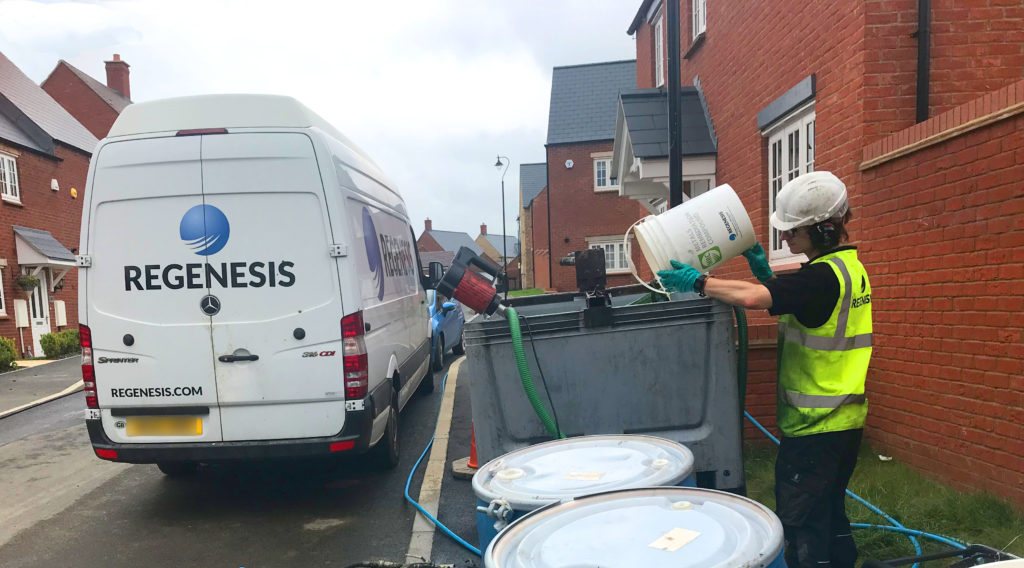
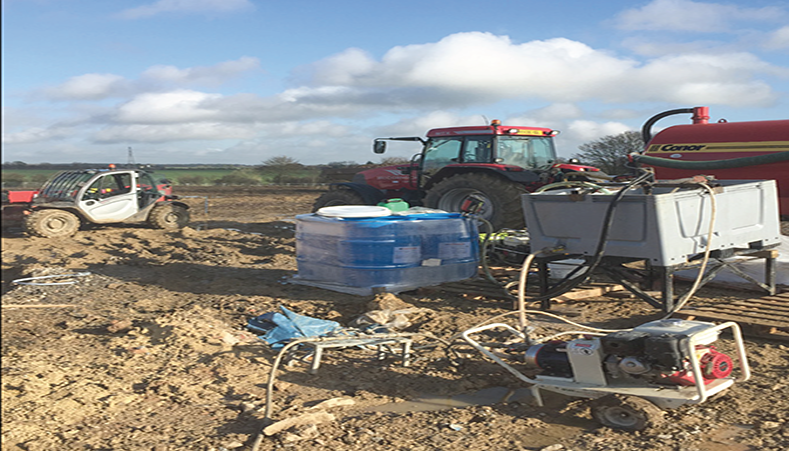
Treatment of Cr(VI) and CHC Groundwater Contamination under a Residential Development
In situ remediation of hexavalent chromium (VI) and chlorinated solvents using combined anaerobic biodegradation and immobilisation in Northampton, UK
Background

On the site of a former chrome plating works, construction and inhabitation had begun on a new residential development. Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) and some chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds (CHCs) had been discovered in the groundwater beneath the development. It was determined by the environmental consultant that the Cr(VI) was driving a risk on the site. The housebuilder required rapid achievement of site targets in order to continue the development of the site.
Case Study Highlights
- REGENESIS provided an accurate and pragmatic design approach for the busy residential construction site
- Full-scale remediation was completed comprising a of a series of rows, totalling 78 injection points, to fit in between the residential properties and services
- A mixed plume of CHCs and Cr(VI) was treated concurrently using a combination of complementary substrates
- The works were completed rapidly with minimal disruption to the construction project and existing residents
- The use of barriers, targeting hotspots and pathways provided a cost-effective and efficient treatment of the plume
- Remediation Cost and Result Graph included
2m 40s reading time
Remediation Products Applied
A combination of ERD and in situ immobilisation using 3-D Microemulsion (3DME) and Metals Remediation Compound (MRC) has been used to primarily to treat the Cr(VI) contamination.
In Situ Treatment of Chrome(VI) Plume in Fast Flowing Aquifer, NW Italy
Summary
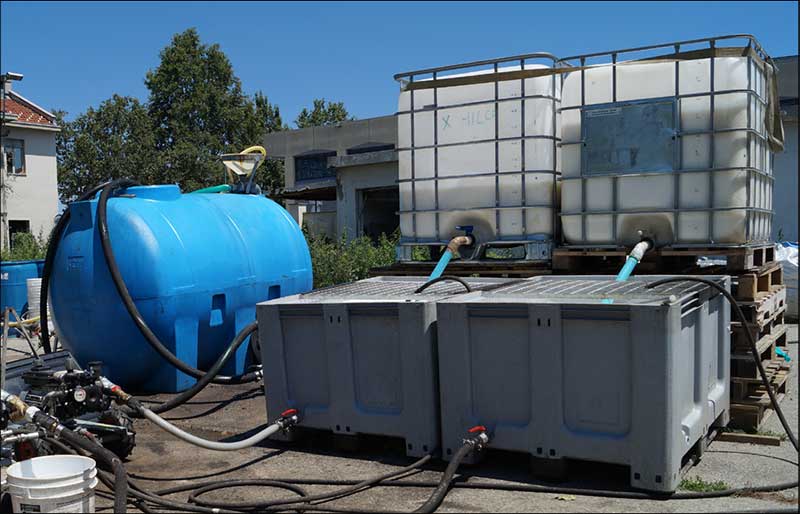 A former chemical manufacturing plant in northwest Italy was due for demolition to allow redevelopment into residential properties. Site investigations showed elevated concentrations of Cr(VI) in the groundwater, which were above the stringent National Standards of 5μg/L, requiring remedial works to be completed. The groundwater under the site is aerobic and fast-flowing, causing the contaminant plume to migrate beyond the site boundary. It was decided that an in situ approach was required to remediate the Cr(VI) prior to sale of the site.
A former chemical manufacturing plant in northwest Italy was due for demolition to allow redevelopment into residential properties. Site investigations showed elevated concentrations of Cr(VI) in the groundwater, which were above the stringent National Standards of 5μg/L, requiring remedial works to be completed. The groundwater under the site is aerobic and fast-flowing, causing the contaminant plume to migrate beyond the site boundary. It was decided that an in situ approach was required to remediate the Cr(VI) prior to sale of the site.
3m 28s reading time
Site plan showing treatment areas, injection wells (pink) and monitoring well (blue) locations
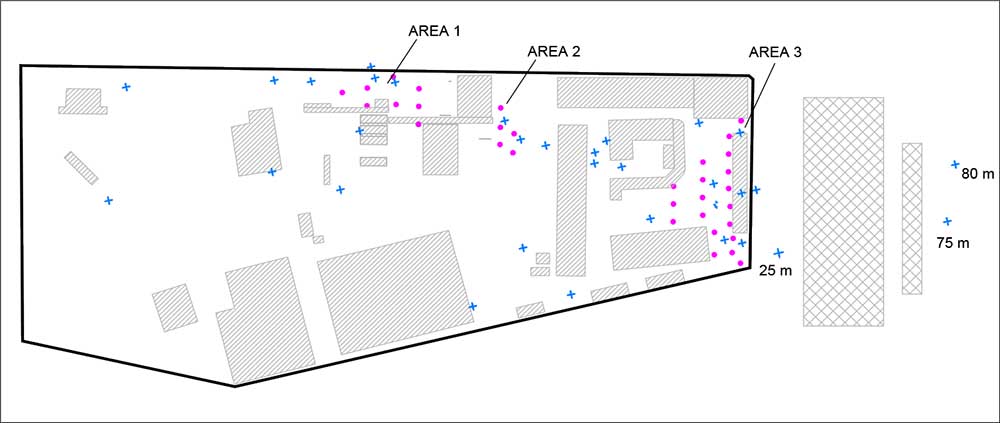
Remedial Approach
Two areas within the plume were identified as being above the site remediation target of 100μg/L. These were targeted with an injection of 3D Microemulsion (3DMe) and MRC in order to reduce the soluble Cr(VI) to non-toxic solid Cr(III) and stabilise it within the aquifer matrix.
The dose of MRC was tailored to match the vertical distribution of the contamination in order to provide the most accurate and cost effective treatment. 3DMe relies upon micellar transportation following injection in order to provide a wide radius of influence from each injection location. This was important on this deep site, in order to minimize the number of injection points required on the site.
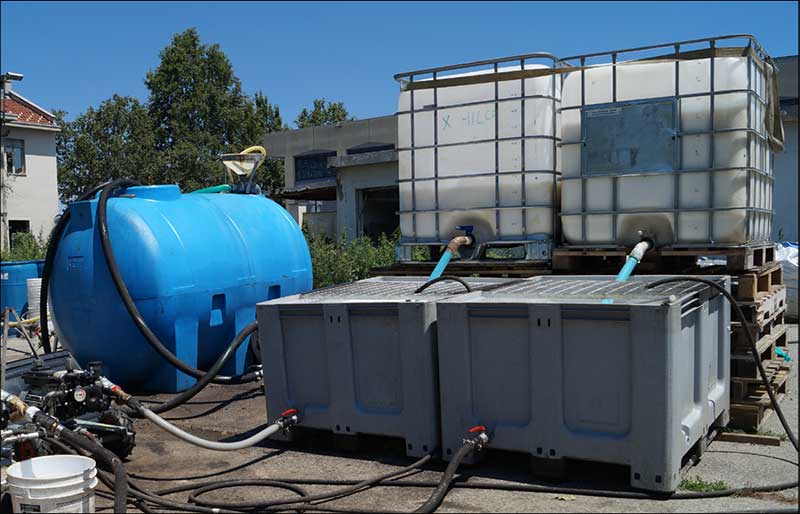
Fixed injection points were installed and a single application of the reagents was completed. The injectable substrates were combined at a central mixing location and then pumped into several injection points simultaneously. The process was repeated until the all of the target areas were treated.
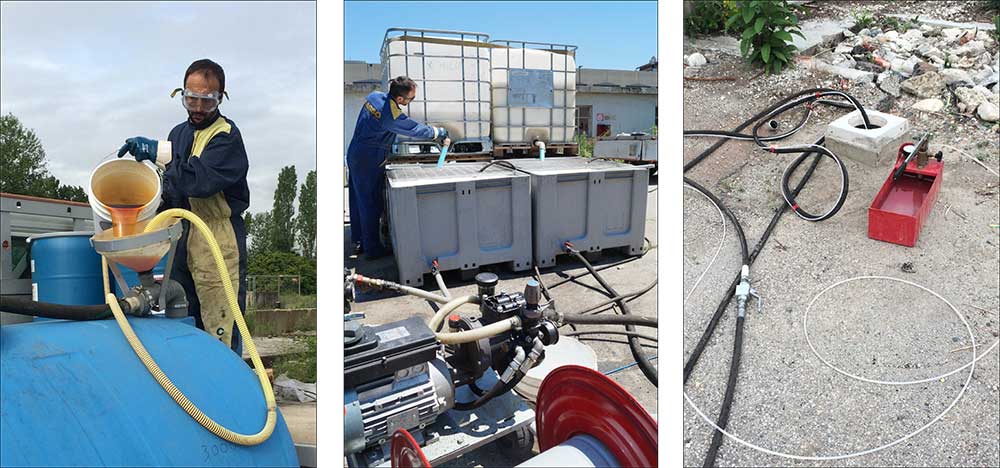

Reagent mixing and injection into fixed wells
3-D Microemulsion (3DMe)®
3DMe provides an immediate, mid-range and long-term, controlled release supply of hydrogen (electron donor) to rapidly create and then sustain anaerobic conditions. This will reduce the Cr(VI) to Cr(III), which will then settle out as a solid. Reversion to natural conditions following the 3DMe treatment (in perhaps five years or more) will not cause this process to reverse.
3DMe is also designed to distribute over very wide areas from each injection point. This is achieved through the molecule having hydrophilic and oliophilic properties hence upon mixing with water, 3DMe forms a microemulsion made of tiny micelles, which propagate through and coat the aquifer. This micelles are also able to transport MRC molecules within them, creating a wide and effective treatment zone, which is then sustained for many years.
Metals Remediation Compound (MRC)®
MRC is a controlled release remediation product designed specifically for the treatment of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) in groundwater. MRC’s active compound is an ester of cysteine (a sulfur-containing amino acid) on a carbon backbone molecule of glycerol and sorbitol. A cysteine-based product such as MRC is well suited for in situ Cr(VI) immobilisation, since it has a strong affinity for metal contaminants and does not alter the properties of the subsurface. The active compound in MRC (sorbitol hexacysteinate) is embedded in a polylactate matrix that provides a carbon source and electron donor for subsurface bacteria. This combination of materials makes MRC a viscous but injectable material that slowly releases the cysteine ester to a contaminated aquifer via hydrolysis by water or enzymatic action by microbes. MRC’s slow release property allows for a longevity of 12 to 18 months in an aquifer, allowing for an effective approach to metals immobilisation.
Chromium VI concentrations in groundwater before and after treatment.
Area 1 and 2 need to reach the site remediation target, Area 3 needs to reach CSC
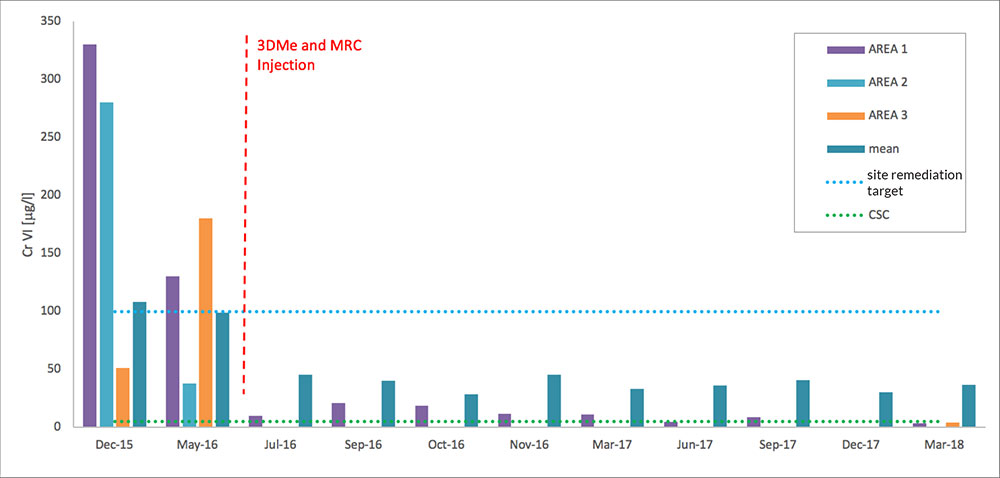
Results
Validation monitoring shows very good substrate distribution at all but one out of thirteen monitoring points. The reduction of the Oxidation- Reduction Potential (ORP) and dissolved oxygen with the simultaneous increase of the Total Organic Carbon (TOC), as well as an increase in iron and manganese, clearly showed the desired trend. The analytical results showed a rapid and significant reduction of CrVI targeting values often below the 5 μg/l limit, with a removal efficiency of 90% on average.
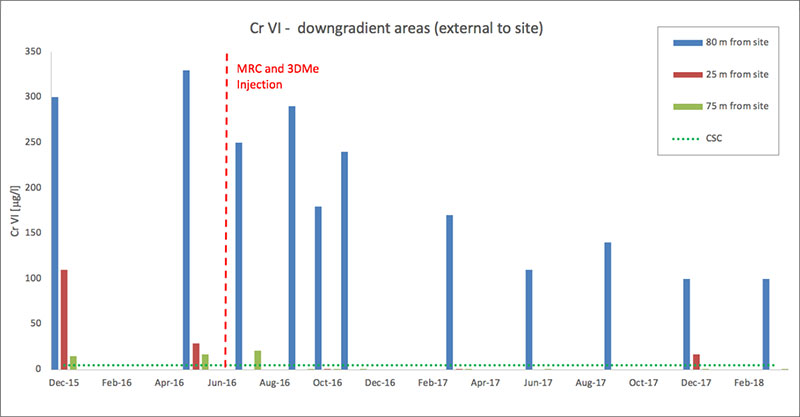
Downgradient Chromium VI concentrations at 25m (red), 75m (green) and 80m (blue) from the site
What’s Special?
- The ability of 3DMe to self-distribute over a wide radius of influence from each injection point allowed the injection grid to be widely spaced. This minimised the number of application wells, which, given the depth of the treatment, greatly reduced the remedial costs.
- Treatment of Cr(VI) was very rapid and sustained despite the aquifer being very aerobic and fast flowing.
- Even though the aquifer was very fast-flowing, the products have not suffered from wash-out and continue to successfully treat the target areas over an extended period of time.
- The seasonal variation in groundwater level at the site has the potential to mobilise contaminants into the groundwater during periods of high precipitation. The longevity of the reagents allows this contaminant influx to be addressed and avoid rebound.
- The injection technology selected saved money by avoiding the use of clustered-wells. The injection rate was high, saving time on site.
- The results of the remediation can be seen over 20m downgradient, through a significant reduction of Cr(VI) in offsite monitoring wells, providing rapid benefit to the environment on and off the site.
Treatment of a Diverse Range of Contaminants, Emilia Romagna, Italy
Treatment of a very low permeability geology with mixed contaminants at varying concentrations, using multiple application methods and a range of different REGENESIS products.Read More
In Situ Remediation at an Active Manufacturing Facility in Northern Italy
Historic leakages at an active manufacturing facility in Northern Italy resulted in the underlying groundwater becoming impacted with hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) contamination of up to 2,000 μg/L, and chlorinated solvents (CHC) concentrations of up to 10,000 μg/L. 3-D Microemulsion® (3DMe) and Metals Remediation Compound (MRC®) were selected to remediate the site because of:Read More
In Situ Hexavalent Chromium Remediation, Northern Italy
Saturated source reduction and hotspot treatment with MRC® and 3DMe®Read More
In Situ Treatment of Chromium on an Industrial Estate, Mansfield, UK
Source, plume and barrier treatment using Metals Remediation Compound (MRC) to protect off-site controlled watersRead More
Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium in Bedrock at Former Saw Mill
Bedrock chrome VI contamination treated to non-detect levels in 2 months, expediting regulatory sign-off and unlocking the site for redevelopmentRead More
Hexavalent Chromium Barrier Treatment Protects River
Summary
w_Reg_20916_MRC_8_inj-rig_UKOn an industrial estate in Ravensthorpe, West Yorkshire, a leak from a storage tank in a chrome-plating works, had resulted in contamination of the underlying groundwater. The contamination was found to be migrating off-site, under neighbouring properties, towards a nearby river. Regenesis was employed to design and install a barrier to protect the river for a guaranteed 12 months in order to allow the building to be cleared of other tenants prior to demolition and source removal.
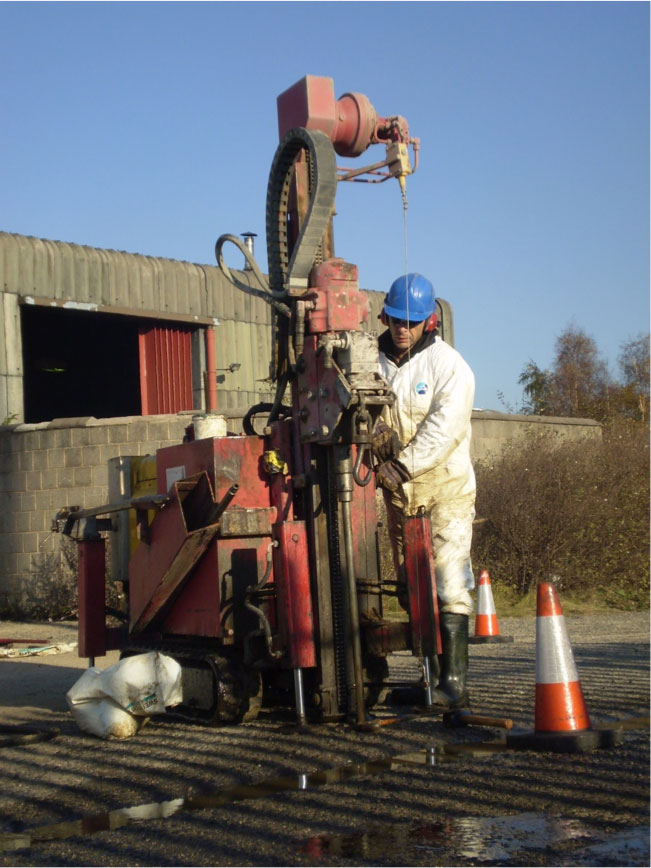

Design & Application
Metals Remediation Compound (MRC) was used to immobilise the contamination by reducing soluble hexavalent chromium into solid, non-hazardous trivalent chromium, which settled out of the groundwater. The MRC was injected in an ‘L’ shaped barrier through the apron and road outside of the industrial unit. The corner of the ‘L’ consisted of three rows of direct push injection locations, in order to provide a wide treatment zone where maximum contaminant influx would occur. The MRC was applied using direct push injection in gravels, from the top of the groundwater at 5 m BGL to 12 m BGL (rock-head).
What’s Special?
- Within weeks of application, the barrier prevented the movement of hexavalent chromium contamination towards the river. Concentrations of 10,000 μg/L Cr(VI) were reduced by >98% to <200 μg/L 5m downgradient of the barrier and non-detect at the river.
- Regenesis provided a warranty on the barrier for a period of 12 months after the application, however the MRC barrier would remain effective between 2 to 3 years.
- The controlled-release mechanism of MRC meant that offsite receptors were protected for an extended period from a single, low-cost injection.
Hexavalent Chromium Remediation at Former Saw Mill
Summary
REGENESIS were retained to carry out the remediation design and site application works to treat groundwater impacted with hexavalent chromium (Cr VI) on the site of a former saw mill in the United Kingdom, Europe. Metals Remediation Compound® (MRC) and 3-D Microemulsion® (3DMe) were applied into the groundwater to provide rapid reduction and immobilisation of the CrVI present. Groundwater samples collected 2 months after application were analysed for CrVI , returning non-detect results.

Treatment
Due to the ground conditions of weathered limestone, treatment was carried out via pre-installed treatment wells at 5 m spacing in the source area and 6 m in the barrier. MRC and 3DMe were co-applied into these wells to target the source area of contamination and to install a reactive barrier at the down-gradient edge of the site to protect a nearby watercourse. MRC and 3DMe provide a powerful combination of wide distribution and strong reducing and immobilising properties.
What’s Special?
- REGENESIS’ injection team completed the site works ahead of schedule to allow the groundwork contractor to prepare the site for housing development.
- The use of MRC and 3DMe allowed for wide spacing of the injection wells and therefore lower drilling costs.
- The treatment approach achieved rapid reductions from up to 15,000 μg/L of Cr(VI) to non-detect within two months, expediting regulatory sign-off and unlocking the site for redevelopment
Technology Descriptions
Metals Remediation Compound (MRC) removes metals such as dissolved Cr(VI) from groundwater via in situ immobilisation (precipitation and/or sorption to soil particles).
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product..

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español











