PFAS Effectively Remediated at Former Naval Air Station Alameda, USA
Case Study Highlights
- >99% PFAS reductions achieved within treatment zone, within one year of implementation
- Results indicate a near-complete halt of PFAS migration into the estuary
- Site establishes a precedent for easy-to-implement, low-cost, and zero-waste PFAS remediation at military sites
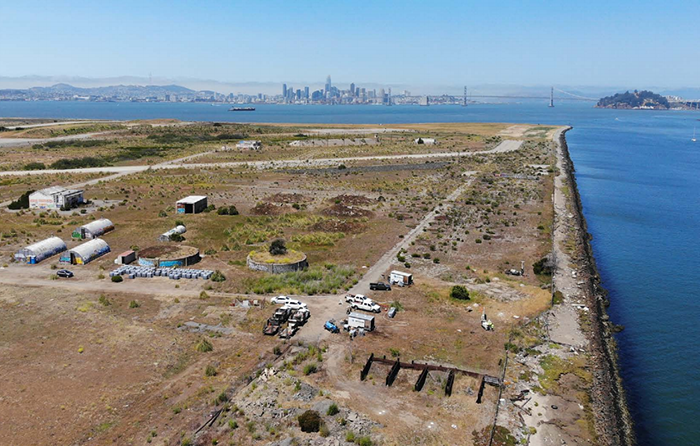

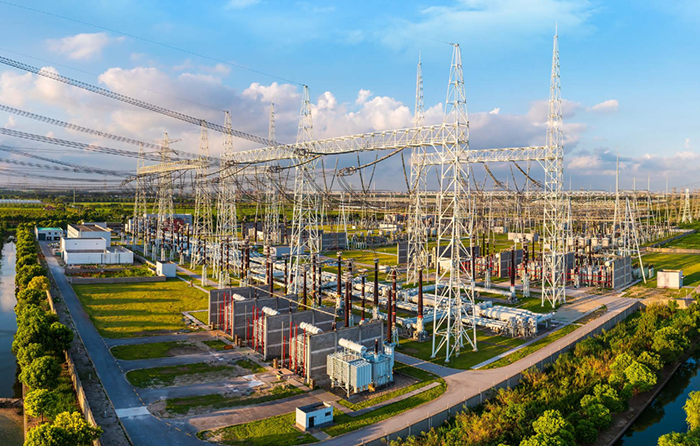
Historical firefighting activities at the former Naval Air Station (NAS) Alameda resulted in high PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) concentrations in the groundwater, threatening the Oakland Inner Harbor. In response, the project team, comprising Bayside Engineering, Construction, Inc. (Bayside), APTIM Federal Services (APTIM), and REGENESIS®, collaboratively implemented a 720-foot in situ permeable reactive barrier (PRB) using PlumeStop® colloidal activated carbon (CAC) technology. This innovative approach created an adsorptive barrier within the polluted aquifer, effectively capturing PFAS and preventing their migration. After one year, the target PFAS compounds were reduced by more than 99% in the treatment zone with significant decreases in the downgradient wells.
High-Mass Petroleum Hydrocarbons Treated to Achieve Closure
Case Study Highlights:
-
PersulfOx injected into subsurface during 3 treatment rounds, sequenced ±2 months apart
-
Toluene reduced by an average of 94% and below the toluene Site-Specific Target Levels (SSTLs) in all 5 performance monitoring wells
-
Toluene remains below its SSTL following the injection of PersulfOx

A former US electric service company reported a release during a UST removal completed at the site in 1988. Previous remediation by others included aggressive fluid vapour recovery events completed from 2004 to 2008 and from 2019 to 2020 to address the release, along with groundwater monitoring. Despite these efforts, high concentrations of petroleum hydrocarbons (PHC) remained. Following years of remediation, the final selection and successful application of PersulfOx® effectively reduced high concentrations of toluene in groundwater below the site cleanup goal. The remediation achieved the site target cleanup objectives and received regulatory closure for the decades-old release incident.
PetroFix Achieves Success at Delaware Service Station
Case Study Highlights:
-
Site closure targets rapidly met through innovative remediation
-
Strategic application of PetroFix® through both grid and barrier injections as well as the direct application of RegenOx® during excavation of highly impacted soils
-
Achieved reductions in benzene, toluene, and EDB to near or below detection limits

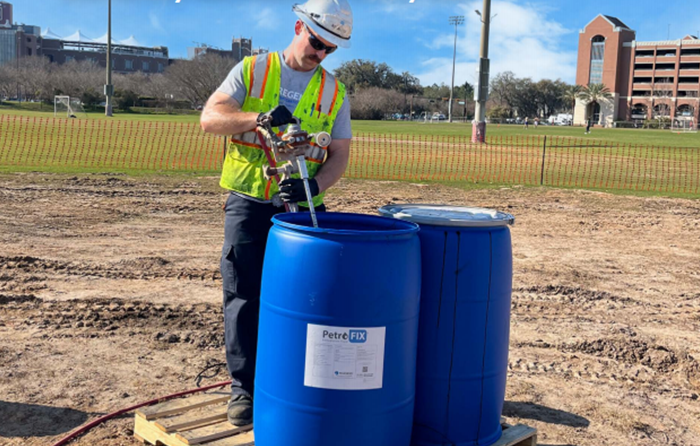
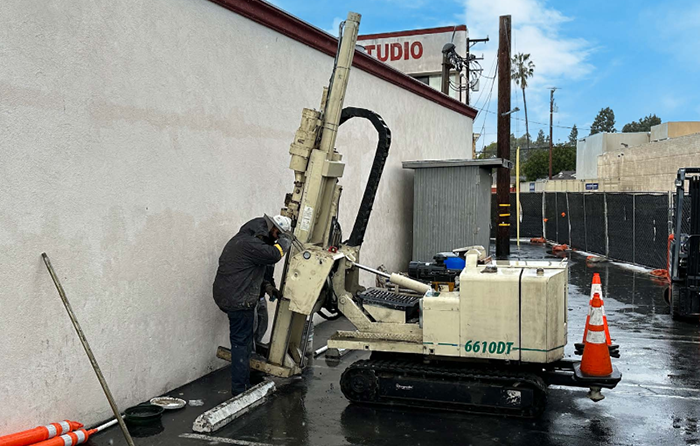
At a vacant, former retail service station in Delaware, the strategic application of PetroFix through both grid and barrier configuration injections, as well as the direct application of RegenOx during excavation of highly impacted soils, significantly reduced high concentrations of benzene and toluene, along with low levels of ethylene dibromide. These interventions brought contaminant levels below the final regulatory cleanup threshold needed to achieve site closure. By implementing PetroFix, the Delaware project achieved reductions in benzene, toluene, and EDB to near or below detection limits, securing an effective, long-term solution for groundwater remediation.
Stringent Site Closure Goals Achieved Using PetroFix
Case Study Highlights:
-
Petroleum impacts effectively remediated at university recreation facility site
-
Project goals met in all treatment areas, within budget and time constraints
-
Low-impact, single injection event minimized disturbance to athletic fields

Terracon, a leading US environmental engineering and consulting firm, completed the remediation of a university recreational facility in Florida impacted by historic petroleum hydrocarbon (PHC) contamination. Under stringent contractual timelines and performance benchmarks set by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP), Terracon excavated PHC-impacted soils and applied PetroFix® in situ to address residual contamination in the saturated zone. The injection area needed to be restored to its original condition to accommodate upcoming seasonal use. A reliable injection technology was required to achieve the project goals, minimize disruption to the athletic fields, and avoid the need for remobilization. This comprehensive approach successfully met FDEP’s cleanup goals for soil and groundwater where the amendment was applied in the treatment area.
Rapid Elimination of Chlorinated Solvents
Case Study Highlights:
-
Combined approach using 3 REGENESIS remediation products resulted in >99% reduction in CVOC concentrations
-
90% reduction goal achieved within 4 months post-application
-
Ongoing monitoring indicates the continued effectiveness of the treatment, with additional reductions expected in the following months

In Southern California, a retail facility with an active food service tenant faced significant groundwater contamination from chlorinated solvents, primarily tetrachloroethylene (PCE) and trichloroethylene (TCE), resulting from a historical release at a former dry cleaners on-site, which also impacted adjacent properties. Despite previous remediation efforts, high contaminant concentrations persisted, feeding a contaminant plume. Using 3-D Microemulsion® (3DME), our sulfidated micron-Scale ZVI : S-MicroZVI® , and Bio Dechlor Inoculum Plus® (BDI Plus), the site achieved a greater than 99% reduction in CVOC concentrations and halted plume migration through biologically enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical reduction (ISCR), meeting the site’s performance goals.
New York Brownfield Site Achieves Site Closure
Case study highlights
In situ remedy replaces ex situ system and achieves PCE and TCE cleanup targets at former metals manufacturing site:
-
a PlumeStop permeable reactive barrier (PRB) replaces pump-and-treat system and achieves site closure
-
Concentrations reduced from 500 µg/L to below 1 µg/L for 6 consecutive quarters
-
Significant cost and energy savings achieved by decommissioned pump-and-treat system
7m 47s reading time

At a former metals manufacturing facility in upstate New York, historic use of chlorinated solvents had resulted in groundwater contamination with tetrachloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethene (TCE). A pump and treat system had been operational on the site for 10 years, successfully reducing contaminant concentrations, but could not reach the clean up targets required for site closure.
Benchmark, a leading engineering and redevelopment consulting company, quickly developed an in situ approach to achieve the project objectives and facilitate site closure. After evaluating remedial alternatives, Benchmark proposed a new Corrective Action Plan (CAP), specifying the in situ application of PlumeStop® (colloidal activated carbon), Hydrogen Release Compound® (HRC), a controlled-release electron donor, and Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus® (BDI Plus), a bioaugmentation culture containing Dehalococcoides sp. and other beneficial microbes.
Challenging Fast-Moving, High Concentration Chlorinated Solvent Plume Effectively Treated
Case study highlights
A permeable reactive barrier installed using advanced colloidal technologies demonstrates pilot test’s effectiveness treating a fast-moving, high-concentration chlorinated solvent plume in groundwater:
-
Within a month of the application, the highest concentrations were reduced by 98 percent.
-
PlumeStop and S-MicroZVI co-injected barrier treats CVOCs for >3 years in high-mass-flux aquifer
-
Additional site design testing used passive flux samplers to better understand contaminant mass flux

Hamp, Mathews & Associates, Inc. (HMA), working on behalf of EGLE, collaborated with REGENESIS to develop a remedial approach to address the contaminant plume. Following data review and modeling, a sorption-ERD approach was selected for implementation in a field-scale test, using the following technologies applied in an in situ permeable reactive barrier (PRB).
In this sorption-ERD approach, PlumeStop® slows the speed of contaminants (i.e., mass flux) entering a barrier, increasing the time available for the added amendments to fully reduce these contaminants into non-toxic end products such as ethene, ethane, carbon dioxide, and chloride before they leave the PRB. In combination, these remedialtechnologies create a highly reactive zone of biogeochemical reduction that can address plumes with high contaminant mass flux.
Remediation of TCE Plume Speeds Sale of Brownfield Site
Case study highlights
At a former manufacturing site in Fullerton, California, a trichloroethylene (TCE) plume in groundwater prevented the sale of the brownfield site despite past remediation efforts, including excavation and thermal treatment. A combined remedy changed that: the combination of a large-diameter auger (LDA) excavation and injection of 50,000 gallons of
S-MicroZVI® has resulted in:
-
98.5% average reduction in TCE concentrations, facilitating the property’s sale and redevelopment
-
Through 4.5 years of monitoring, TCE remains at 99.7%, reduced in the treatment zone, confirming the remediation’s long-term effectiveness.

This case study reviews a former manufacturing site in Fullerton, CA, where a trichloroethylene (TCE) plume contaminated the groundwater and prevented sale of the brownfield site. REGENESIS designed an injection plan using micronscale Zero Valent Iron (ZVI) due to its proven ability to effectively reduce contaminant levels within a subsurface environment. In order to complete the remediation and move forward with the sale, Hargis + Associates worked with REGENESIS to develop an in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) design to address the plume. Regulatory limits on pounds per square inch (psi) were enforced for all injections. REGENESIS, Hargis + Associates, and Gregg Drilling worked closely with the regulatory agency to ensure that the remediation and injection of the ZVI would be completed at a low pressure.
In Situ Treatment of Hexavalent Chromium Results in Site Closure
Case study highlights:
This case study focuses on the successful remediation of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) contamination at a chrome plating facility in the Midwest of North America. Decades of ineffective pump & treat (P&T) operations led to the need for a cost-effective and rapid solution to achieve regulatory closure.
- Commodity ZVI and 3-D Microemulsion/CRS rapidly reduced Cr(VI) concentrations, achieving remarkable reductions within months.
- S-MicroZVI® and 3-D Microemulsion offered improved distribution and reactivity, addressing previous limitations in the remediation process.
- The use of S-MicroZVI® and 3-D Microemulsion led to a rapid 99% reduction in Cr(VI) concentrations, securing regulatory closure for a long-standing contamination case.
2m 55s reading time

PlumeStop Treatment Allows for Shut Down of Pump & Treat System
Case study highlights:
- PlumeStop treatment prevents plume migration and protects nearby community drinking water wells
- This sustainable approach eliminates the massive carbon footprint created by outdated pump-and-treat approaches
- 224,800 lbs. of PlumeStop colloidal activated carbon were safely injected into the target treatment zones
This case study reviews a large federally operated Superfund site in the USA where REGENESIS Remediation Services (RRS) completed a large-scale PlumeStop application to eliminate the risk of exposure to chlorinated solvents. Amentum, a leading American governmental and commercial services contractor, is the responsible party’s contractor. Amentum has worked with the client at this site for years, providing oversight and management of their contracting partners. The project’s sensitive nature required an enhanced awareness of health, safety, and security issues and seamless coordination between RRS, Amentum, and their client.

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español