98% PCE Reduction Achieved After 16 Months
The site is a former dry-cleaning supply distribution business that operated from 1957 to 2000. The former facility provided laundry chemicals, including detergents and spotting chemicals, packaging products such as hangers and polyethylene bags, and bulk deliveries of tetrachloroethene (PCE). Remediation at the site was completed in two primary phases. The first phase was a targeted excavation and soil mixing event focused on addressing the highly impacted shallow soils and smear zone. The second phase was focused on treating the groundwater PCE plume onsite and preventing further plume migration offsite.
Case study highlights:
- High PCE concentrations were detected in soil and groundwater during a site investigation
- A pragmatic, phased approach was used to target PCE in soil and groundwater
- The multi-component treatment was immediately effective and has maintained 98% PCE reduction in onsite groundwater
4m 23s reading time

Site Closure Achieved: Sustainable Remediation of PFAS at New York Refinery
Green, Sustainable Remediation Reduces Cost and Environmental Impact
A 25-acre former refinery located in a mixed-use industrial/commercial area in New York was contaminated with PFAS. Benchmark & TurnKey, a leading engineering and redevelopment consulting company, engaged REGENESIS for an in situ remedy that would effectively and economically cut off the groundwater plume and prevent migration of PFAS offsite.
The site was entered into the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s (NYSDEC’s) Brownfield Cleanup Program (BCP) to facilitate its commercial redevelopment. Remedial alternatives were evaluated for a comprehensive site closure strategy, and approaches were scored based on NYSDEC’s Green Remediation Policy Document (DER-31), which considers the “environmental impacts of treatment technologies and remedy stewardship over the long term.”

Case study highlights:
- Brownfield cleanup program’s green remediation policy leads to PlumeStop for PFAS treatment
- Skilfully managed PlumeStop application achieves sustainability and cost reduction objectives
- NYSDEC confirms cleanup requirements have been achieved, making the site eligible for redevelopment
8m 45s reading time
PFAS Eliminated for 3.5 Years and Counting
This case study reviews a pilot test to remove PFAS risk via an in situ colloidal activated carbon barrier at Camp Grayling in Crawford County, Michigan, a large year-round military training center operated by the Michigan Army National Guard (MIARNG).
Colloidal activated carbon was selected because of the expected rapid reductions of PFAS by removal from the dissolved mobile phase, as well as its expected lower total project costs when compared to operating a mechanical system over a similar time. The MIARNG decided to conduct a PlumeStop pilot test to determine if this treatment would meet their site goals prior to a possible full-scale application. The goals for this pilot project were to utilize an approach that could both protect the Grayling community from exposure and cost-effectively expand to a full-scale application.

This case study features the following:
- Results 3.5 years post-application show PFAS and PCE reduced to non-detect
- New, innovative approach using an in situ colloidal activated carbon barrier to eliminate PFAS exposure pathway and protect the community
- Collaborative effort amongst various State of Michigan and military departments
- Economical and effective pilot study design
8m 59s reading time
PlumeStop Barrier Protects Drinking Water Supply Wells
This case study reviews a former chemical manufacturing facility in Texas where PlumeStop® Colloidal Activated Carbon was used in a permeable reactive barrier (PRB) to halt the movement of chlorinated solvents in groundwater. EA Engineering, Science, and Technology, Inc., PBC, a leading multi-disciplinary environmental and engineering consulting firm, contracted REGENESIS to implement the solution. PlumeStop was to be applied as part of an in situ bioremediation PRB near the distal end of the plume to promote sorption-enhanced natural attenuation of the contaminants.

Case study highlights:
- Innovative remedial approach addresses large PCE plume at a bedrock site under the CERCLA-Regulatory Framework
- Substrates successfully addressed contaminants in the Ogallala Sandstone
- PlumeStop PRB successfully cut off PCE and chlorinated solvent daughter products and prevented further movement downgradient toward private water supply wells
9m 46s reading time
PFAS Removal from Aquifer at Hazardous Site Where AFFF Was Used
This case study reviews an ongoing Pennsylvania Hazardous Site Cleanup Act (HSCA) project where aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF) extinguished a large fire in the 1980s was the target of an innovative pilot study to address per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
Working closely on behalf of the PADEP, Tetra Tech, a leading provider of consulting, engineering, and technical services worldwide, was principally involved in assessing the options and choosing a technology for the pilot test. This effort led to the decision to conduct a pilot study using PlumeStop®, a patented colloidal activated carbon amendment known to eliminate the risk of PFAS.

Case study highlights:
- Total PFOS and PFOA reduced from 91,400 to <50 ng/L in one month
- Injection testing effectively used for design confirmation in PlumeStop PFAS remediation pilot study
- Application included innovative injection using straddle packer system to isolate vertical zones
8m 46s reading time
Effectively Engineering Rapid Closure of UST Release Sites
This multi-site case study reviews eight underground storage tank (UST) sites where the leading global environmental consulting firm Antea® Group has closed the site or positioned it to be on-track for closure using PetroFix.
Antea Group is amongst the first environmental consulting companies to recognize and adopt PetroFix as a tool to rapidly reduce PHC impacts and achieve remedial objectives in groundwater. Applying PetroFix with economic efficiency, the company successfully advanced a portfolio of legacy UST release sites through the closure process over a short timeframe. In this effort, Antea Group sought and obtained approvals through multiple state regulatory agencies, self-completed the designs to determine dosing and injection layouts, implemented PetroFix treatments using different in situ application methods, and conducted performance monitoring to demonstrate remedial objective attainment.
Multi-site case study highlights:
- Case studies of eight UST sites closed or on-track for site closure using PetroFix, including contaminants treated, approach, remedial design and results
- Antea Group applied PetroFix using in situ application methods which included direct push injections through grid and barrier arrays and excavation emplacement
- Why Antea Group readily adopted a promising new remedial amendment for site closures
13m 45s reading time

PlumeStop and S-MicroZVI Application Paves The Way For Redevelopment
Case study highlights
This case study reviews a contaminated chlorinated solvent site in northern California, USA, where advanced design verification testing and predictive modeling methods were used to guide a remarkably successful in-situ remediation effort:
-
Highly successful remediation solution using colloidal technologies: PlumeStop and S-MicroZVI
-
Complete reduction of PCE, TCE and daughter products in the treatment areas
-
Flux-based predictive modeling used to optimise remediation to meet two-year timeline
-
Remedial objectives achieved allowed redevelopment of the property

Site Goals Met Within 60 Days
Case study highlights:
This case study reviews the confidential site of a large-scale in situ groundwater treatment of trichloroethene (TCE) at a former industrial manufacturing facility with challenging project objectives and an agressive remediation timeline.
-
TCE eliminated within 60 days post-application
-
This reduction has been continuously maintained more than 5 years to date.
-
The highly controlled PlumeStop injection resulted in no ‘day lighting’ or ‘surfacing’ inside the building.

A collaborative remedial design and strategic implementation effort between REGENESIS and the consulting firm resulted in the project’s success. This collaboration led to a dynamic remediation application strategy entailing planned, in-field adjustment to the design based on information obtained and assessed during remediation. An innovative remediation approach was needed to meet a very stringent deadline for the work’s completion. Through careful planning and scheduling, RRS met the implementation deadline, which included work inside an active warehouse and retail business.
TCE and low concentrations of other chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs), cis-1,2-dichloroethene, vinyl chloride, and 1,1,1-trichloroethane, were treated using an innovative sorption-enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach that virtually eliminated groundwater contaminants within 60 days of application. The permeable reactive barrier (PRB) installed at the site property boundary has eliminated TCE for over five years, meeting the application’s performance objectives by cutting off the site’s contribution to a more extensive groundwater TCE plume.
Over 8 Million Cubic Feet of Groundwater Treated In 13 Days
This case study reviews the site of a large-scale enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) treatment of chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) applied in a fractured bedrock aquifer at a voluntary remediation site in Pennsylvania. REGENESIS Remediation Services (RRS) began the application in May 2020 and completed it in less than 13 days, averaging nearly 7,000 gallons of fluid volume injected per day at this active facility. In total, more than 260,000 combined pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS) and Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI Plus) were injected for ERD treatment of the CVOCs. The extensive injection well network and large injection volume required RRS to develop an innovative injection process and containment design. Two 21,000-gallon frac tanks were delivered to the site to hold deoxygenated water used for mixing and to chase product injections. Mixing for the main high-flow system was performed in two large polyethylene tanks that were constantly recirculated to ensure a homogenous mixture.
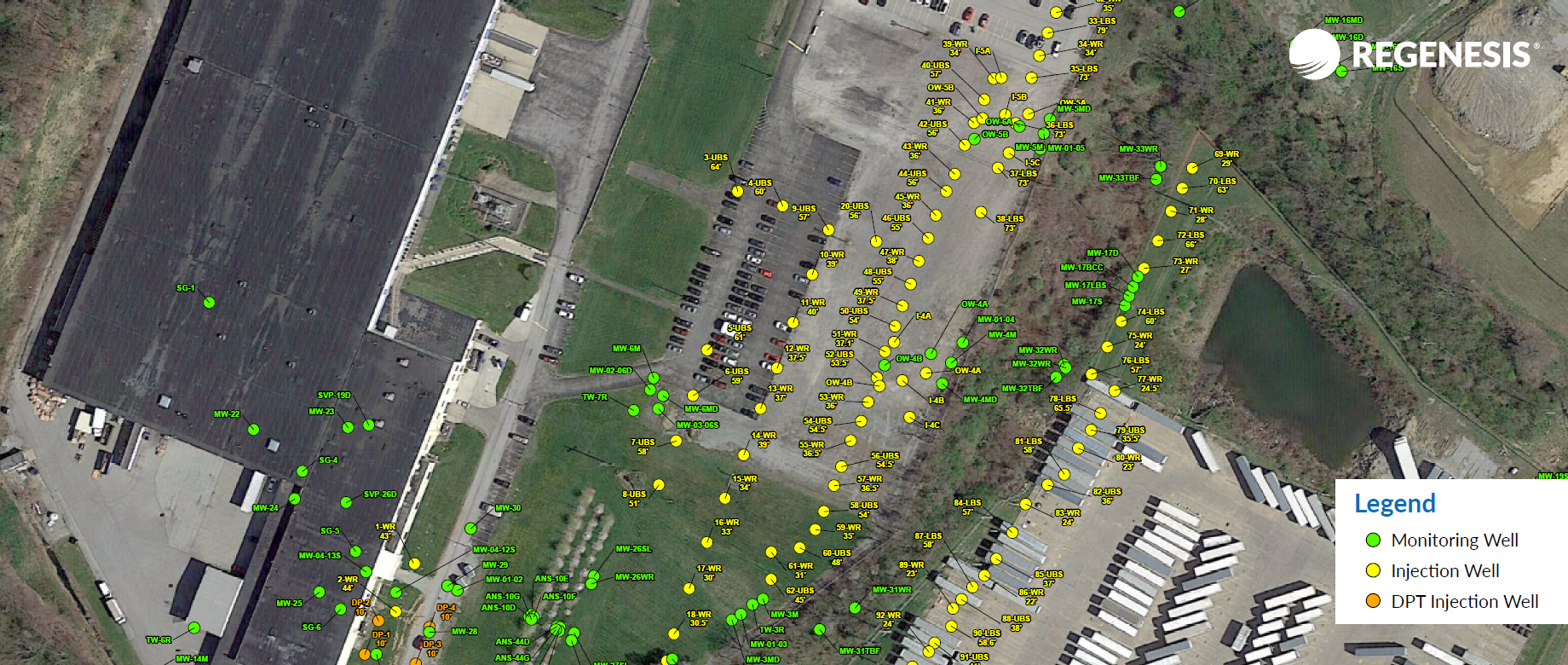
Case study highlights:
- 8 million cubic feet of CVOC impacted groundwater treated
- 88,000 gallons of ERD remedial amendments applied in less than 13 days using novel, innovative tooling and application approach
- The project was completed more than 40% faster than originally scheduled.
7m 30s reading time
PetroFix Pilot Study Leads To Successful Full-Scale Application
This case study reviews a full-scale PetroFix remediation program that was designed and implemented at seven locations to treat petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) following a successful field pilot test.
Two post-injection groundwater sampling events were completed in June and September 2019. In December 2019, a supplemental PetroFix injection was completed in the PHC source area onsite following the PersulfOx and ORC-A pretreatment step and groundwater equilibration. Additionally, a new treatment area was added where a small quantity of PetroFix was injected.

Case study highlights:
- Previous pilot testing results provided promising results leading to a full-scale application
- PetroFix is designed to remediate petroleum contamination completely at the lowest total cost to closure
- Site closure strategy included reducing groundwater concentrations, inhibiting plume migration, and demonstrating plume stability site-wide
7m 54s reading time

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español








