New Jersey Manufacturing Facility Achieves Non-Detect with PersulfOx® Application where Pump and Treat Solution Failed
Project Highlights
- Replacing a costly pump and treat solution, REGENESIS® was able to efficiently inject PersulfOx® into bedrock, saving time and money
- Maximum 580 μg/L levels of 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane within the source area reduced to non-detect
- Low-level concentrations of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area also reduced to non-detect

Project Summary
A former manufacturing facility in New Jersey was contaminated with 1,1-dichloroethylene (1,1-DCE) and 1,4-dioxane in a fractured bedrock aquifer. The previous treatment approach utilized a pump and treat method that was successful at containing and reducing contaminant concentrations within the source area, but the associated off-site transportation and disposal of recovery water was expensive.
Historic concentrations for 1,1-DCE within the source area ranged from 43-580 μg/L, and concentrations outside of the immediate source area persisted at low levels above Ground Water Quality Standards. 1,4- dioxane concentrations within the source area peaked at 580 μg/L.
PersulfOx in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was selected as a lower-cost alternative to the pump and treat method and also as a way to address the diffuse contamination surrounding the immediate treatment area. After application of PersulfOx, both 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane concentrations within the source area rapidly decreased below detection levels and remained non-detect. In addition, the low levels of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area were also reduced to non-detect. Quarterly groundwater sampling will continue to track treatment performance.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology that destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst that activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Results
Application of PersulfOx resulted in the rapid reduction of source area 1,1-DCE and 1,4-dioxane concentrations to below detection limits. Low concentrations of 1,1-DCE surrounding the original treatment area were also reduced to non-detect. The concentrations of contaminants in both areas have remained below groundwater quality standards, meeting site requirements.
Open Excavation Treatment at Former NJ Service Station
RegenOx® and ORC® Advanced Pellets Remediate Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination
Project Highlights
- Former service station contaminated with BTEX levels measuring 11 ppm in groundwater and soil impacts removed through excavation
- Combined remedy to treat the open excavation with both in situ chemical oxidation and enhanced aerobic bioremediation technologies
- RegenOx and ORC Advanced Pellets technologies are compatible/non-corrosive with underground infrastructure and utilities infrastructure in the subsurface

Project Summary
A former service station in New Jersey was contaminated with high levels of BTEX (measuring 11 ppm in groundwater pre-treatment). Due to significant amounts of contaminated soil mass remaining at the former service station, an excavation was proposed by the environmental consultant. RegenOx and ORC Advanced Pellets were applied to the open excavation to chemically oxidize remaining saturated impacts and to promote enhanced aerobic biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in the dissolved phase. Both of these technologies utilize alkaline chemistry (pH > 8), which is non-corrosive to nearby public utilities and the underground infrastructure at the service station.
Remediation Approach
RegenOx and ORC Advanced were co-applied into an open excavation at the former service station site. The excavation extended approximately four feet into the saturated zone. Because the excavation was limited by physical constraints, RegenOx, a chemical oxidant, was applied to the base of the excavation to oxidize and desorb residual petroleum mass from the soil. ORC Advanced Pellets were co-applied to provide a slow release of oxygen (up to 12 months longevity) that promotes enhanced aerobic biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. In total, 2,000 pounds of RegenOx and 882 pounds of ORC Advanced Pellets were co-applied to the 2,600 square foot excavation area.
Technology Description
The advanced formulation of the Oxygen Release Compound (ORC Advanced) is a proprietary formulation of food-grade, calcium oxy-hydroxide that produces a controlled-release of molecular oxygen for periods of up to 12 months upon hydration. The pelletized form of ORC Advanced were designed to improve safety and handling for excavation applications.
RegenOx is an advanced chemical oxidation technology that destroys contaminants through powerful, yet controlled direct oxidation and free-radical reactions. This product maximizes in situ performance through the use of a solid alkaline oxidant (a sodium percarbonate complex) and a multi-part catalyst. These oxidation reactions do not inhibit natural bacterial populations and are compatible with biological treatment methods.
Bedrock Treatment Remediates NJ Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- 3-D Microemulsion injections created 30-foot ROI in fractured bedrock
- TCE concentrations reduced through reductive dechlorination and daughter products reduced to ethene within 12-month study
- Pilot study results allowed for: full-scale design, maximized product ROI, minimized bedrock injection well drilling, and resulted in reduced overall project costs
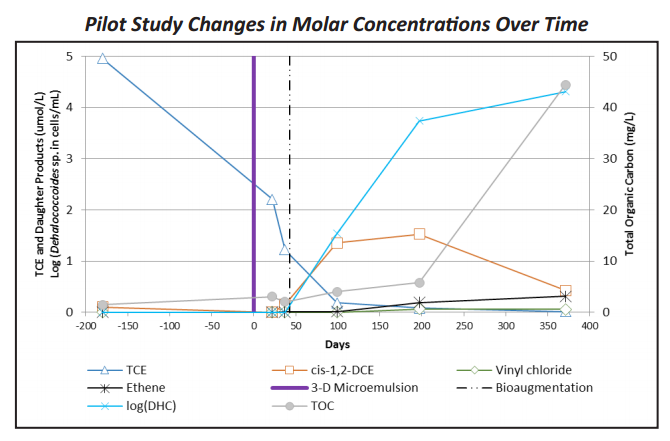
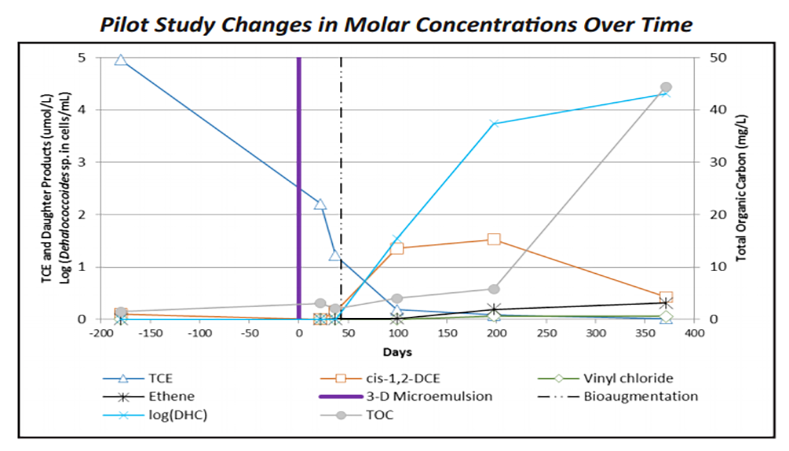
Project Summary
Previous manufacturing activities impacted a fractured bedrock aquifer with TCE. The plume migrated approximately 600 feet downgradient along fractures at 70-80 feet (shallow) and 105-115 feet (intermediate) below ground surface. Remediation at the site was planned as a phased approach including a source area pilot evaluation of enhanced reductive dechlorination, bioaugmentation, and radius of influence (ROI). A larger source area treatment and property boundary barrier was to be determined based upon the pilot study results.
The pilot study found that injection of 3-D Microemulsion was capable of initially influencing a 30-40 feet ROI based on visual (turbidity) and geochemical data. Over a 12-month period, TOC levels remained elevated at concentrations above 10 mg/L at a shallow well 20-feet away. At the two intermediate wells 40-feet away, TOC concentrations increased to >40 mg/L during this period. During this same pilot study period, TCE concentrations decreased, cis-1,2-DCE concentrations increased then attenuated, and VC and ethane concentrations increased. Bioaugmentation, occurring 6 weeks after the 3-D Microemulsion injection resulted in Dehalococcoides sp. populations that increased and sustained at elevated concentrations (104 cells/mL).
Remediation Approach
Injections of 3-D Microemulsion were introduced by packer into 2 injection wells across four 10-foot fracture intervals (60-115 feet bgs). Monitoring was conducted in two shallow bedrock wells at 70-80 feet bgs and two intermediate bedrock wells at 105-115 feet bgs. ROI monitoring was conducted at these four monitoring wells that were located 20 feet, 40 feet, and 55 feet away from the injection wells. Bioaugmentation was performed 6 weeks after 3-D Microemulsion injections. Full-scale treatment is planned, which will include a larger treatment in the source area and a downgradient barrier at the property boundary.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor technology that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile pHneutral chemistry, and unique subsurface distribution properties.
PersulfOx® Rapidly Treats TBA Contamination
Project Summary
Site operations at this manufacturing facility located in New Jersey caused groundwater to be impacted with tert-butyl alcohol (TBA). Previous attempts at site remediation using alkaline activated persulfate had not met performance goals. PersulfOx was subsequently applied in an area of significant TBA contamination resulting in orders of magnitude reductions within just three weeks’ time.
Alkaline Activated Persulfate – Unsuccessful
An initial attempt at remediation using alkaline activated persulfate included a full-scale injection of persulfate and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This approach was deemed unsuccessful, as sampling after one week showed pH to be below the range required for persulfate activation, leaving significant untreated TBA in site groundwater. Additionally, the large volume of NaOH required for this approach raised concerns of impacting nearby storm sewers.
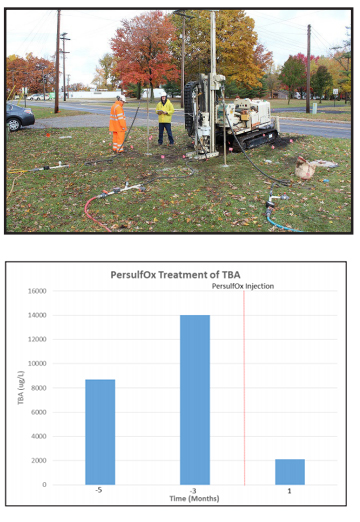
Remediation Approach
The treatment approach included a grid of six injection points placed 15-feet apart into the sandy aquifer. Each point received >1,800 pounds of PersulfOx across of 5-foot thickness.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
Results
Following the PersulfOx application, site monitoring indicated a significant reduction in TBA contamination in the target zone. TBA concentrations were reduced from >14,000 ug/L to 2,100 ug/L with a single injection of PersulfOx in only three weeks’ time.
Regenesis Remediation Services™ – PCE Treated with RegenOx®
Soil Mixing Using In Situ Chemical Oxidation Reduces Contamination Concentrations at Former Dry Cleaning Facility
Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) was hired for this large-scale soil mixing project to treat tetrachloroethylene (PCE) in shallow surface soils. The application used in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) technology to oxidize residual chlorinated solvents at this former dry cleaner site. The goal was to reduce chlorinated volatile organic compounds (cVOCs), particularly PCE, from >20 ppm to less than 5 ppb. The design of the project was divided into a grid with twelve sections, each 25 feet (ft.) by 21.5 ft., and 5 ft. deep.

Using RegenOx® remediation chemistry and an excavator to complete the soil mixing, the impacted soils were removed by an excavator and a proportional amount of RegenOx was evenly dispersed throughout the excavated soil, then thoroughly mixed using the excavator.
Once mixing was complete, the soils were placed back into the treatment cell while being hydrated with a RegenOx solution made up of RegenOx, water and hydrogen peroxide. By optimizing the contact between the soil, contaminants, and RegenOx, powerful desorption effects strip PCE off of the soil matrix and onto the RegenOx catalytic surface. This catalytic surface contributes to localized free-radical generation, leading to focused and efficient contaminant destruction via soil mixing. After eight days of the completion of the project, 98-100% reductions were achieved in the twelve sections of the grid.
RegenOx Treats #2 Fuel Oil Plume Beneath Residential Home
CASE SUMMARY
Home Heating Oil, New Jersey
A 550-gallon leaking underground storage tank (UST) containing #2 fuel oil was removed from a single family residence in New Jersey (Figure 1). In addition, the surrounding soil was excavated and sampling was performed to determine the extent of the petroleum hydrocarbon plume within soil and groundwater. The plume was delineated at approximately 1,800 ft2 with
concentrations of total petroleum hydrocarbons as high as 40,000 parts per million (ppm) in soil and approximately 40,000 parts per billion (ppb) in groundwater. An estimated 20% of the plume was determined to be located beneath the home itself, eliminating the option for extensive soil excavation. Other remedial strategies such as pump & treat, monitored natural attenuation, and enhanced fluid recovery were ruled out as they did not provide a timely, cost-effective solution.

Figure 1. Residential Site
- Soil Type: Fine to Medium Sands
- Treatment Thickness: 5 to 12 feet bgs
- Free Product: 1” to 3” observed
- Contaminants of Concern:
- TPH – Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons
- TVOC – Total Volatile Organic Carbon
- TSVOC – Total Semi-Volatile Organic Carbon
| Contaminant | Concentration |
| TPH – soil | 40,000 ppm |
| TVOC – gw | 7,900 ppb |
| TSVOC – gw | 40,000 ppb |
REMEDIATION TECHNOLOGY
In Situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) using RegenOxTM was chosen as the most appropriate technology to treat the soil and groundwater plume. In addition, an application of a slow-release oxygen compound, ORC Advanced®, was applied following RegenOx to stimulate aerobic biodegradation of any residual contaminants. RegenOx was applied based on the following:
- Least disruptive to the homeowner
- Successful track record
- Feasible site conditions – sandy soils and a shallow water table paired well with direct-push injection
- Low natural organic carbon in saturated zone
- Safe to use and easy to apply

Ten permanent injection points were installed around the source area, at the edge of the plume and beneath the house in the crawl space as seen in Figure 2. During the installation, free phase product was observed in monitoring wells at approximately 1 to 3 inches. The NJDEP’s Permit-by- Rule prohibited the injection of any remediation technology should free product be present. Once the removal was complete, RegenOx could be applied as designed.
CONTAMINANT PLUME TREATMENT
Free Product Removal
The free product was removed using a mild surfactant and a high powered vacuum extraction truck within the source area. This process also effectively distributed the surfactant across the impacted zone for further desorption of contaminants from the soil matrix. Three free product recovery events were performed which effectively removed all free product from the wells and surrounding areas. TVOC concentrations in groundwater dropped only slightly as a result of the free product removal. However, concentrations of TSVOCs more than doubled in groundwater as a result of desorption from soil.
ISCO Injection for TPH Reduction
The application design included two RegenOx injection events and a third combined RegenOx and ORC Advanced injection for on-going biostimulation to treat residual contaminants. Using temporary and permanent injection points, a total of 6,210 pounds of RegenOx was applied from 5 to 11 feet bgs. The third injection included 650 pounds of ORC Advanced.


Conclusion
No free product, sheen or film was observed after the injections were completed (Figure 5). Levels of dissolved oxygen 30 days following the final application were measured at approximately 10-20 ppm indicating the presence of ORC Advanced in the subsurface.
Within 6 months, significant reductions in petroleum hydrocarbons were observed. TVOCs declined from 7,900 to <50 ppb and TSVOCs were reduced from 40,000 to <150 ppb. Further Action status from the NJDEP. The site is currently seeking No Further Action status from the NJDEP.


 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español