PCE Treated at Active Dry Cleaner in Less Than 200 Days
Project Receives “No Further Action” Letter Following Combined Application of 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus
Project Highlights
- Enhanced reductive dechlorination used to treat PCE contamination under an active dry cleaning facility
- Total cVOC concentrations reduced by three orders of magnitude in less than 200 days
- Total cVOC concentrations were below remediation goal

Project Summary
Groundwater below a Missouri dry cleaning facility was contaminated from a cleaning solvent spill, resulting in PCE concentrations >4,000 μg/L. An enhanced reductive dechlorination approach was developed that integrated biodegradation and bioaugmentation via application of a controlled-release electron donor and a microbial consortium of dechlorinating bacteria.
REGENESIS® Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to co-apply 3-D Microemulsion® and Bio-Dechlor Inoculum® Plus to the affected groundwater. The products were applied to the affected groundwater underneath the building via direct-push injections.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion factory emulsified is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Results
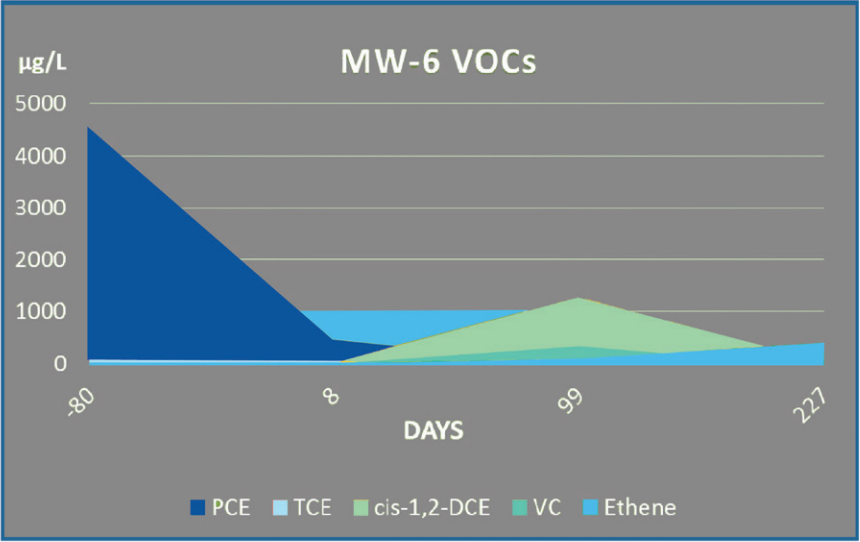
Following treatment, total cVOC were reduced by 99.9%. Concentrations were reduced by three orders of magnitude from a baseline concentration of >4,000 μg/L to <10 μg/L in less than 200 days.
Furthermore, monitoring data indicated complete dechlorination with no remaining daughter products above the remediation goals. As a result of the rapid and complete reduction of chlorinated solvents, the project received a “No Further Action” letter (NFA) through the Missouri Department of Natural Resources.
| Download the PDF |
Project Receives “No Further Action” Letter Following Combined Application of 3-D Microemulsion® and BDI® Plus
Project Highlights
- Enhanced reductive dechlorination used to treat PCE contamination under an active dry cleaning facility
- Total cVOC concentrations reduced by three orders of magnitude in less than 200 days
- Total cVOC concentrations were below remediation goals
Project Summary
Groundwater below a Missouri dry cleaning facility was contaminated from a cleaning solvent spill, resulting in PCE concentrations >4,000 μg/L. An enhanced reductive dechlorination approach was developed that integrated biodegradation and bioaugmentation via application of a controlled-release electron donor and a microbial consortium of dechlorinating bacteria.
REGENESIS® Remediation Services (RRS) was contracted to co-apply 3-D Microemulsion® and Bio-Dechlor Inoculum® Plus to the affected groundwater. The products were applied to the affected groundwater underneath the building via direct-push injections.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion factory emulsified is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Results
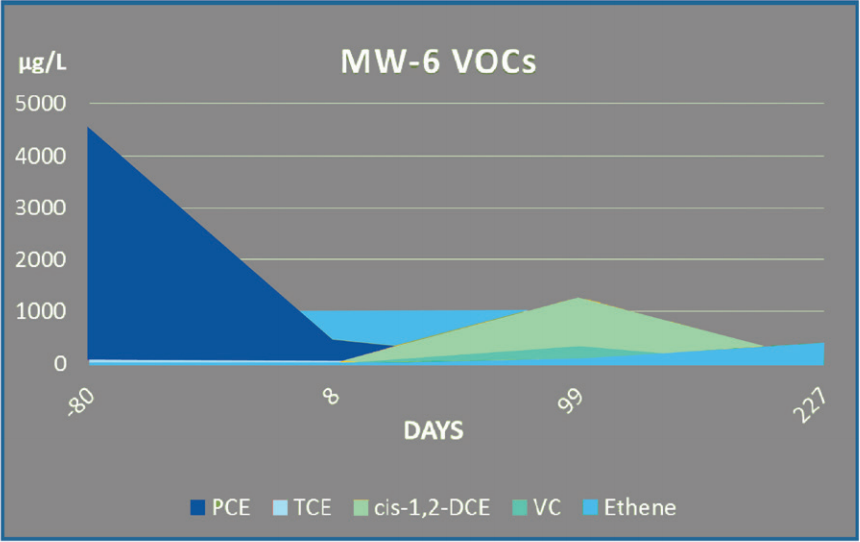
Following treatment, total cVOC were reduced by 99.9%. Concentrations were reduced by three orders of magnitude from a baseline concentration of >4,000 μg/L to <10 μg/L in less than 200 days.
Furthermore, monitoring data indicated complete dechlorination with no remaining daughter products above the remediation goals. As a result of the rapid and complete reduction of chlorinated solvents, the project received a “No Further Action” letter (NFA) through the Missouri Department of Natural Resources.
Combined Remedies Used at Historic Illinois Chemical Company
cVOCs in Bedrock Treated at Active Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) used combined technologies to work toward the shutdown of a pump and treat (P&T) system.
- Previous Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) technology applications did not achieve COC reductions.
- Advanced ERD, Bioaugmentation and ISCR remedies were combined and applied into weathered bedrock.
- The project required RRS to be PICS certified. PICS is a contractor prequalification services used many large E&C and fortune 500 companies.

Project Summary
The site is home to an active chemical manufacturing facility with historic spills of cVOCs. Within the contamination impact zones, a groundwater P&T system is being used to mitigate off-site migration of cVOCs in the groundwater. The consultant was seeking ways to turn off the P&T system by treating the plume in-situ. They had previously used an ERD technology without fully achieving primary COC reductions. RRS designed and implemented a pilot study for the site.
Remediation Approach
The pilot study was designed to test Regenesis’ combined remedy approach which incorporated ERD using 3-D Microemulsion, Bioaugmentation with BDI Plus and ISCR with CRS. RRS applied the integrated technologies through direct-push borings. The 2,500-square-foot treatment zone included 10-foot vertical injections into silty sand and clay over weathered dolomite bedrock.
Technology Description
- 3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory–emulsified product.
- HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).
- Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
- CRS® (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Combined Remedies Used at Former Chemical Company in Illinois, USA
cVOCs in Bedrock Treated at Active Manufacturing Facility
Project Highlights
- Regenesis Remediation Services (RRS) used combined technologies to work toward the shutdown of a pump and treat (P&T) system.
- Previous Enhanced Reductive Dechlorination (ERD) technology applications did not achieve COC reductions.
- Advanced ERD, Bioaugmentation and ISCR remedies were combined and applied into weathered bedrock.
- The project required RRS to be PICS certified. PICS is a contractor prequalification services used many large E&C and fortune 500 companies.

Project Summary
The site is home to an active chemical manufacturing facility with historic spills of cVOCs. Within the contamination impact zones, a groundwater P&T system is being used to mitigate off-site migration of cVOCs in the groundwater. The consultant was seeking ways to turn off the P&T system by treating the plume in-situ. They had previously used an ERD technology without fully achieving primary COC reductions. RRS designed and implemented a pilot study for the site.
Remediation Approach
The pilot study was designed to test Regenesis’ combined remedy approach which incorporated ERD using 3-D Microemulsion, Bioaugmentation with BDI Plus and ISCR with CRS. RRS applied the integrated technologies through direct-push borings. The 2,500-square-foot treatment zone included 10-foot vertical injections into silty sand and clay over weathered dolomite bedrock.
Technology Description
- 3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory–emulsified product.
- HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).
- Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
- CRS® (Chemical Reducing Solution) is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
Biodegradation Successfully Treats High Levels of PCE/TCE Contamination
Combined Remedies Used to Remediate Active Dry Cleaner in Northern California
Project Highlights
- Pilot study used enhanced biodegradation coupled with bioaugmentation to treat high PCE levels.
- High PCE levels above 5,000 ug/L were detected in groundwater.
- Regenesis optimized injection of the bioamendments into the target treatment zone.
- Significant contaminant reduction resulting from enhanced biodegradation within six months

Project Summary
This project was located at an active dry cleaner in northern California. The site had elevated levels of PCE in groundwater due to releases over a period of approximately 60-years. Enhanced anaerobic biodegradation (EAB) was chosen to remediate the site. A pilot study program was implemented using a combination of 3-D Microemulsion®, HRC® Primer and BDI® Plus. Significant contaminant reductions were observed within six months of the first application.
Remediation Approach
An in situ EAB pilot study program was implemented to address elevated levels of PCE concentrations in middle zone groundwater just north of site. 3-D Microemulsion, HRC Primer and BDI Plus were applied through 15 bore holes to depths of 60 feet. Early injection attempts posed challenges due to the formation not accepting the required volume (surfacing). Regenesis provided a modified design reducing the amount of water needed for 3-D Microemulsion and suggested an alternative injection approach in the field which allowed for a more efficient injection within the target treatment zone.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory emulsified product.
HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM® Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Successful Bioremediation at a Former Air Force Base Fire Training Area
Carbon Tetrachloride Concentrations Reduced Below Treatment Goal within 8 Months
Project Highlights
- Air Force Base contaminated with high levels of carbon tetrachloride due to on-site firefighting training.
- 97% reduction in contaminant within three months.
- Carbon tetrachloride reduced to below detection limits.

Project Summary
Training exercises at Texas Air Force Base resulted in an impact to soil and groundwater by trichloroethylene (TCE) and carbon tetrachloride. A monitored natural attenuation study conducted indicated that chlorinated solvents at the plume would naturally decline to acceptable levels after 30 years of monitoring.
After over 14 years of monitoring, contaminant reductions were not proceeding as quickly as predicted and additional remediation was advised. It was determined that limited anaerobic activity was present and biostimulation was a viable option. A pilot test was conducted on-site. The objective of the project was to determine the feasibility of injection into the shallow, discontinuous groundwater unit. The pilot test was also designed to determine if the residual TCE and carbon tetrachloride could be biodegraded through enhanced bioremediation and reduced to below 5 ppb (the Texas Risk Reduction Program limit).
Remediation Approach
3-D Microemulsion® was injected into 30 points at the site; approximately 380 gallons of the product was applied per boring at the site. Initial results indicated a significant reduction in concentrations of parent chemicals – carbon tetrachloride was reduced by 95% within 1 month post-injection and 97% within 3 months of injection within the source area. A monitoring well 50-feet downgradient of the source area experienced a 69% reduction by the third month as 3-D Microemulsion began to reach the well location.
Follow-up injections were applied downgradient of the source area and also in a barrier configuration several hundred feet dowgradient of the source were implemented about 6 months after the pilot test. The combination of the pilot test and full-scale application resulted in a 97.8% reduction in carbon tetrachloride 8 months post-injection with chloroform, methylene chloride, and chloromethane remediation daughter products on a downward trend. High TCE concentrations were effectively treated as well with TCE peaking after injections to 126 ppb and then being reduced within a 3-month period to 0.2 ppb.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
REGENESIS® Achieves MCL Cleanup Goals at New York Manufacturing Facility
cVOC Contamination Successfully Treated Using PersulfOx® and 3-D Microemulsion®
Project Highlights
- 99% reduction of target compounds achieved on-site
- TCE levels reduced from 8,000 ug/L to <5 ug/L to meet site goals
- Integrated remediation approach using PersulfOx® and 3-D Microemulsion® (3DME)
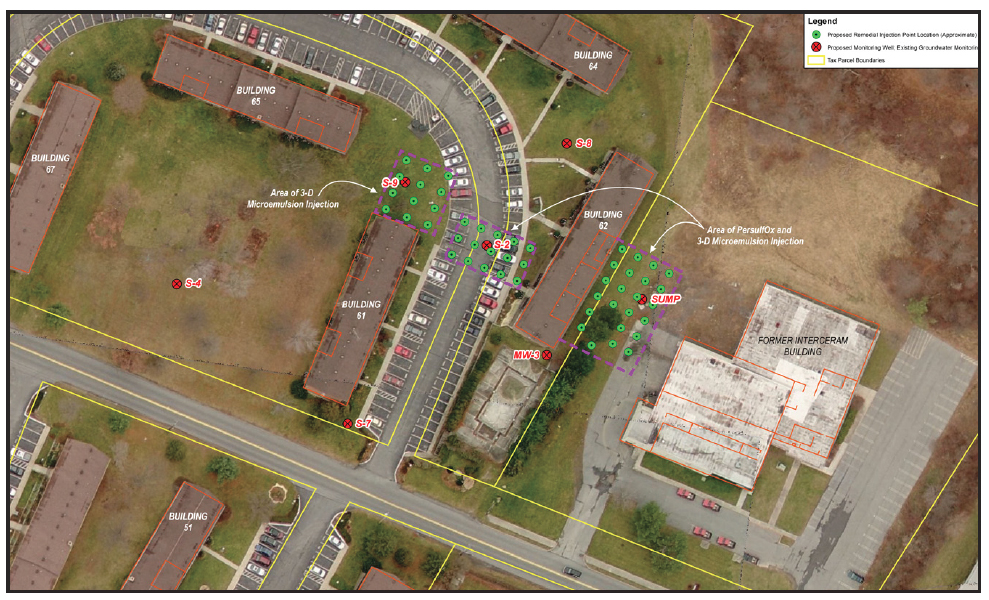
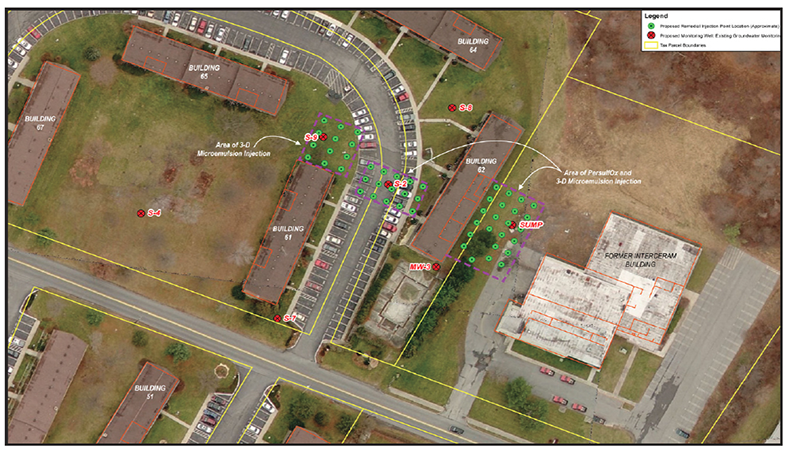
Project Summary
A manufacturing facility in New York was contaminated with high levels of chlorinated solvents. TCE levels were as high as 8,000 ug/L. A combined remedies approach was established to address the migrating plume. The goal of the application design was to reduce cVOCs in the source area, reduce potential for vapor intrusion and address any cVOCs that may migrate into the area downgradient of the manufacturing facility.
An integrated remediation strategy using PersulfOx and 3DME was implemented on-site. Two PersulfOx applications were completed. Results from the In Situ Chemical Oxidation (ISCO) treated area showed >99% reduction of target compounds. A total of 11,600 pounds of PersulfOx was applied on-site. 3DME was applied to enhance anaerobic biodegradation in downgradient locations and within the PersulfOx-treated area. A total of 8,400 pounds of 3DME was applied. While groundwater contamination in the ISCO treated area was reduced to clean-up standards, the goal of the 3DME application was strictly preventative. The client wished to address any potential plume migration from any cVOCs that may be present beneath the building.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Results
The use of PersulfOx safely and effectively reduced TCE levels to regulatory standards providing a 99% reduction of cVOC’s achieved on-site. In addition, the integration of 3DME as a precautionary safety measure addressed the potential for plume migration that was thought to be present.
ISCO/ERD Treat PCE Contamination at Indiana Dry Cleaner
Remediation Plan Addresses Concentrations Below Facility and Downgradient
Project Highlights
- PersulfOx utilized subslab near the source to inhibit vapor issues within the building.
- Combined remediation plan addressed impacts both below the building and downgradient of the facility.
- PCE contamination was nearly depleted and TCE levels below 10 ppb were observed.
- The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.

Project Summary
A release of PCE from a former dry cleaning operation in Indianapolis resulted in groundwater contamination below the facility and downgradient. Contamination impacts were also observed in shallow fill below the concrete slab. Along with the groundwater/soil contamination, vapor intrusion was also detected within the facility and adjacent spaces in the strip mall. A combination of enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was used for remedial action. Analytical results obtained indicate nearly complete reduction of PCE and less than 10 ppb of TCE in all wells. Currently, elevated VC concentrations in two wells were observed but reductions are expected as the ERD process is completed.
Remediation Approach
PersulfOx® Catalyzed Persulfate was injected below the floor slab of the dry cleaner to inhibit vapor production within the facility and adjacent spaces. 3-D Microemulsion® and Bio-Dechlor INNOCULUM® Plus were injected into the uppermost water-bearing area below the dry cleaner and into two areas downgradient on either side of the building. Supplemental ERD injections were applied in two areas approximately 9 months after the initial injection to address minor sand stringers that were contributing to continued contamination impacts. The supplemental injection resulted in immediate elimination of PCE/TCE and a rapid production of VC. The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
ISCO/ERD Treat PCE Contamination at Indiana Dry Cleaner
Remediation Plan Addresses Concentrations Below Facility and Downgradient
Project Highlights
- PersulfOx utilized subslab near the source to inhibit vapor issues within the building.
- Combined remediation plan addressed impacts both below the building and downgradient of the facility.
- PCE contamination was nearly depleted and TCE levels below 10 ppb were observed.
- The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.

Project Summary
A release of PCE from a former dry cleaning operation in Indianapolis resulted in groundwater contamination below the facility and downgradient. Contamination impacts were also observed in shallow fill below the concrete slab. Along with the groundwater/soil contamination, vapor intrusion was also detected within the facility and adjacent spaces in the strip mall. A combination of enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) and in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) was used for remedial action. Analytical results obtained indicate nearly complete reduction of PCE and less than 10 ppb of TCE in all wells. Per the recent sampling event, VC concentrations have dropped in all wells. Monitoring is ongoing.
Remediation Approach
PersulfOx® Catalyzed Persulfate was injected below the floor slab of the dry cleaner to inhibit vapor production within the facility and adjacent spaces. 3-D Microemulsion® and Bio-Dechlor INNOCULUM® Plus were injected into the uppermost water-bearing area below the dry cleaner and into two areas downgradient on either side of the building. Supplemental ERD injections were applied in two areas approximately 9 months after the initial injection to address minor sand stringers that were contributing to continued contamination impacts. The supplemental injection resulted in immediate elimination of PCE/TCE and a rapid production of VC. The site is currently being monitored to demonstrate plume stability with approximately 3-4 more monitoring events prior to site closure.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Combined Remedies Treatment Results in a $650,000 Cost Savings for End User
Project Highlights
- By implementing this strategy with a clear path to closure, KERAMIDA saved their client approximately $650,000 versus the alternative containment plan. KERAMIDA’s sophisticated and aggressive remedial approach matched the technologies (ISCO, ISCR, ERD) to the technical challenges at the site.
- PCE was virtually eliminated in most other impacted wells, and continued evidence of reductive dechlorination is ongoing.
- Project currently in the monitoring phase to establish plume stability for closure.

Project Summary
A PCE spill from a 55 gallon drum in the late 1980s contaminated a manufacturing site in Indiana. Contaminated soil was excavated in the spill area and a pump and treat interceptor system was installed downgradient of the plume. The system continued to operate intermittently throughout the 1990s. A previous consultant had submitted a remediation work plan proposing the use of a permeable reactive barrier. However, the plan was rejected because the intended goal was remedial closure, not containment. KERAMIDA proposed a combined in-situ chemical oxidation (ISCO)/enhanced reductive dechlorination (ERD) approach focusing on the spill area (source) and the downgradient, on-site plume, with a small injection off-site. The remediation plan was approved and the injection was completed in November 2013. KERAMIDA’s cost to closure is likely to be achieved for less than $500,000 – saving $650,000-800,000 over the life of the project. (The rejected remediation plan from the previous consultant had an estimated cost of $1.3 million with no plan for closure.)
Remediation Approach
The combined remedies treatment included an initial application of PersulfOx® Catalyzed Persulfate in the source area with subsequent applications of 3D Microemulsion® (3DME), BioDechlor INNOCULUM® Plus (BDI-Plus) and Chemical Reducing Solution (CRS®). In addition, 3DME and BDI-Plus were applied in two downgradient areas of the plume. Groundwater monitoring performed in the eight months since injection indicates dramatic reductions in PCE concentrations. Within the source area, an initial PCE concentration of approximately 70,000 ppb was reduced to 278 ppb (with a corresponding increase in cis-1,2-DCE, which is currently being degraded). PCE was virtually eliminated in most other impacted wells and evidence of reductive dechlorination is ongoing.
Technology Description
PersulfOx is a sodium persulfate-based chemical oxidation technology which destroys both hydrocarbon and chlorinated solvent-type contaminants in the subsurface. PersulfOx contains a built-in catalyst which activates the persulfate component and generates contaminant-destroying free radicals without the need for the addition of a separate activator.
CRS is an iron-based amendment for in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants such as chlorinated ethenes and ethanes.
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
Bio-Dechlor INOCULUM Plus is an enriched natural microbial consortium containing species of Dehalococcoides sp. (DHC). This microbial consortium has since been enriched to increase its ability to rapidly dechlorinate contaminants during in situ bioremediation processes.
Historic California Site Treated with 3-D® Microemulsion and HRC® Primer
Project Highlights
- Site was open for over 20 years with the Central Coast Regional Board
- Immediate results showed a TCE decrease from 2,260 ppb to 12 ppb
- Site is currently under review for closure
- Cost per cubic yard was under $10 per cubic yard complete turn-key

Project Summary
This California site has been open with the Central Coast Regional Board for over 20 years with groundwater VOC concentrations thousands of times higher than the MCL. The site also had limited metal concentrations above MCL. A remediation plan was created to treat the groundwater plume using enhanced anaerobic bioremediation via Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC®) Primer and 3-D Microemulsion®. Immediate results showed a decrease in TCE concentrations from 2,260 ppb to 12 ppb.
Remediation Approach
Seven separate designs were developed to treat the 60,450-square-foot area. Several water bearing zones were treated throughout the site. Initial concerns for treatment included the possibility of a buildup of methane in the soil gas. However, because 3-D Microemulsion is a controlled-release, high-volume electron donor, no methane issues were observed. Cost for the product and application was less than $10 per cubic yard and the site is currently under review for closure.
Technology Description
3-D Microemulsion is an engineered electron donor material that offers a novel 3-stage electron donor release profile, pH neutral chemistry and is delivered on-site as a factory-emulsified product.
HRC Primer is a less viscous version of the standard Hydrogen Release Compound (HRC) product. It is a thinner, water-like compound that is typically injected into an aquifer where it releases lactic acid at a rate faster than standard HRC (several weeks), but at a slower, more controlled rate than dispersing aqueous simple sugar solutions or straight lactic acid (several days).

 Americas
Americas Europe
Europe Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Español
Español