Over 8 Million Cubic Feet of Groundwater Treated In 13 Days
This case study reviews the site of a large-scale enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) treatment of chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) applied in a fractured bedrock aquifer at a voluntary remediation site in Pennsylvania. REGENESIS Remediation Services (RRS) began the application in May 2020 and completed it in less than 13 days, averaging nearly 7,000 gallons of fluid volume injected per day at this active facility. In total, more than 260,000 combined pounds of 3-D Microemulsion, Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS) and Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI Plus) were injected for ERD treatment of the CVOCs. The extensive injection well network and large injection volume required RRS to develop an innovative injection process and containment design. Two 21,000-gallon frac tanks were delivered to the site to hold deoxygenated water used for mixing and to chase product injections. Mixing for the main high-flow system was performed in two large polyethylene tanks that were constantly recirculated to ensure a homogenous mixture.
Case study highlights:
- 8 million cubic feet of CVOC impacted groundwater treated
- 88,000 gallons of ERD remedial amendments applied in less than 13 days using novel, innovative tooling and application approach
- The project was completed more than 40% faster than originally scheduled.
7m 30s reading time
Multiple Lines of Evidence Show CVOCs Degrading on PlumeStop, Leading Site to NFA Status
This case study reviews one of the original PlumeStop® pilot tests for in situ groundwater treatment of chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs or chlorinated solvents) at a former dry cleaner location in Marina, California. REGENESIS treated the CVOCs using a novel, sorption-enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach. This approach consisted of immediate sorption followed by the sequential elimination of chlorine from the CVOC molecules, transforming them into non-toxic end products such as ethene, carbon dioxide, and chloride.
Case study highlights:
- Combined remedy approach proves successful in treating chlorinated solvents at former dry cleaner
- This site provided ideal challenge conditions to demonstrate complete biodegradation using a sorption-ERD approach
- The site was granted NFA status in June 2019 as a result of this pilot study
9m 31s reading time

PlumeStop Treatment of Chlorinated Solvents in a Bedrock
Successful pilot study uses colloidal activated carbon to protect
nearby surface waters, United Kingdom
Introduction
REGENESIS was asked to provide a remediation solution for a Trichloroethylene (TCE) plume in the UK. We worked closely with Golder to design and implement a novel solution that combined Plumestop, HRC and BDI+ to sorb and biologically degrade the contamination, rapidly and effectively reducing contamination downstream to nondetectable
levels.
Case Study Highlights
This pilot study shows that treatment of chlorinated solvent plumes is possible using PlumeStop even with challenging conditions such as a: co-mingled plume, fractured bedrock setting, and a highly variable hydraulic conductivity.
The PlumeStop in situ permeable reactive barrier rapidly reduced downgradient contaminant concentrations and maintained these through a combination of sorption and biological degradation,protecting the adjacent surface water receptor.
3m 50s reading time

PlumeStop Arrests PCE in Fast Moving Aquifer
This case study reviews a former dry-cleaning site in Martinsville, Indiana that had a perchloroethylene (PCE) release which contaminated the community’s groundwater with concentrations in excess of 370 parts per billion (ppb). The sand and gravel aquifer created a challenging problem due to the high flow regime, with a groundwater velocity of approximately 1,560 ft/year and oxygenated geochemistry which had limited natural attenuation. After a thorough evaluation of possible technologies, environmental consulting firm Wilcox Environmental Engineering determined that PlumeStop® Liquid Activated Carbon™ in combination with HRC® and BDI Plus® could prevent the plume from migrating and would work in the well-oxygenated, sand and gravel lithology.

Case study highlights:
- PlumeStop effectively treated the plume in the well-oxygenated, sand and gravel lithology
- 99% reduction of PCE ~30 days after the application in key monitoring wells
- Demonstration of PRB leading to full-scale treatment in Spring 2020
6m 44s reading time
Global Retailer Enters Into Elective Site Cleanup Agreement and Achieves NFA
This case study reviews the site of a global retailer based in Arkansas, where historic offsite dry cleaning operations caused tetrachloroethylene (PCE) contamination in the groundwater. A previous bioremediation attempt successfully remediated a majority of the site but one persistent well remained. After time passed with little change to the B-45 well, ESGI sought out a bioremediation strategy that would work quickly with long term success. ESGI partnered with REGENESIS to design a bioremediation plan that would apply PlumeStop®, Liquid activated Carbon, Hyrdogren Release Compound® (HRC) and Bio-Dechlor Inoculum® (BDI Plus) to eliminate the remaining contaminants of concern (COCs). After the applications of PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI Plus, all COCs were below the acceptable threshold levels, and as a result the site achieved No Further Action (NFA) in January of 2020.

Case study highlights:
- PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI Plus successfully remediated persistent PCE, VC, and Cis-1,2-DCE contamination.
- Environmental services firm ESGI and REGENESIS adapted the injection design according to the difficult site geology and weather conditions.
- After one round of injections, successful results led to the site achieving NFA.
6m 3s reading time
Combined Amendment Approach Treats Chlorinated Solvents
This case study reviews a formerly undeveloped site in downtown Jacksonville that was impacted with chlorinated solvents in the groundwater and metal-impacted soils. To treat the chlorinated solvent groundwater plume, Terracon selected multiple technologies from REGENESIS, including PlumeStop, zero-valent iron (ZVI), Bio-Dechlor Inoculum Plus (BDI Plus), and Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC). The site required remediation prior to moving forward with development. Ryan Companies US, Inc. (Ryan) was under contract to purchase the property from the site owner and was seeking an expedited closure of the site prior to completion of construction. Ryan plans to develop the site with a nine-story office building and an associated nine-level parking deck. Site rehabilitation through remediation and regulatory closure is being sought through Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) voluntary cleanup. Environmental engineering and consulting firm Terracon evaluated a variety of remedial technologies as well as existing site conditions to determine the most appropriate application for the site.

Case study highlights:
- Combined remedy approach ensured effective remediation.
- FDEP Voluntary Cleanup program provided tax credits making the remediation and redevelopment possible.
- Remediation allowed the undeveloped block to be developed into a nine-story office building in a growing area of downtown Jacksonville.
6m 39s reading time
Combined approach to remediate chlorinated solvents in Cambridge, UK
In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR), Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) and bioaugmentation used on active construction site to allow redevelopment to be completed
Summary
 This site is currently undergoing redevelopment from a former industrial estate and trade park, into a business park. The underlying groundwater is impacted with chlorinated solvents from an adjacent industrial site. REGENESIS provided an in situ approach that could provide full reductive dechlorination of the contamination from a single injection, allowing redevelopment to occur during the remediation period.
This site is currently undergoing redevelopment from a former industrial estate and trade park, into a business park. The underlying groundwater is impacted with chlorinated solvents from an adjacent industrial site. REGENESIS provided an in situ approach that could provide full reductive dechlorination of the contamination from a single injection, allowing redevelopment to occur during the remediation period.
1m reading time
Application
It was decided that a combination of In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR) using Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS) and Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) using 3-D Microemulsion (3DME) as well as bioaugmentation with Bio-Dechlor Inoculum Plus (BDI+) would be applied at this site. This combined approach was designed to provide rapid contaminant degradation, minimised daughter product creation and long term treatment from the single injection. The treatment used seven direct push injection points to accurately target the contamination in a heterogeneous gravels, sands and clay.
What’s Special?
- The ISCR, bioaugmentation and biostimulation approach was used to optimise the remedial approach by combining:
- Wide radii of influence to minimise the number of injection points required
- Rapid onset of ERD
- Minimisation of daughter product creation
- Long-term treatment from a single application
- The application took only one day, with remediation occurring in situ, allowing the site development to continue unimpeded.
Real Estate Transaction Requires Fast-Acting Treatment of PCE Contamination
 This case study reviews a multi-tenant commercial plaza in the greater Boston area that required remediation of tetrachloroethylene (PCE) contamination in groundwater where a combined remedy approach used at delivered accelerated results using PlumeStop®, BDI Plus® and HRC®.
This case study reviews a multi-tenant commercial plaza in the greater Boston area that required remediation of tetrachloroethylene (PCE) contamination in groundwater where a combined remedy approach used at delivered accelerated results using PlumeStop®, BDI Plus® and HRC®.
Due to the owner’s objective to sell their property, a multi-tenant commercial plaza in the greater Boston area required remediation of tetrachloroethylene (PCE) contamination in groundwater associated with historical operations. Because contamination had been identified during due diligence, it was very important to implement a time-effective remediation strategy with minimal disruption to the various operating businesses. Wilcox & Barton, Inc. chose a combined remedial approach to treat the PCE contamination. This included liquid activated carbon (PlumeStop), an enriched, microbial consortium (BDI Plus), and an engineered, hydrogen release compound (HRC).
This case study highlights:
- Due to the high-traffic and operational hours at this site, injections were performed from 10pm-7am in January.
- The speed in which Wilcox & Barton, Inc. addressed the contaminants was crucial for the site owners to achieve their goal of marketing the property for sale.
- Site engineers innovatively included heating systems, additional lighting, and warming facilities to ensure that the remedial agents stayed in their liquid form and to provide necessary amenities to the injection specialists.
- The combined remedy approach of PlumeStop, BDI Plus, and HRC was selected amongst other remediation strategies for its fast-acting capabilities and its effectiveness in completely dechlorinating contaminants.
6m 33s reading time
Former Taxi Maintenance Site Successfully Treated with Enhance d Anaerobic Biodegradation and Bioaugmentation
Project Highlights
- Combined introduction of HRC® hydrogen release compounds and BDI Plus® bioaugmentation cultures resulted in reduction in chlorinated solvent concentrations, meeting site goals
- Successful remediation permitted redevelopment of the site into an elementary school
Project Summary
A former taxi maintenence facility located in Los Angeles, California was used as a garage and maintenance facility containing seven underground storage tanks (USTs), four hydraulic hoists, an elevator, a clarifier, and a spray paint booth. Environmental assessment related to the planned redevelopment of the garage and nearby commercial properties and residences revealed contamination of the soil and groundwater beneath the site with trichloroethene (TCE) and 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE) due to release from the former USTs and paint shop areas.
Under the jurisdiction of the California Department of Toxic Substance Control, an enhanced anaerobic biodegradation approach in conjunction with bioaugmentation was developed to remediate the chlorinated solvent contamination. This approach combined the introduction of the dechlorinating microcosm BDI Plus® with the application of supporting hydrogen release compounds 3-D Microemulsion® and HRC Primer®. Following treatment of the site, reduction in TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations have been observed after four quarters of postremediation monitoring. Microbial data supports the benefits of the bioaugmentation effort by showing a steep increase in dehalococcoides populations, which increased by nearly four orders of magnitude. In addition, all geochemical parameters are in range for a reductive state.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel three-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry, and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
HRC Primer is derivative of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound product and is designed to provide a controlled but fast release of hydrogen to assist in initiating anaerobic biodegradation.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus (BDI Plus) is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Results
Reduction of TCE and 1,2-DCE concentrations by enhanced anaerobic biodegradation and bioaugmentation facilitated the redevelopment of a former taxi garage and maintenance facility. Following a reduction in contaminant concentrations, the site was redeveloped to an elementary school.
45s reading time
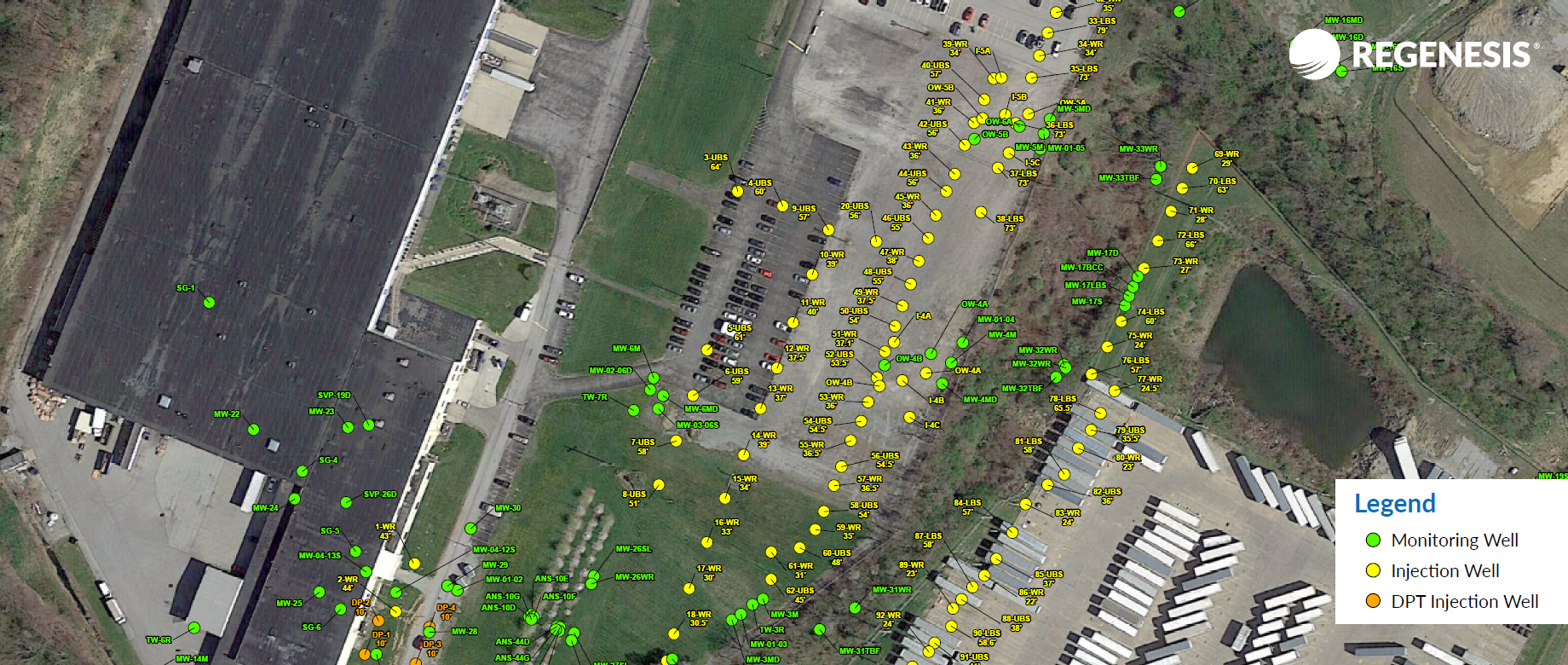
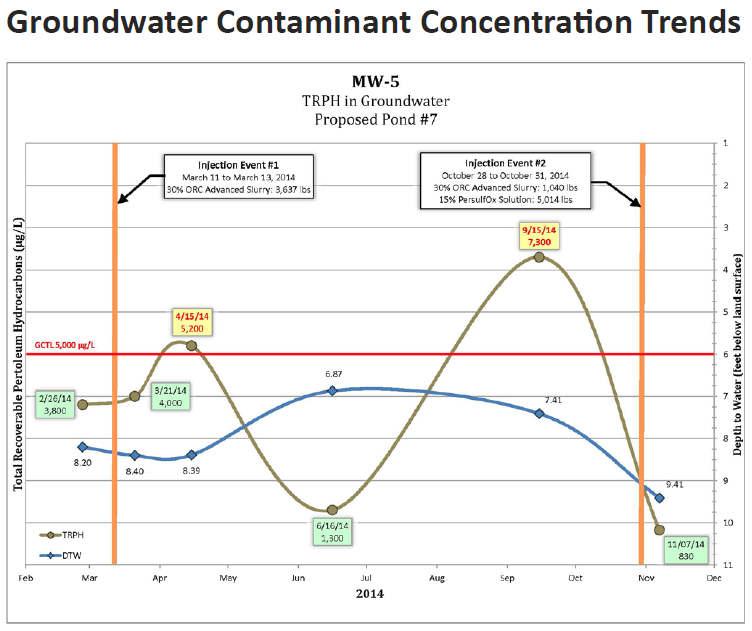
Historic Site On Track To Reach Remediation Goals
 This case study reviews a site in the Ohio River Valley where historic industrial operations over the last 100 years at a manufacturing facility have resulted in PCE and TCE impacts to 7,500 square feet of shallow groundwater. To move the redevelopment of this site forward, groundwater VOC sample results must meet the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for four consecutive quarters. Download the case study to learn about the combined remedy using PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI+ to address the contaminants.
This case study reviews a site in the Ohio River Valley where historic industrial operations over the last 100 years at a manufacturing facility have resulted in PCE and TCE impacts to 7,500 square feet of shallow groundwater. To move the redevelopment of this site forward, groundwater VOC sample results must meet the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for four consecutive quarters. Download the case study to learn about the combined remedy using PlumeStop, HRC, and BDI+ to address the contaminants.
This case study features the following:
- Creative combined remedy approach addressed accumulated contaminants from over 100 years of manufacturing operations
- Innovative application approach using 1.5” diameter wells effectively accommodated low ceiling and tight spaces, allowing for successful reagent injection
- 180 days post-injection, all VOCs were measured at greatly reduced concentrations and geochemical conditions remain ideal for biodegradatio
2m 40s reading time

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español














