Ohio Brownfield Site Receives “No Further Action” Status within One Year of Implementation
Project Highlights
- Combined remedy approach allowed for immediate redevelopment within same year of implementation.
- Efficiencies resulted in vapor intrusion mitigation cost of $3.34 per sq. ft., with no long term operation and maintenance required.
- Cost for groundwater treatment approximately $10 per cubic yard (product + application).
1m 25s reading time

Project Summary
A former industrial magnet manufacturing facility in Ohio received a $2.34 million Clean Ohio Revitalization Fund (CORF) grant through the Ohio Department of Development in 2011. Site investigation activities identified chlorinated VOC’s in groundwater and vapors above the state standards, requiring remediation. Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination, using 3D Micro-Emulsion®, and BDI-Plus® were implemented within the defined 24,000 sq. ft. treatment area via direct push injection.
This work was conducted in the Spring of 2012. In the Fall of 2012, the Geo-Seal Vapor barrier system was installed below a 15,522 sq. ft. apartment complex raised at the site. Utilizing a combined approach of enhanced reductive dechlorination with vapor mitigation addressed the immediate risk of vapor intrusion, in addition to the long term risk of groundwater impacts. By implementing this strategy, the site was allowed to be redeveloped as an apartment complex roughly 6 months following the groundwater treatment. The cost for groundwater treatment was approximately $10/cy (product + application) and Geo-Seal® was $3.34/sq. ft. (product + installation).
Technology Description
BDI Plus is an enriched, natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC) which are capable of completely dechlorinating contaminants during in situ anaerobic bioremediation processes.
3-D Microemulsion is a wide-area distribution, staged release, electron donor emulsion for the optimized enhanced anaerobic biodegradation of chlorinated compounds.
Geo-Seal is a composite system that creates the ideal blend between constructability and chemical resistance by using both high density polyethylene (HDPE) and spray-applied asphalt latex.
Results
Housing developers face many considerations, including approvals for land excavation and required building permits. By implementing a combined remedy approach, consisting of enhanced reductive dechlorination with vapor mitigation, this site was able to qualify for NFA status in less than a year, allowing the developer to begin new construction without further delay.
Successful Bioremediation at a Former Air Force Base Fire Training Area
Project Highlights
- Air Force Base contaminated with high levels of carbon tetrachloride due to on-site firefighting training
- 97% reduction in contaminant within three months
- Carbon tetrachloride reduced to below detection limits
1m 20s reading time

Project Summary
Training exercises at Texas Air Force Base resulted in an impact to soil and groundwater by trichloroethylene (TCE) and carbon tetrachloride. A monitored natural attenuation study conducted indicated that chlorinated solvents at the plume would naturally decline to acceptable levels after 30 years of monitoring.
After over 14 years of monitoring, contaminant reductions were not proceeding as quickly as predicted and additional remediation was advised. It was determined that limited anaerobic activity was present and biostimulation was a viable option. A pilot test was conducted on-site.
The objective of the test was to determine the feasibility of injection into the shallow, discontinuous groundwater unit. The pilot test was also designed to determine if the residual TCE and carbon tetrachloride could be biodegraded through enhanced bioremediation and reduced to below 5 ppb (the Texas Risk Reduction Program limit). Follow-up injections were applied downgradient of the source area and also in a barrier configuration several hundred feet dowgradient of the source were implemented about 6 months after the pilot test.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion® is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Results
The combination of the pilot test and full-scale application resulted in a 97.8% reduction in carbon tetrachloride 8 months post-injection, with chloroform, methylene chloride, and chloromethane remediation daughter products on a downward trend. High TCE concentrations were effectively treated as well with TCE peaking after injections to 126 ppb within a 3-month period to 0.2 ppb.
RegenOx® Technology Expedites Hollywood Brownfield Site Transaction
Project Highlights
- Reduction of TCE, naphthalene, and styrene levels to below risk-based closure levels via in situ chemical oxidation clears the way for property sale
- Flexibility of RegenOx® application allowed the remediation to be completed faster and more effectively
- Treatment of over 18,000 cubic yards of vadose soil completed within 30 days

Project Summary
A pending real estate transaction of a industrial property in Hollywood, CA was held up by contamination of the vadose zone with a mixture of chlorinated and petroleum solvents. Before the transaction could be finalized, high levels of perchloroethene (PCE), naphthalene, and styrene in the vadose zone soil had to be reduced to below risk-based closure levels. To achieve this, the engineering firm in charge of remediation selected chemical oxidation using RegenOx based on the product’s proven effectiveness, low-cost, and handling safety.

Direct-Push Injection
A remediation plan was developed for the contaminated site that involved two rounds of direct-push application of RegenOx separated by 4 to 6 weeks. The direct-push methodology uses specialized equipment to apply RegenOx to discrete areas of the subsurface without soil removal (i.e., in situ). In order to determine the effectiveness of the treatment, composite soil samples from various grid cells were taken before and after application of RegenOx. Before treatment, significant variation was seen in the contaminant concentrations, with maximum concentrations of 140 μg/kg for PCE, 1200 μg/kg for naphthalene, and 400 μg/kg for styrene. Following the first direct-push application of RegenOx, the average PCE concentration was reduced to 4 μg/kg, a decrease of 86%. Similar results were seen for the petroleum solvents and other chlorinated volatile organic compounds (cVOCs) in the composite soil samples.
Soil Mixing Applicationhollywood2
Despite the contaminant reductions achieved by the first direct-push application of RegenOx, REGENESIS® Remediation Services determined that the speed and effectiveness of the remediation effort could be significantly improved by switching to soil mixing application of RegenOx. In this more aggressive approach, RegenOx was mechanically blended into the vadose soil in order to maximize the contact between the product and the contaminated soil. RegenOx was added as an eight percent solution and mixed throughout the soil using soil mixing equipment. With this treatment method, approximately twice as much soil was treated per day compared to direct-push application.
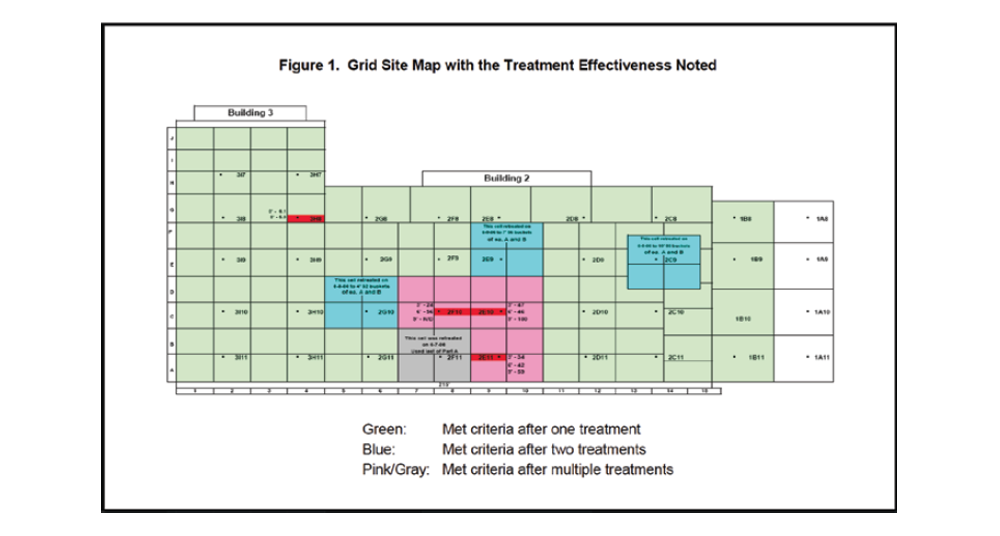
Of the 111 grids treated with RegenOx by soil mixing (Figure 1), 83 required only one treatment (green) to achieve levels below risk-based closure, 12 required two treatments (blue), and 16 required more than two treatments (pink and gray).
Technology Description
RegenOx is a percarbonate-based in situ chemical oxidation technology that rapidly destroys petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated contaminants through powerful chemical reactions. It directly oxidizes contaminants while a catalytic component generates oxidizing free radicals to destroy the target compounds.
Results
The mixed chlorinated and petroleum solvent contamination of the vadose soil was effectively reduced using RegenOx in both direct-push and soil mixing applications. Soil mixing was used to complete the remediation effort rather than a second round of direct-push injections because it maximized contact between RegenOx and the contaminated soil, achieving more rapid and effective treatment. In 74% of the treatment grids, concentrations of all the contaminants were reduced below the risk-based cleanup goal with a single application by soil mixing. Additional applications in the remaining 26% of the treatment grids also achieved the targeted levels for all the contaminants. This remediation approach successfully treated nearly 18,000 cubic yards of soil within 30 days. Using RegenOx and flexible application methods, the site was quickly and effectively remediated, allowing for the real estate transaction to be completed.
Non-Detect Levels Reached with Application of PlumeStop® at Former Dry Cleaning Site
Lines of evidence for post-sorption solvent degradationRead More
New Jersey Manufacturing Facility Achieves Non-Detect with PersulfOx® Application where Pump and Treat Solution Failed
Project Highlights
- Replacing a costly pump and treat solution, REGENESIS® was able to efficiently inject PersulfOx® into bedrock, saving time and money
- Maximum 580 μg/L levels of 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane within the source area reduced to non-detect
- Low-level concentrations of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area also reduced to non-detect

Project Summary
A former manufacturing facility in New Jersey was contaminated with 1,1-dichloroethylene (1,1-DCE) and 1,4-dioxane in a fractured bedrock aquifer. The previous treatment approach utilized a pump and treat method that was successful at containing and reducing contaminant concentrations within the source area, but the associated off-site transportation and disposal of recovery water was expensive.
Historic concentrations for 1,1-DCE within the source area ranged from 43-580 μg/L, and concentrations outside of the immediate source area persisted at low levels above Ground Water Quality Standards. 1,4- dioxane concentrations within the source area peaked at 580 μg/L.
PersulfOx in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was selected as a lower-cost alternative to the pump and treat method and also as a way to address the diffuse contamination surrounding the immediate treatment area. After application of PersulfOx, both 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane concentrations within the source area rapidly decreased below detection levels and remained non-detect. In addition, the low levels of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area were also reduced to non-detect. Quarterly groundwater sampling will continue to track treatment performance.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology that destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst that activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Results
Application of PersulfOx resulted in the rapid reduction of source area 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane concentrations to below detection limits. Low concentrations of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area were also reduced to non-detect. The concentrations of contaminants in both areas have remained below groundwater quality standards, meeting site requirements.
Remediation of Chlorinated Solvents Allows for Redevelopment in Sweden
98-99% concentration reduction within 18 months using 3‐D Microemulsion® (3DMe) for in situ reductive dechlorinationRead More
Redevelopment of Former Manufacturing Facility, Northern Italy
Low concentration chlorinated solvent contamination in difficult geology treated via enhanced reductive dechlorination using 3DMeRead More
Enhanced Abstraction of Chlorinated Solvents using PetroCleanze
An extensive chlorinated solvent plume is treated by pump-and-treat augmented with PetroCleanze injections, followed by long term treatment via Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination using 3-D MicroemulsionRead More
Bioremediation of Chlorinated Solvents at an Operational Facility
HRC successfully degrades TCE plume, protecting sensitive receptor. With consultant: AECOM. Based on Richard Bewley’s presentation & article: ‘Meeting The Challenges For Bioremediation Of Chlorinated Solvents Posed At Operational Sites: A Comparison of Case Studies’ – AquaConsoil, 2015Read More
Remediation at Active Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Facility, Italy
High concentrations of chloromethane contamination in groundwater successfully remediated in situ at operational pharmaceutical manufacturing facilityRead More

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español