designed specifically for direct application into excavations, tank pits and trenches. This pelletized, dry application material minimizes airborne dust while eliminating the need for specialized equipment and spray water required for powder-slurry applications.
Site Closure Achieved at Colorado Service Station
Benzene Levels Reduced to Below 5 PPB in Clay Soils through Use of ORC® Advanced
Project Highlights
- Benzene concentrations remained on-site despite previous excavation efforts.
- Enhanced aerobic biodegradation using ORC Advanced produced a 99.8% reduction over 12 months.
- Benzene reduced to below detection limits.
- “No Further Action” letter granted in October 2010.

Project Summary
Three underground storage tanks (USTs) were removed at a former tire store as part of corrective measures. Roughly 108 cubic yards of soils were excavated to reduce contamination levels. However, the excavation did not extend below the groundwater interface and residual sorbed contaminant mass remained, resulting in a lingering benzene plume. The client was interested in an in situ approach to reduce the remaining benzene contamination to below the Tier 1 risk based screening level of 5 ppb.
Remediation Approach
A direct-push injection of Oxygen Release Compound Advanced (ORC® Advanced) was chosen to reduce remaining soil and groundwater contamination at the location of the former excavation and well BW-1. Maximum TVPH and benzene concentrations in the prior two years were as high as 2.4 mg/L and 0.48 mg/L, respectively. Due to tighter soils, a 7-footon-center grid pattern with 15 injection points was implemented on-site. ORC Advanced was injected from approximately 6 to 13 feet below ground surface with about 1 foot of the injection interval extending above groundwater in the event of rising water levels. A total of 725 pounds of ORC Advanced was injected for this project.
Despite the relatively tight soils and high potential for contaminant back diffusion, the ORC Advanced treatment resulted in consistent downward trends of benzene contamination. A 96.3% reduction in benzene after only 3 months was observed. By month 12, a 99.8% reduction to below detection limits (The site was granted a no further action letter.)
Technology Description
ORC Advanced® is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration.
RegenOx® Injected Into Frozen Permafrost at Alaska Site
Seasonal Access and Remote Location Require Unique Remediation Plan at Service Station
Project Highlights
- Sensitive ecosystem and limited seasonal accessibility required a unique remediation plan design.
- RegenOx® injected into frozen permafrost.
- Overall remediation plan requires three applications while site is accessible in summer months.

Project Summary
Located in Deadhorse, Alaska, this service station site was contaminated through multiple releases from the diesel and gasoline tanks. When this lease site was originally bid, it was required to be constructed with a minimum of 5 feet of gravel on the pads to protect the tundra. This lease requirement remains today.
The remote location on the North Slope of Alaska made it challenging to design, plan, and implement a remediation plan considering the temperatures were just above freezing. The area can only be accessed seasonally for monitoring/application and shipping products to the site proved to be a challenge. Located in a very sensitive native ecosystem (tundra/permafrost), in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was chosen as the remediation approach to avoid enlarging the plume.
Overall treatment goal for the project is to reduce hydrocarbon concentrations in approximately 365 cubic yards of source area soil to below cleanup levels. Treatment will be conducted in multiple phases and this project summary will summarize steps taken within the first year to address one-third of the exceedance area.
Remediation Approach
Surface soil to down to one-foot below ground surface was removed and stockpiled before subsurface soil from (1-5 feet below ground surface) was treated via in situ soil mixing using RegenOx®. Based on the effectiveness of Year 1 treatment; the plan is to use the same treatment method on remaining soil in subsequent years.
For the 125 cubic yards (or 1/3 of contaminated soil at the site), a total of 3,430 pounds of RegenOx (2,500 pounds of RegenOx Part A and 930 pounds of RegenOx Part B) were applied to treat BTEX, TPH, and naphthalene concentrations. Due to the sensitive and remote nature of the site, the application was staggered and the methodology was ultimately modified to prevent oversaturation and reduce the risk of plume migration. The Part B was mixed with a small amount of water and then applied and mechanically mixed thoroughly into the treatment area, followed by the Part A being applied dry and then well-mixed over the same area.
Technology Description
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled chemical reactions and not through biological means. This product maximizes in situ performance while using a solid alkaline oxidant that employs a sodium percarbonate complex with a multi-part catalytic formula.
REGENESIS Remediation Services – LNAPL Treated with Combined Remedies
Active Michigan Service Stated Remediated Through Use of PetroCleanze® and ORC® Advanced
RRS was contracted to remediate a residual LNAPL and dissolved phase petroleum plume from historic gasoline and diesel fuel releases at an active service station. PetroCleanze® was chosen as the primary remediation technology to facilitate recovery of residual LNAPL and chemically oxidize contaminants without negatively impacting sensitive infrastructure. ORC® Advanced was also applied with the final PetroCleanze application event and in a downgradient plume cut off barrier to promote the enhanced aerobic bioremediation of the dissolved-phase petroleum hydrocarbons.
Eight injection/extraction wells and 28 direct-push injection points were used to apply the remediation reagents in the silty sand aquifer and smear zone over three application/injection events. Vacuum extraction was conducted between PetroCleanze applications to recover residual free phase petroleum hydrocarbons liberated from the soils. Reagent distribution monitoring confirmed PetroCleanze was dispersed across the targeted source area during each application event.
Prior to the first PetroCleanze application event, no measurable free product was observed on this site since 2006. Less than twenty-four hours after the first PetroCleanze application event, LNAPL was observed in four of the eight wells in the source area at quantities up to three inches thick.

Not more than a sheen was observed in any wells on site after the third injection event. A total of 2,160 pounds of PetroCleanze and 1,120 pounds of ORC Advanced were injected.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – LNAPL Plume Treated at Iowa Service Station
PetroCleanze and ORC Advanced Remediate Historic Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination
RRS was contracted to remediate a dissolved phase LNAPL petroleum hydrocarbon plume petroleum fuel releases at a former service station PetroCleanze® was chosen as the primary remediation technology to facilitate recovery of residual LNAPL and chemically oxidize contaminants without negatively impacting sensitive infrastructure. ORC Advanced was also applied with the final PetroCleanze application enhanced aerobic bioremediation of hydrocarbons.
Eighteen direct-push injection points were used to apply the reagents in the silty sand aquifer and application events. Three vacuum extraction conducted after each PetroCleanze application to recover residual free phase petroleum hydrocarbons liberated from the soils.
Reagent distribution monitoring confirmed PetroCleanze was dispersed across the targeted source area during events.
Direct-push injection points were advanced to 15 feet below ground surface where bottom-up injections were performed to 5 feet. A total of 4,470 pounds of PetroCleanze and 720 pounds were injected.

Regenesis Remediation Services™ – TCE Plume Treated with Combined Remedies
Wisconsin Manufacturing Facility Remediated with RegenOx®, 3-D Microemulsion ®
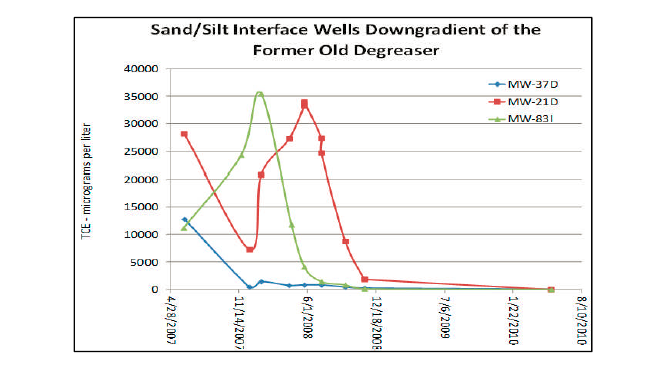
A stainless steel tube manufacturing facility and their environmental consultant, Symbiont, selected Regenesis as a team member to assist in the design and implementation an in situ chemical oxidation and ERD remediation plan. The goal was to reduce trichloroethene (TCE) in source area groundwater over a 1.5 acre site from as high as 110,000ug/L to less than 10,000 ug/L using RegenOx, then transition to ERD. RegenOx® was applied through injection wells over three to five applications from 11/2007 to 6/2008. Five month later, ERD was started using 3-D Microemulsion® in this sandy surficial aquifer.


 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español

